Introduction: Why Lung Health Matters for Endurance and Performance
Lung health is one of the most overlooked components of physical performance and endurance training. Whether you’re an athlete aiming to boost stamina or a recovering patient working to regain respiratory capacity, optimal pulmonary function is essential. Unlike skeletal muscles that can be visibly toned and flexed, the lungs work behind the scenes, quietly fueling every movement by delivering oxygen to the blood and expelling carbon dioxide. Enhancing respiratory efficiency isn’t just beneficial for those with chronic conditions; it’s a performance multiplier for anyone engaged in physical activity. This is where pulmonary rehabilitation exercises come into play. Rooted in medical science yet adaptable for at-home use, these exercises can significantly improve lung capacity, endurance, and overall physical output when implemented correctly and consistently.
You may also like: How to Increase Stamina and Endurance Naturally: Smart Training Tips and Nutrition Habits That Support Cardiovascular Fitness
The growing field of pulmonary therapy exercises bridges the gap between clinical care and everyday fitness. For individuals managing chronic respiratory conditions such as COPD, asthma, or recovering from infections like pneumonia or COVID-19, targeted respiratory rehabilitation exercises are often prescribed by healthcare professionals. But as more people seek preventive and performance-enhancing strategies, these routines have found a place in mainstream wellness regimens. Understanding the science and methods behind pulmonary physical therapy exercises can empower individuals to take charge of their lung health, whether they are following a formal rehab program or integrating pulmonary rehab exercises at home into their daily routine. This article explores how to strengthen your lungs naturally through proven methods, blending clinical insight with practical advice to support endurance and physical performance at every level.
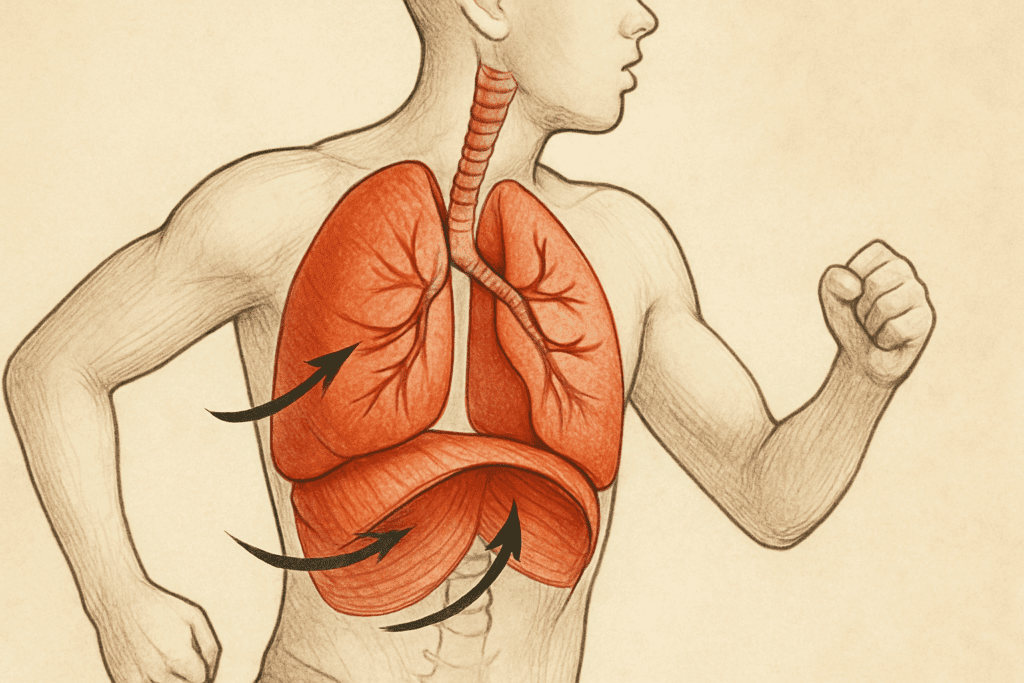
The Physiology of Pulmonary Performance: How the Lungs Power the Body
To fully appreciate the impact of pulmonary rehabilitation, it’s important to understand how the lungs function in physical activity. The lungs are responsible for oxygenating blood and removing carbon dioxide, a process critical for sustaining muscular activity. During exercise, the demand for oxygen increases dramatically. The heart and lungs respond by ramping up circulation and respiratory rates. If lung function is compromised or underdeveloped, oxygen delivery becomes inefficient, leading to fatigue, poor performance, and in more severe cases, medical complications.
The diaphragm, intercostal muscles, and accessory respiratory muscles work in tandem to expand and contract the lungs. These muscles, like any others in the body, can be trained to improve efficiency and strength. Pulmonary therapy exercises often target these very muscles to improve ventilatory mechanics and reduce the sensation of breathlessness. For individuals involved in endurance sports, this means improved stamina and delayed onset of fatigue. For those recovering from illness, enhanced muscle function can dramatically improve quality of life.
Moreover, improving lung elasticity and airway clearance can aid in maintaining open air passages, reducing resistance during breathing. Pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises aim to optimize these physiological processes through controlled breathing patterns, postural techniques, and mild physical exertion. With consistent practice, these exercises enhance lung volume, oxygen uptake, and overall respiratory efficiency, supporting better performance in both clinical and athletic settings.

Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercises: An Evidence-Based Overview
Pulmonary rehabilitation exercises are typically part of a medically supervised program designed for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions. However, they are increasingly being used for preventive and performance-enhancing purposes. These exercises combine physical activity, breathing retraining, education, and psychosocial support, offering a holistic approach to respiratory wellness. The most common components include aerobic conditioning, strength training, flexibility exercises, and specific breathing techniques.
A key goal of these exercises is to improve oxygen efficiency and reduce the effort required for each breath. Techniques such as pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing are fundamental to pulmonary therapy exercises. These methods help control the rate and depth of breathing, promoting better oxygen exchange and reducing hyperinflation in the lungs. For individuals with COPD, these techniques can significantly reduce dyspnea and improve tolerance for physical activity.
Another important aspect of pulmonary physical therapy exercises is airway clearance. This includes huff coughing and active cycle breathing techniques, which help mobilize and expel mucus from the lungs. Effective mucus clearance reduces the risk of infections and improves airflow. Additionally, light resistance training and low-impact aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, or water aerobics support cardiovascular fitness without overburdening the respiratory system. Together, these techniques form the foundation of effective pulmonary rehabilitation.
The Science Behind Respiratory Rehabilitation Exercises for Athletic Performance
Respiratory rehabilitation exercises are not only beneficial for individuals with diagnosed lung conditions; they are also increasingly recognized as performance enhancers for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. High-level endurance athletes often utilize respiratory muscle training to gain a competitive edge. By conditioning the muscles involved in breathing, they can improve ventilatory thresholds, enhance oxygen utilization, and reduce respiratory fatigue during prolonged exertion.
Inspiratory muscle training (IMT) is one of the most widely studied methods in this domain. This technique uses devices that provide resistance during inhalation, forcing the respiratory muscles to work harder. Studies have shown that IMT can increase inspiratory muscle strength, delay the onset of breathlessness, and improve performance in sports such as cycling, rowing, and running. These results align with the broader goals of pulmonary rehabilitation exercises, making them a valuable addition to endurance and stamina training programs.
Moreover, the integration of pulmonary rehab exercises at home into an athlete’s routine can be especially beneficial during off-season periods or when recovering from illness or injury. Controlled breathing practices, postural alignment, and relaxation techniques can enhance recovery and support mental focus, which are critical aspects of peak performance. By incorporating principles of respiratory rehabilitation, athletes can not only enhance their physical capacity but also reduce the likelihood of respiratory complications that may hinder training progress.
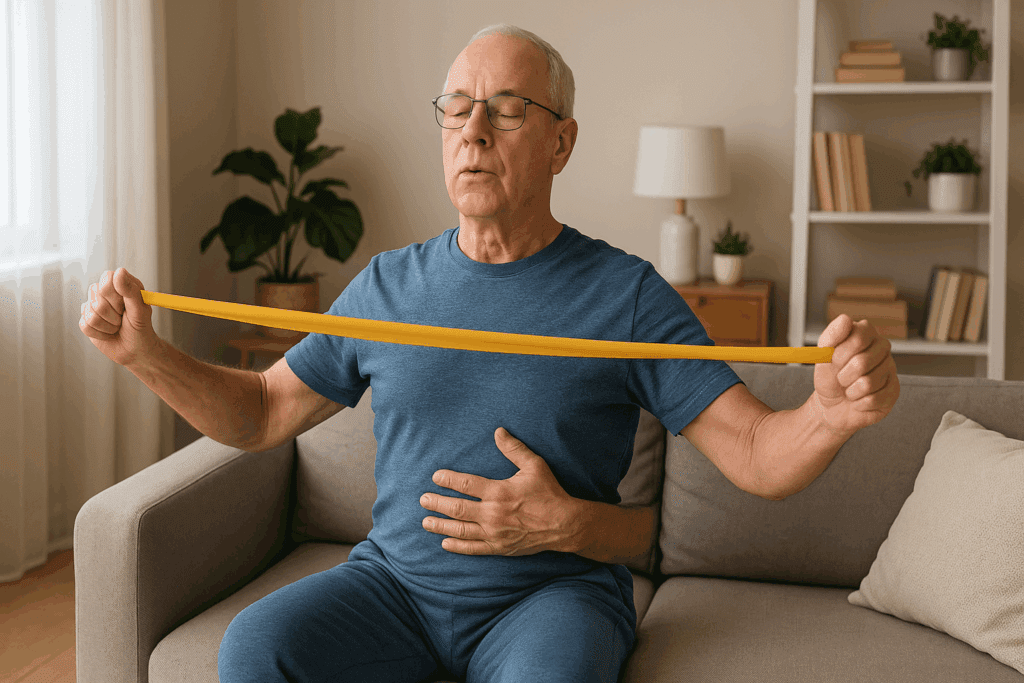
Designing Effective Pulmonary Rehabilitation Home Exercises
Developing a home-based pulmonary rehabilitation routine requires thoughtful planning, especially when the goal is to support endurance and performance. Unlike traditional gym workouts, pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises prioritize controlled breathing, gradual progression, and attention to respiratory mechanics. These routines can be safely performed in a variety of settings, making them accessible for individuals with limited mobility, those recovering at home, or athletes seeking low-impact supplemental training.
Start with foundational breathing techniques such as pursed-lip and diaphragmatic breathing. These should be practiced in a relaxed setting, ideally in a seated or semi-reclined position to support diaphragmatic movement. The goal is to reduce reliance on accessory muscles and encourage full expansion of the lower lungs. Once these techniques are mastered, mild aerobic activity can be added. Walking indoors or outdoors at a steady pace while focusing on synchronized breathing patterns can significantly improve lung endurance.
Resistance training using light weights or resistance bands can further enhance muscular support for respiration. Upper body exercises like shoulder presses, rows, and chest flies target accessory breathing muscles, promoting better posture and lung expansion. Flexibility and mobility exercises such as yoga or tai chi can also be integrated, as they emphasize breath control and fluid movement. With consistency, these pulmonary rehab exercises at home can contribute to measurable improvements in respiratory strength and physical stamina.

Psychological and Cognitive Benefits of Pulmonary Therapy Exercises
The benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation exercises extend beyond the physical. Engaging in regular respiratory training has been shown to support mental clarity, reduce anxiety, and improve overall emotional well-being. For individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, the sensation of breathlessness can be emotionally distressing, leading to avoidance of physical activity and a reduced quality of life. Pulmonary therapy exercises help break this cycle by empowering individuals to take control of their breathing.
Controlled breathing techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing are known to activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes a state of calm and relaxation. This can lead to reduced heart rate, lower blood pressure, and improved focus. Mindful breathing, often integrated into practices like yoga or meditation, has been associated with reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression. When applied within the context of pulmonary rehabilitation, these techniques offer dual benefits: physiological improvements in lung function and psychological resilience.
Additionally, the structure and routine of respiratory rehabilitation exercises provide a sense of purpose and achievement. Tracking progress, setting goals, and observing measurable improvements in stamina and respiratory function can boost confidence and motivation. For athletes, this psychological edge is essential for maintaining consistency in training. For clinical populations, it represents a pathway to greater independence and well-being. The integration of mental and physical health through these exercises underscores the holistic value of pulmonary rehabilitation.
Integrating Pulmonary Physical Therapy Exercises into Endurance Training
For individuals focused on endurance and stamina training, incorporating pulmonary physical therapy exercises into their routine can yield substantial benefits. These exercises not only improve the mechanics of breathing but also enhance the efficiency of oxygen delivery during extended physical exertion. For runners, cyclists, swimmers, and other endurance athletes, optimizing respiratory performance can be the key to pushing past performance plateaus.
Begin by pairing aerobic workouts with breathing exercises. During warm-ups and cool-downs, practice slow, controlled diaphragmatic breathing to prepare the lungs and aid recovery. Mid-workout, focus on rhythmic breathing patterns synchronized with movement. For example, runners may use a 3:2 inhale-to-exhale pattern to maintain steady oxygen intake. These small adjustments help reduce the work of breathing and conserve energy for muscular output.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) sessions can also benefit from the integration of respiratory techniques. Between intervals, using pursed-lip breathing can accelerate recovery by promoting better gas exchange and reducing breathlessness. Postural alignment is equally important; maintaining an open chest and neutral spine facilitates optimal lung expansion. Over time, consistent use of these pulmonary physical therapy exercises helps improve VO2 max and overall endurance capacity, contributing to more efficient and effective training sessions.

Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Pulmonary Rehabilitation Plans
Tracking progress is a crucial element of any rehabilitation or performance-enhancement program. With pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises, it’s important to monitor changes in breathing patterns, endurance levels, and overall physical function. Tools such as respiratory rate logs, pulse oximeters, and perceived exertion scales can provide valuable feedback. These data points help users understand how their respiratory system is adapting and when it may be time to increase the intensity or complexity of exercises.
Regular assessments with a healthcare provider, physical therapist, or certified trainer can also support safe progression. These professionals can evaluate technique, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that the exercises are aligned with individual goals and health status. For those managing chronic conditions, periodic lung function tests may be recommended to measure improvements in forced expiratory volume and overall pulmonary capacity.
Adjustments should be made gradually, with attention to signs of overexertion such as dizziness, extreme breathlessness, or chest discomfort. Increasing duration, adding resistance, or incorporating new movements should always be done incrementally. The adaptability of pulmonary rehab exercises at home allows for a personalized approach, ensuring that each step forward is grounded in safety, efficacy, and long-term sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions: Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Endurance and Performance
What is the ideal environment for performing pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises? While pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises can be performed almost anywhere, the ideal environment is one that promotes relaxation, concentration, and comfort. A quiet, well-ventilated space free of distractions supports proper breathing mechanics and posture. For those who require additional support, such as oxygen therapy or mobility aids, having easy access to these tools ensures safety and consistency. Natural light and indoor plants may enhance the psychological benefits of these exercises by reducing stress and fostering calmness. Ultimately, the goal is to create a supportive space that encourages adherence to pulmonary therapy exercises without unnecessary obstacles or interruptions.
Can pulmonary rehab exercises at home help prevent respiratory infections? Yes, when practiced regularly and correctly, pulmonary rehab exercises at home may contribute to a stronger respiratory system that is more resilient against infections. Techniques that promote airway clearance, such as controlled coughing and deep breathing, can help mobilize mucus and reduce the risk of bacterial accumulation in the lungs. Furthermore, improved ventilation and oxygenation may enhance immune response on a cellular level. While these exercises don’t replace vaccines or medical interventions, they serve as a proactive complement, especially during cold and flu seasons. For individuals prone to bronchitis or pneumonia, integrating pulmonary physical therapy exercises into daily life can serve as a protective strategy.
How do pulmonary therapy exercises influence sleep quality? Sleep quality is often affected by breathing irregularities, especially in individuals with chronic lung or cardiovascular issues. Pulmonary therapy exercises can help normalize breathing patterns and reduce nocturnal symptoms such as wheezing or shortness of breath. Diaphragmatic breathing before bed may ease anxiety and support deeper, more restorative sleep. Additionally, consistent engagement with pulmonary rehabilitation exercises may help regulate circadian rhythms by reducing cortisol levels and promoting relaxation. Over time, improved nighttime breathing may translate to better daytime energy, emotional balance, and exercise readiness.
Are there gender-specific considerations in pulmonary rehabilitation exercises? While the core techniques in pulmonary rehabilitation exercises apply to all genders, anatomical and hormonal differences may necessitate slight modifications. For instance, women typically have smaller lung volumes and may benefit from prolonged breathing phases during respiratory rehabilitation exercises to maximize oxygen intake. Hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle can influence respiratory rate and effort, which may require adaptive pacing or breath-holding adjustments. Men, on the other hand, might benefit from added resistance in strength-based pulmonary physical therapy exercises to match their typically higher baseline muscle mass. Individualized programs that account for gender-specific respiratory physiology can result in more effective outcomes for both performance and lung health.
How can older adults benefit from integrating pulmonary rehab exercises at home into daily routines? Older adults often experience reduced lung elasticity, muscle mass, and aerobic capacity, making pulmonary rehab exercises at home a valuable addition to daily health routines. These exercises support the maintenance of functional independence by enhancing respiratory strength, posture, and balance. Consistency in pulmonary therapy exercises can also mitigate age-related declines in oxygen efficiency, allowing for better engagement in other physical activities. Moreover, older adults may experience psychological benefits such as reduced fear of breathlessness, which often limits mobility. By tailoring respiratory rehabilitation exercises to suit mobility levels and health status, seniors can experience enhanced quality of life and reduced hospitalizations related to pulmonary complications.
Can pulmonary rehabilitation exercises support recovery from long COVID symptoms? Emerging evidence suggests that pulmonary rehabilitation exercises can play a pivotal role in managing post-COVID respiratory symptoms, particularly in individuals experiencing lingering fatigue, breathlessness, and decreased lung function. Techniques like paced breathing and graded aerobic training help rebuild respiratory muscle strength without exacerbating symptoms. Pulmonary rehab exercises at home also offer flexibility, allowing long COVID patients to control intensity and frequency based on fluctuating energy levels. Additionally, pulmonary physical therapy exercises may aid in clearing residual inflammation from lung tissue, contributing to faster recovery. Personalized rehabilitation plans with oversight from healthcare professionals can significantly improve outcomes for long COVID sufferers.
How do pulmonary therapy exercises intersect with mental health strategies? Breathing is a powerful bridge between the body and mind, and pulmonary therapy exercises can reinforce that connection. When practiced mindfully, these exercises stimulate the vagus nerve and reduce activation of the body’s stress response, helping to manage anxiety and depressive symptoms. Pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises that incorporate relaxation techniques or guided imagery can further enhance emotional regulation. For patients with chronic illness, improving breathing efficiency often leads to increased confidence and reduced fear around physical activity. These psychological shifts may create a positive feedback loop that encourages regular participation and long-term commitment to wellness routines.
What technological tools can assist in tracking progress with pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises? A variety of tech tools are now available to enhance the effectiveness and accountability of pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises. Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches can monitor respiratory rate, heart rate, and blood oxygen levels in real time. Mobile apps designed for breath training can guide users through structured pulmonary therapy exercises with visual or auditory cues. Some platforms offer integration with healthcare providers, allowing professionals to monitor adherence and adjust routines remotely. Additionally, digital spirometers and peak flow meters provide tangible metrics for lung function, offering motivation and data-driven insight into progress. Incorporating these tools can optimize results and personalize the experience.
What are the best ways to stay motivated with long-term respiratory rehabilitation exercises? Staying motivated with long-term pulmonary rehabilitation exercises requires a mix of strategy, support, and goal-setting. Gamifying progress with measurable targets, such as increasing breath-hold duration or walking distance, can create a sense of achievement. Social support, whether through online communities or family involvement, provides encouragement and accountability. Rotating through different pulmonary rehab exercises at home can keep the routine fresh and engaging. Visual reminders, such as improvement charts or milestone tracking, also serve as positive reinforcement. Importantly, linking each session to a larger goal—like preparing for a hike, managing a condition, or enhancing athletic performance—can sustain motivation over months or even years.
Are there advanced techniques in pulmonary physical therapy exercises for trained athletes? Yes, trained athletes often benefit from more advanced pulmonary physical therapy exercises that focus on optimizing respiratory mechanics under high physical stress. Techniques such as resisted inspiratory muscle training (IMT), breath-hold training, and intermittent hypoxia exposure can enhance respiratory muscle endurance and oxygen efficiency. These methods are particularly effective when preparing for high-altitude competitions or endurance events. Athletes may also use customized breathing sequences to manage pacing and recovery between high-intensity intervals. Integrating these advanced strategies into pulmonary rehabilitation exercises allows for improved aerobic performance, delayed fatigue onset, and superior respiratory control during competition.
Conclusion: Enhancing Endurance and Physical Capacity Through Pulmonary Rehab Exercises at Home
Improving lung strength and respiratory efficiency is no longer limited to clinical settings or specialized facilities. Through consistent practice of pulmonary rehabilitation home exercises, individuals at all fitness levels can unlock new levels of physical endurance and performance. The integration of breathing techniques, aerobic conditioning, and strength training into daily routines provides a holistic pathway to better health and fitness. Whether managing a chronic condition, recovering from illness, or striving to enhance athletic performance, these exercises serve as a powerful tool for optimizing lung function and overall vitality.
By understanding the science behind pulmonary therapy exercises and applying them with intention, users can support not only their respiratory health but also their mental and emotional well-being. The connection between the lungs and the broader physiological systems of the body is profound. When the lungs function efficiently, every other system benefits—from circulation and energy metabolism to focus and emotional stability. Embracing pulmonary rehabilitation exercises as part of a broader endurance and stamina training strategy is a smart, science-backed decision that pays dividends in both health and performance. As we continue to explore the limits of physical capability, it becomes increasingly clear that the breath is not just a background process—it is a foundation for strength, resilience, and excellence.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.

