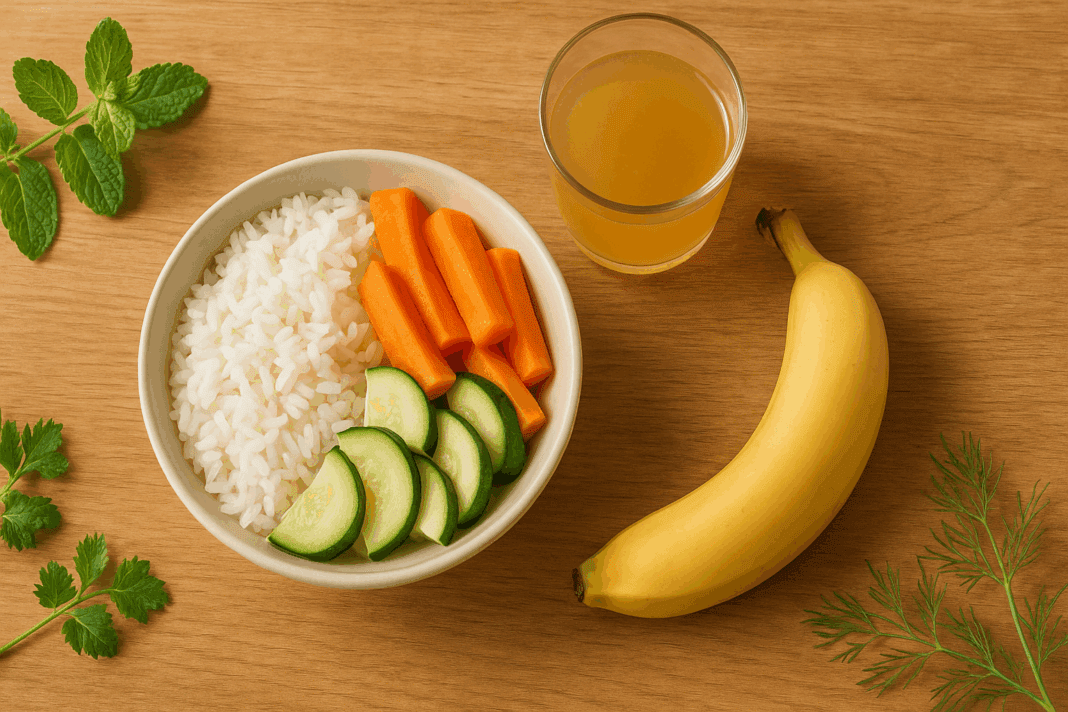
Digestive health plays a central role in our overall well-being, yet it is often overlooked until discomfort strikes. Whether you’re recovering from an illness, managing a digestive disorder, or simply seeking to support your gut through nutrition, incorporating easy-to-digest foods into your diet can have transformative effects. These foods reduce strain on the digestive system, allowing the gut to function more efficiently while promoting nutrient absorption, minimizing bloating, and maintaining regularity. In this guide, we explore the science behind digestion, reveal which foods are the easiest to digest, and show how these gentle choices can foster a more resilient and balanced gut.
You may also like: The Ultimate Guide to Gut Healthy Meals: Best Meals for Gut Health and Nourishing Recipes You’ll Love
Understanding Digestion and Why Gentle Foods Matter
Digestion is the complex process through which the body breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and utilized. It involves mechanical action, like chewing and stomach churning, and chemical processes facilitated by enzymes and gastric acids. When this process becomes impaired due to stress, illness, or dietary imbalances, symptoms such as gas, bloating, and discomfort can occur. Consuming foods that are gentle on the stomach helps minimize these issues and supports optimal gastrointestinal function.
The easiest foods to digest often require minimal enzymatic breakdown and contain low levels of fat and fiber. While fiber is generally beneficial for long-term digestive health, during periods of sensitivity or flare-ups, high-fiber foods can be irritating. In such cases, choosing foods that are digested quickly can ease the workload of the stomach and intestines, allowing healing and restoration.
Understanding what nutrient digests the fastest can also guide food choices. Carbohydrates, especially simple ones, are broken down more quickly than fats or proteins. For instance, rice, bananas, and certain vegetables offer quick energy without overburdening the gut. Recognizing these patterns empowers individuals to tailor their diets to their digestive needs.
Easy-to-Digest Foods for Everyday Wellness
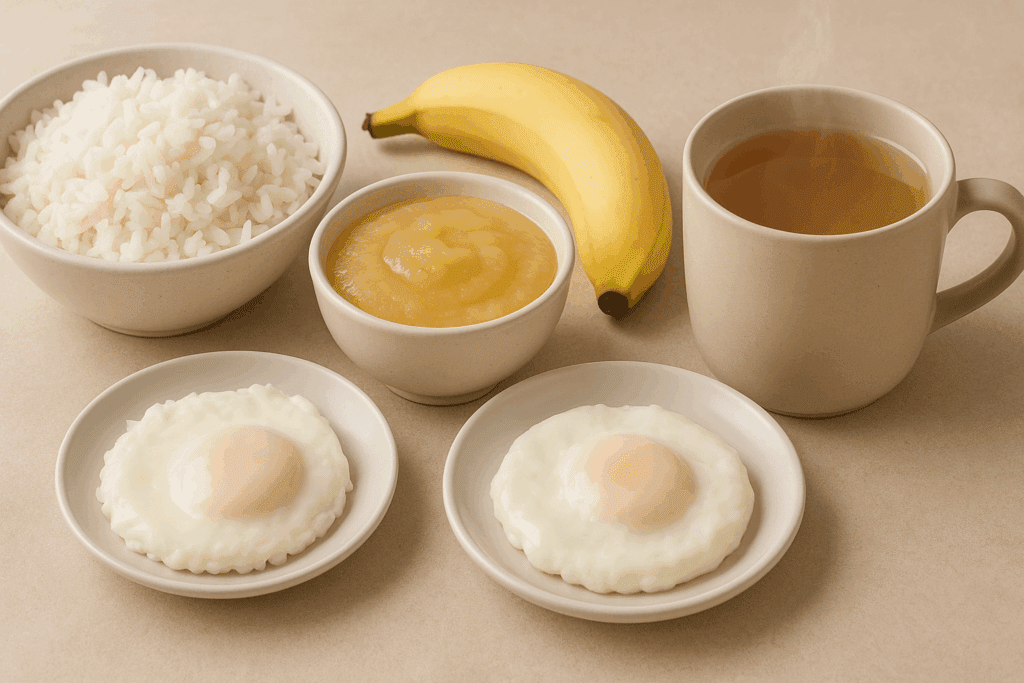
Among the many options available, certain foods consistently rank as easy to digest and are favored in gastrointestinal nutrition. White rice is a staple in this category. Unlike brown rice, which is high in fiber and can be harder to break down, white rice is processed to remove the bran and germ, making it a more digestible choice. The question “is rice easy to digest?” is answered with a resounding yes, particularly in its white form.
Bananas are another top-tier option. Rich in potassium and low in fiber, they are soothing to the stomach and help replenish electrolytes during gastrointestinal distress. Applesauce, made by cooking down apples and removing the skins, provides a gentle form of fruit that retains beneficial antioxidants without the harshness of raw apple fiber. Similarly, bone broth, with its high collagen content, is hydrating, nourishing, and light on the stomach, making it one of the gentlest foods for stomach healing.
Incorporating eggs into a soft diet also comes highly recommended. For those wondering, “are eggs easy to digest?” the answer lies in preparation. Soft-boiled or poached eggs are particularly mild and provide high-quality protein in a form that is relatively simple for the digestive system to process. When scrambled with minimal fat, they offer an easy-to-digest meal that is both nutritious and satisfying.
Why Easy-to-Digest Foods Are Essential for Gut Health
The gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of microorganisms living in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in immune function, nutrient absorption, and mental health. Easy-to-digest foods allow the microbiome to thrive by reducing inflammation and providing substrates that support beneficial bacteria.
Foods that are digested quickly don’t linger in the gastrointestinal tract, which helps prevent the buildup of gas and toxins. This is especially important for those with conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastritis, or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), where slow digestion can exacerbate symptoms.
An easy digestion diet is also vital during periods of stress or recovery from illness. Stress can slow gastric emptying and alter enzyme secretion, making digestion less efficient. During such times, the body benefits from light foods for the stomach that require minimal effort to process. Incorporating easily digestible vegetables and proteins ensures that the body continues to receive essential nutrients without exacerbating gastrointestinal issues.
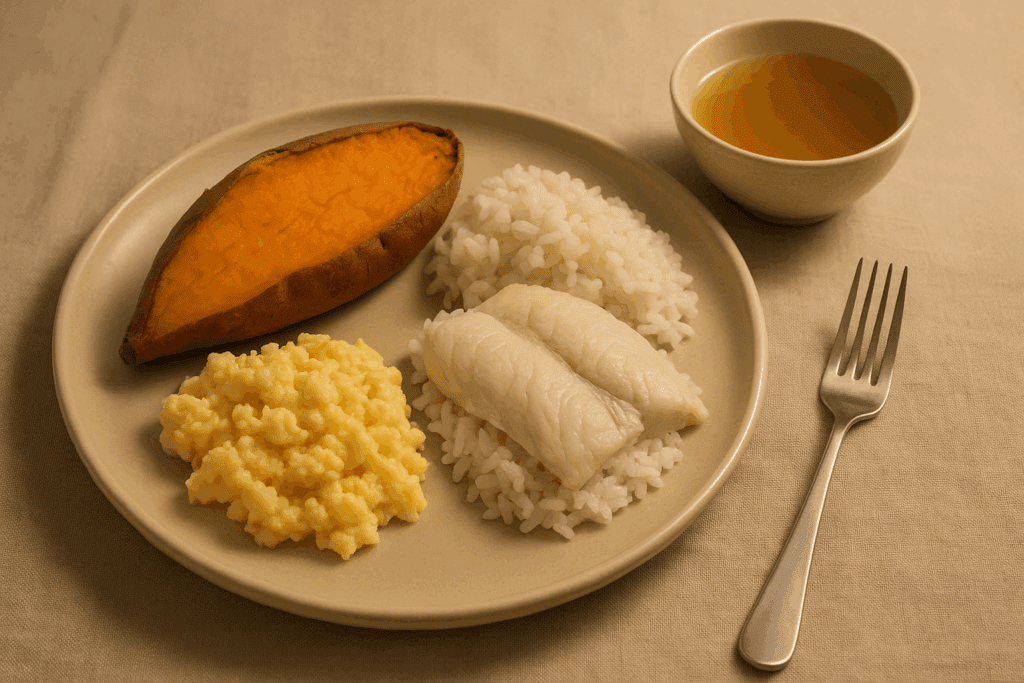

Easy-to-Digest Vegetables: The Best Choices for Gut-Friendly Nutrition
Vegetables are indispensable for a balanced diet, but not all are created equal when it comes to digestion. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower, though nutrient-dense, are often difficult to digest due to their high fiber content and gas-producing compounds. For sensitive stomachs, it is better to choose easy to digest vegetables that have been cooked to soften fibers and break down complex carbohydrates.
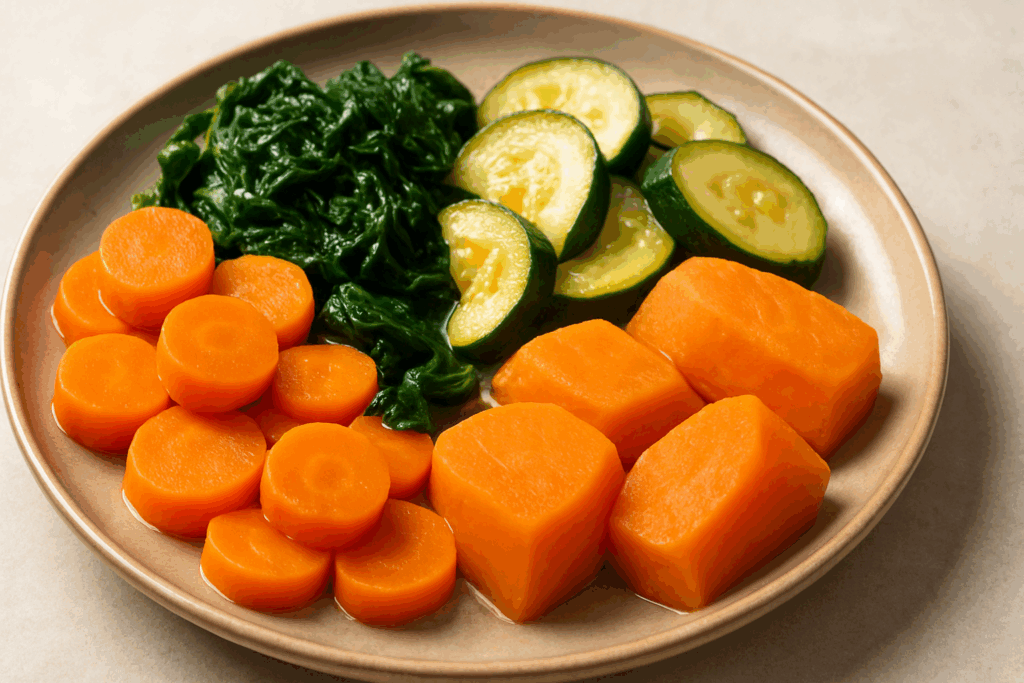
Carrots, for example, are among the easiest vegetables to digest. When cooked, they become soft and lose much of their fibrous texture, while retaining valuable nutrients such as beta-carotene. Zucchini is another excellent choice. With its high water content and soft texture when sautéed or steamed, it places minimal strain on the gut. Spinach, when cooked, offers a wealth of vitamins and minerals without the digestive resistance of raw leafy greens.
For those seeking veggies easy to digest that also provide a soothing effect, peeled and cooked sweet potatoes are ideal. Their natural sweetness and smooth texture make them palatable and nourishing. This class of foods, referred to collectively as easily digestible vegetables, forms the foundation of an effective easy digestion diet. They provide energy and micronutrients while allowing the gastrointestinal system to operate without stress.
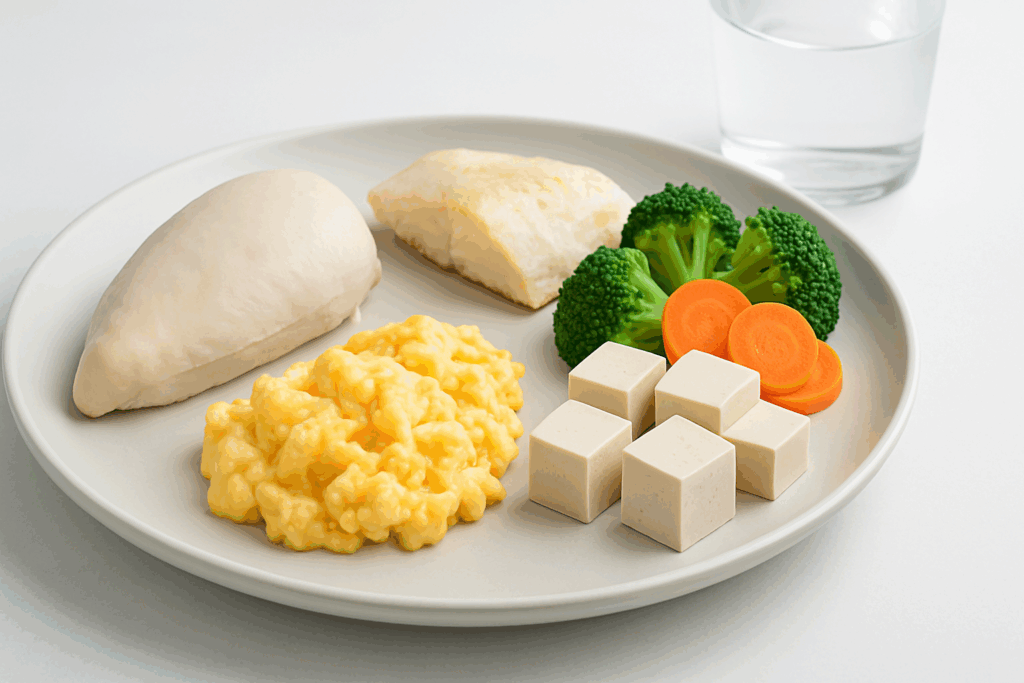
Easy-to-Digest Meals for Daily Support
Building meals around easy-to-digest foods allows for consistency in digestive comfort. A typical easy-to-digest breakfast might include oatmeal made with water or a lactose-free milk alternative, topped with mashed banana or cooked apples. These ingredients offer soluble fiber in a gentle form, along with slow-burning carbohydrates that sustain energy without bloating.
For lunch and dinner, soups made with well-cooked vegetables and lean proteins such as chicken or tofu are both nutritious and easy to digest. Incorporating rice noodles or white rice adds bulk without digestive burden. A comforting example is a chicken and rice soup with carrots and zucchini, seasoned lightly to avoid triggering acid reflux or stomach upset.
Dinner might feature a baked sweet potato paired with scrambled eggs or steamed fish, which represents what is considered the easiest meat to digest. Fish like cod or sole are not only low in fat but also cook quickly and flake easily, minimizing the digestive effort required. Such meals provide a balance of protein, vitamins, and easy-to-absorb carbohydrates, making them ideal for those seeking gut-friendly nourishment.
Exploring Protein Options: What Is the Easiest Meat to Digest?
While protein is vital for tissue repair and immune function, not all protein sources are equally digestible. Fatty cuts of meat, processed sausages, and heavily spiced dishes can be taxing on the digestive system. When considering what is the easiest meat to digest, lean cuts and cooking method matter greatly.
Poached chicken breast and baked or steamed white fish are consistently recommended as fast digesting foods in the protein category. Their low fat content and simple muscle structure allow them to be broken down efficiently by digestive enzymes. Turkey is another gentle option, especially when served ground and well-cooked.
Avoiding fried meats or those with heavy sauces is key, as added fat slows gastric emptying and increases the risk of bloating. For vegetarians, eggs and tofu are excellent protein alternatives. In particular, tofu is versatile and soft in texture, making it one of the foods that are easy on the stomach when seasoned simply and cooked thoroughly.
Are Avocados and Peanut Butter Easy to Digest?
Avocados and peanut butter, while nutrient-rich, present a more nuanced discussion when it comes to digestion. Both are high in fat—albeit healthy fat—which naturally slows digestion. However, when consumed in moderation and in the right context, they can still be part of a diet that supports gut health.
So, is avocado easy to digest? For most people, the answer is yes, provided it is consumed in small amounts and is ripe. Its creamy texture and soluble fiber content can actually help soothe the digestive tract. It is particularly beneficial when paired with faster-digesting carbohydrates like rice or toast.
Similarly, is peanut butter easy to digest? That depends on the brand and portion size. Natural, smooth peanut butter without added sugars or oils is easier on the stomach than processed varieties. However, due to its density and fat content, it should be limited during periods of acute digestive distress. Incorporating small amounts in an otherwise easy-to-digest meal can provide healthy calories without overwhelming the digestive system.
How Fast Digesting Foods Affect Energy and Comfort
Fast digesting foods, such as white bread, rice, ripe fruits, and boiled vegetables, are broken down rapidly into glucose, providing quick energy. This is especially beneficial before physical activity or during recovery from illness. However, relying solely on these foods can lead to blood sugar spikes and crashes, so they are best balanced with proteins or fats when appropriate.
These foods are particularly useful during times when the digestive system needs a break, such as after gastrointestinal infections, surgery, or during episodes of chronic illness. They also serve a purpose in sports nutrition, where immediate energy availability is crucial. Athletes often consume bananas, rice cakes, or applesauce as pre-event snacks for their digestibility and energy release.
In a broader wellness context, foods that are digested quickly can serve as dietary bridges—gentle options that reintroduce nourishment after fasting, stress, or poor appetite. Their inclusion in an easy digestion diet ensures that the gut is not overworked, while still receiving the sustenance it requires to function optimally.

Easy-to-Digest Foods for Adults With Sensitive Stomachs
Digestive sensitivity is not uncommon among adults, whether due to age, medical conditions, or stress. For these individuals, choosing foods that are easy on the stomach becomes a daily necessity rather than an occasional adjustment. Understanding what foods are easily digested allows them to manage symptoms proactively.
Foods easiest on the stomach often overlap with those recommended during recovery from illness. These include rice, applesauce, bananas, toast (often referred to collectively as the BRAT diet), as well as low-fat yogurt, gelatin, and herbal teas. These foods provide hydration, electrolytes, and energy without irritating the stomach lining.
An easy digestion diet for adults may also limit raw vegetables, dairy products high in lactose, spicy seasonings, and greasy meals. Cooking techniques such as steaming, boiling, and baking are preferred over frying or grilling. Consistency in choosing easy-to-digest foods reduces the frequency and intensity of digestive flare-ups, contributing to a more stable and comfortable day-to-day life.
The Role of Supplementation and Holistic Support for Gut Health
While whole foods are the foundation of digestive wellness, targeted supplements can enhance the benefits of an easy digestion diet. Probiotics, for example, help populate the gut with beneficial bacteria, improving both digestion and immune function. Prebiotics, found in small amounts in cooked onions, garlic, and bananas, serve as food for these bacteria.
Digestive enzymes, when taken with meals, can help break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates more efficiently, especially for those with pancreatic insufficiency or food intolerances. Herbal supplements such as ginger, fennel, and peppermint have been shown to relax intestinal muscles and reduce bloating.
From a holistic perspective, stress management also supports digestive health. Mindful eating, adequate hydration, and regular physical activity all contribute to gut motility and comfort. Combining these approaches with easy-to-digest meals creates a comprehensive strategy for long-term digestive resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Easy-to-Digest Foods and Gut Health
How can easy-to-digest foods benefit people with high stress lifestyles?
High stress levels can significantly impair digestion by slowing gastric emptying, reducing enzyme production, and increasing gut permeability. For individuals leading stressful lives, easy-to-digest foods provide much-needed relief to an overtaxed gastrointestinal system. These foods allow the body to extract essential nutrients with minimal energy expenditure, helping maintain energy levels and reduce inflammation. When consumed regularly, light foods for the stomach such as bananas, oatmeal, and well-cooked vegetables can improve mental clarity and even sleep quality by lessening the physiological burden on the gut. A consistent easy digestion diet may also support adrenal recovery by freeing up resources for hormonal balance rather than continuous digestive effort.
What are some surprising foods that are digested quickly but often overlooked?
Beyond the commonly recognized choices like rice and applesauce, there are lesser-known foods that are digested quickly and can easily be integrated into a gut-friendly routine. For example, ripe papaya contains a natural enzyme called papain that aids protein digestion and soothes the stomach lining. Mashed pumpkin, when cooked thoroughly, is another underrated option; it is rich in antioxidants and very gentle on the digestive tract. Gelatin-based snacks, often seen as desserts, actually help repair gut lining due to their collagen content and are considered fast digesting foods. Rice noodles are also overlooked; they provide simple carbohydrates that convert rapidly to energy without irritating the gut. All of these are examples of foods that are digested quickly and can be easily added to easy to digest meals.
Are there benefits to rotating the easiest foods to digest in your meal planning?
Absolutely. Rotating the easiest foods to digest within your diet can prevent nutrient gaps and reduce the risk of developing food sensitivities due to overexposure. While the BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, toast) is a staple during flare-ups, relying exclusively on this set for extended periods may cause deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. Introducing a rotation of easy to digest vegetables like carrots, zucchini, and peeled squash ensures that the body receives diverse phytonutrients. Incorporating occasional protein changes—such as switching from fish to tofu or eggs—can optimize amino acid intake while maintaining digestive ease. Rotational planning supports digestive resilience and fosters long-term adherence to an easy digestion diet without boredom or nutritional imbalance.
How does food temperature impact the digestibility of easy-to-digest foods?
Temperature plays a subtle but important role in how foods are tolerated by the digestive system. Warm or room temperature foods are generally easier on the stomach than those served cold or very hot. This is because extreme temperatures can irritate the gastrointestinal lining, especially for individuals with conditions like gastritis or acid reflux. For instance, gently heated soups containing easily digestible vegetables and lean proteins are often more soothing than refrigerated meals. Moreover, heating helps break down fibers and starches in veggies easy to digest, such as sweet potatoes and carrots, making them even more palatable for sensitive systems. Therefore, food preparation techniques should consider both content and temperature to optimize digestion.
What is the easiest meat to digest and how should it be prepared for best results?
Among all animal-based proteins, the easiest meat to digest is typically white fish, such as cod or sole, due to its low fat content and delicate structure. When prepared by steaming or baking without heavy oils or spices, fish digests efficiently and minimizes the risk of bloating or gastric discomfort. Skinless chicken breast and ground turkey are also favorable when simmered or baked with minimal seasoning. The preparation method can significantly influence how the body handles meat—grilling or frying adds fats and compounds that slow down digestion. For individuals transitioning back to solid food after illness, finely shredded meat added to soups or broths offers a protein-rich, easy to digest meal that supports tissue repair without overburdening the stomach.
Can easy-to-digest foods still be high in fiber?
While high fiber foods are generally more difficult to digest, certain types of fiber—especially soluble fiber—are easier on the digestive tract and can be found in many easy-to-digest foods. Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, which can help regulate digestion and soothe the gut lining. Examples include cooked carrots, peeled apples, oats, and mashed sweet potatoes. These are often classified as foods that are easy on the stomach because they provide bulk without irritating the intestinal walls. Incorporating easily digestible vegetables with soluble fiber can improve stool consistency and feed beneficial gut bacteria without causing gas or bloating, which is crucial for maintaining gut balance in an easy digestion diet.
Is peanut butter easy to digest for all individuals?
Peanut butter is somewhat of a gray area in digestive health. While it is a good source of protein and healthy fats, its digestibility largely depends on individual tolerance, portion size, and product formulation. For example, natural peanut butter with minimal ingredients is generally easier on the stomach than commercial varieties containing hydrogenated oils and added sugars. For many adults, a small spoonful of smooth peanut butter paired with bread or bananas constitutes one of the more comforting easy to digest foods for adults. However, those with fat malabsorption issues, IBS, or sensitivities to legumes may find that even small amounts of peanut butter lead to discomfort. Moderation, mindfulness, and brand selection are key when considering whether is peanut butter easy to digest in your personal routine.
Do easy-to-digest foods support gut health during antibiotic therapy?
Yes, integrating easy-to-digest foods during and after antibiotic therapy can significantly reduce digestive disruption and promote faster gut microbiome recovery. Antibiotics not only kill harmful bacteria but also reduce populations of beneficial microbes in the intestines. This can lead to temporary digestive issues like bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. During this vulnerable phase, easy to digest meals composed of white rice, yogurt with active cultures, and steamed veggies easy to digest can support microbial balance while avoiding further irritation. Additionally, fermented foods such as miso or kefir—which are also often foods easiest on the stomach—can help reintroduce beneficial bacteria. The strategy should be to combine microbial replenishment with dietary gentleness to stabilize the gut ecosystem.
Why are easy-to-digest vegetables better tolerated when peeled or cooked?
The outer skins of many vegetables contain insoluble fiber, which resists digestion and can aggravate sensitive digestive systems. Peeling vegetables like zucchini, carrots, and cucumbers removes much of this fiber, making them easier for the gut to process. Cooking breaks down tough cell walls and starches in the vegetables, transforming them into softer, easily digestible forms. For example, steaming spinach significantly reduces its oxalate content, which can otherwise interfere with mineral absorption and digestion. The process of peeling and cooking essentially pre-digests the vegetables, converting them into the easiest vegetables to digest, especially for individuals recovering from illness or managing chronic gastrointestinal conditions.
How do easy-to-digest foods fit into long-term wellness and not just short-term recovery?
While often associated with temporary digestive distress, easy-to-digest foods have enduring value in preventive health and chronic disease management. These foods help maintain a balanced gut microbiota, reduce inflammation, and support metabolic efficiency. In cultures with high longevity rates, such as Japan and parts of the Mediterranean, diets emphasize foods that are gentle on stomach function, like steamed vegetables, fermented grains, and mild broths. By routinely including easy to digest foods for adults in daily meals, individuals may experience improved mood, better energy levels, and enhanced immune resilience. The long-term adoption of an easy digestion diet is not about restriction, but rather about fostering digestive harmony that supports holistic health for years to come.
Conclusion: Embracing Easy-to-Digest Foods for Lifelong Gut Health
Incorporating easy-to-digest foods into your daily routine is not just a temporary solution for digestive distress—it’s a sustainable strategy for fostering long-term gut health and overall wellness. By understanding what foods are easily digested, such as white rice, cooked vegetables, soft proteins, and gentle fruits, you empower your digestive system to function more efficiently and comfortably.
These foods, when used as part of an easy digestion diet, offer relief to adults with sensitive stomachs and support the recovery process for those managing illness or stress. They can be personalized based on tolerance levels and combined with holistic practices and supplements to enhance their effects. The question of whether eggs, rice, avocado, or peanut butter are easy to digest becomes less about a simple yes or no, and more about how, when, and in what form they are consumed.
As you consider the importance of gut health, remember that the foods you choose have the power to soothe, support, and strengthen your digestive system. Prioritizing light foods for the stomach and listening to your body’s cues can lead to greater comfort, vitality, and resilience in your everyday life. This essential guide offers a starting point, but your journey with easy-to-digest foods can evolve into a transformative lifestyle rooted in nourishment and care for your gut.
Further Reading:
What Foods Are Easy to Digest?
18 Easy-to-Digest Foods and What to Avoid with a Sensitive Stomach

