The heart is more than a pump; it is the silent powerhouse that sustains life through each beat. Yet for millions of people, heart health is compromised by injury, disease, or lifestyle factors. Whether due to a heart attack, myocarditis, or long-term strain from high blood pressure or poor diet, heart muscle damage is a serious concern. Understandably, many ask: can you heal your heart after such an event? With rising interest in holistic and lifestyle-based approaches to recovery, emerging research suggests that yes, there are ways to support heart repair naturally. This article explores the science and strategies behind how to repair heart muscle damage, focusing on the role of smart training, evidence-based nutrition, and integrative lifestyle changes that promote genuine healing.
You may also like: Smart Nutrition Choices for a Healthier Lifestyle: What to Know About Whole Grain Rice and Whole Wheat Rice
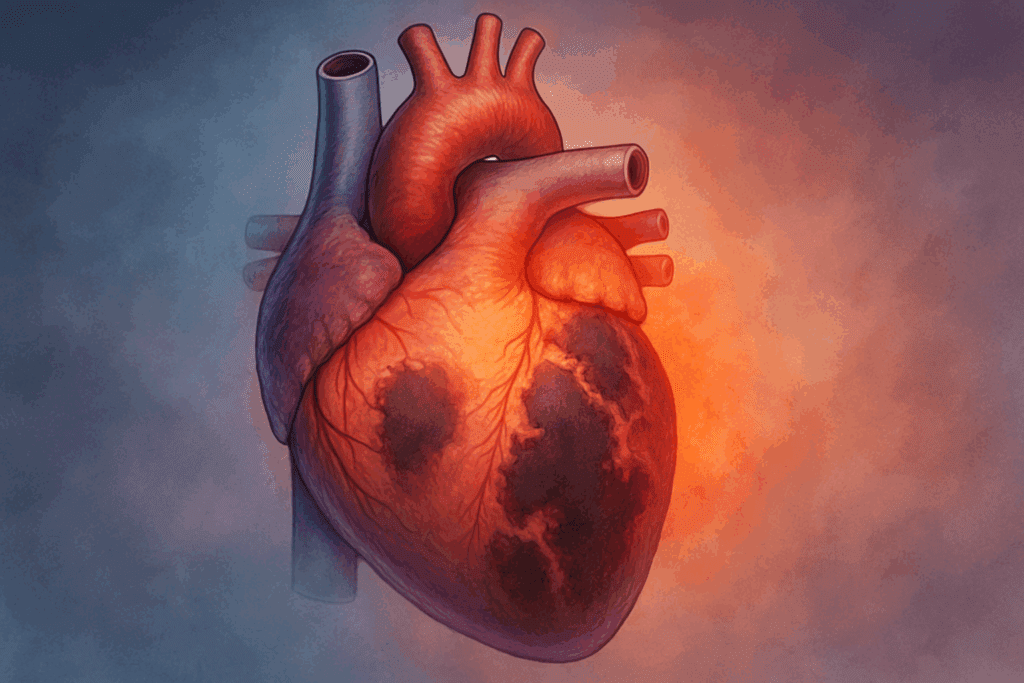
Understanding Heart Muscle Damage and Its Causes
Heart muscle damage—also known as myocardial injury—occurs when the cells of the heart muscle (myocytes) are stressed, inflamed, or deprived of oxygen. This may result from acute events like a heart attack or chronic conditions such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy. Damage can also stem from viral infections, autoimmune disorders, or exposure to toxins. One of the key challenges is that unlike skeletal muscle, which can regenerate efficiently, cardiac muscle has very limited regenerative capacity. Thus, once damaged, the heart often compensates with scar tissue rather than rebuilding healthy muscle fibers.
Despite this limitation, the heart is remarkably adaptive. It can undergo remodeling to preserve function, and research into cardiac stem cells and molecular pathways has opened up new possibilities for promoting healing. This brings us back to the original question: can you heal your heart? The answer lies not just in medical interventions but in the synergy between exercise, nutrition, and whole-body health practices that may influence cellular repair and reduce further harm.

The Role of Exercise in Supporting Cardiac Recovery
Exercise is not only safe for most individuals recovering from heart muscle damage—it is essential. Cardiac rehabilitation programs have long been the gold standard in post-heart-attack care, combining monitored physical activity with education and counseling. These programs show that structured exercise improves cardiovascular function, enhances oxygen delivery, reduces inflammation, and boosts quality of life. Even more intriguing is the concept of hormesis—the idea that moderate stress (like that from exercise) triggers the body’s adaptive repair mechanisms.
Moderate-intensity aerobic training, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, is especially effective. It enhances endothelial function, helps manage blood pressure, and can gradually improve left ventricular function even in patients with heart failure. Resistance training, when done under guidance, may also build muscular endurance without overstressing the heart. Importantly, individualized programming is key. Training must be progressive and responsive to one’s baseline cardiovascular health, ensuring that exercise heals rather than harms. This tailored approach aligns with the principle that you can heal your heart best when movement is structured to support, not strain, recovery.
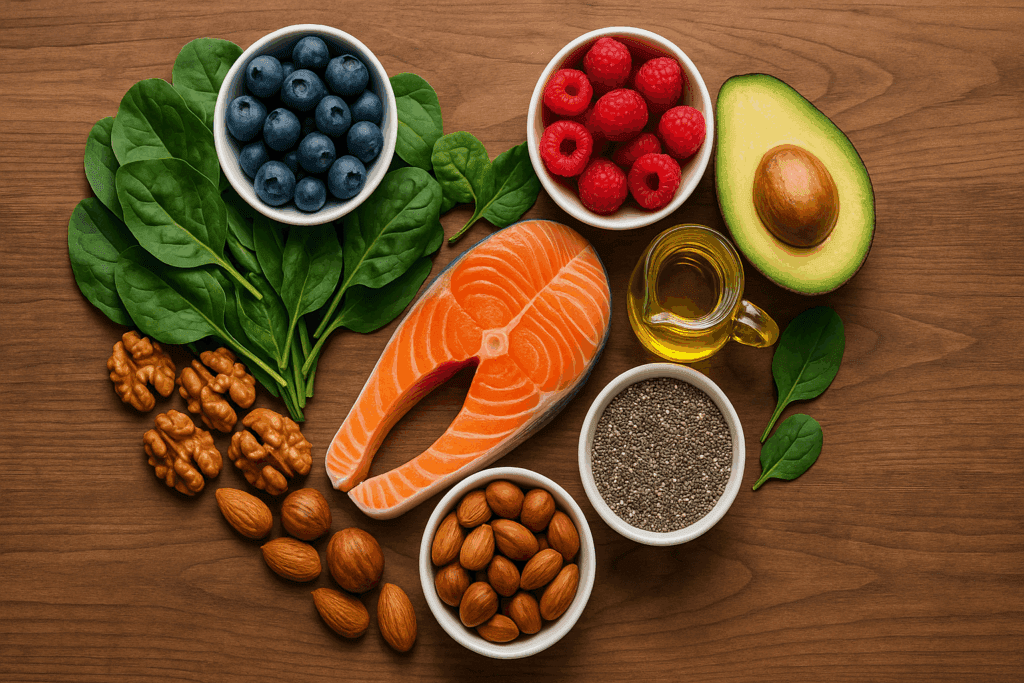

Nutrition as a Foundation for Cardiac Repair
If movement is medicine for the heart, then food is fuel for its healing. Scientific evidence strongly supports the role of nutrition in reducing cardiovascular risk and improving heart function. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and nutrient-dense foods provides the building blocks for repair while minimizing further damage. Whole foods—especially those from the Mediterranean and DASH dietary patterns—are repeatedly associated with improved cardiovascular outcomes.
Key nutrients that play a role in heart muscle health include omega-3 fatty acids, which support anti-inflammatory pathways and cell membrane stability. Found in fatty fish like salmon and sardines, or in plant sources like flax and chia seeds, these fats may reduce arrhythmia risk and improve heart rate variability. Magnesium, potassium, and CoQ10 are also vital, aiding in electrical conductivity, muscle contraction, and mitochondrial function. In fact, individuals recovering from heart muscle damage may benefit from targeted supplementation under medical guidance.
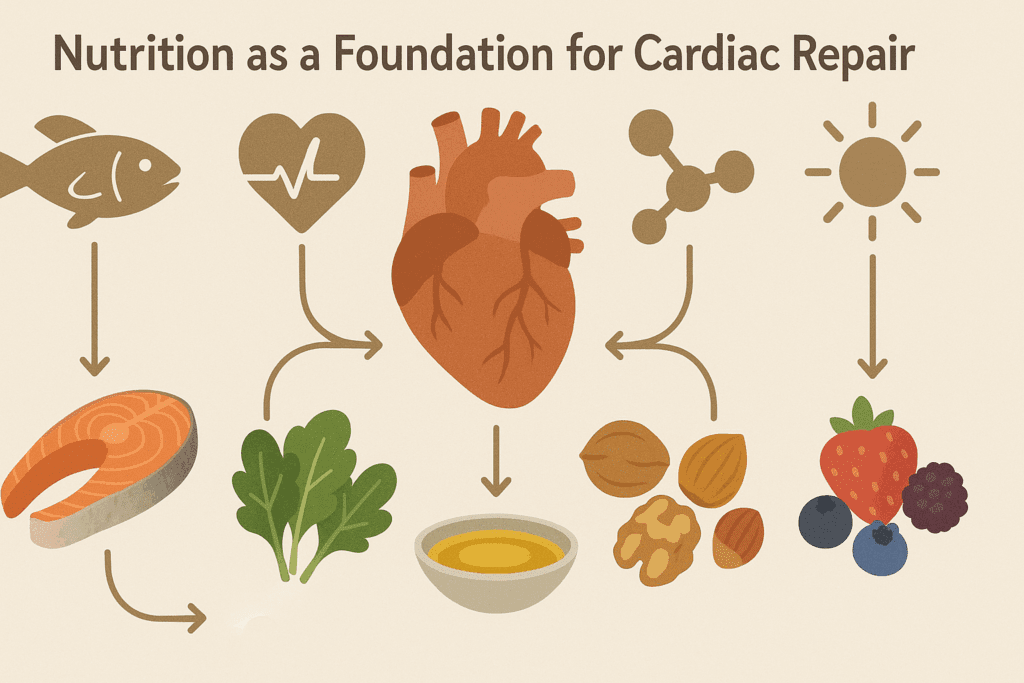
Antioxidants from fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds help neutralize oxidative stress—a major contributor to cell damage in the heart. Polyphenols in berries, green tea, and dark chocolate have cardioprotective effects that go beyond basic nutrition. Together, these elements form a dietary strategy not only to prevent further injury but to create conditions in which the heart can begin to repair itself. So yes, in this way, nutrition contributes directly to the question of how to repair heart muscle damage.
The Impact of Chronic Inflammation on Heart Healing
Inflammation is a double-edged sword in heart recovery. While it is part of the initial healing response, chronic low-grade inflammation impairs tissue regeneration and promotes fibrosis (scar formation). Many lifestyle factors—including poor diet, sleep deprivation, chronic stress, and environmental toxins—can drive systemic inflammation, making it harder for the heart to heal.
To promote a more favorable healing environment, strategies that reduce inflammation are crucial. This includes prioritizing anti-inflammatory foods, managing blood sugar, and avoiding highly processed items that trigger immune responses. Regular physical activity, adequate hydration, and healthy sleep hygiene also help regulate inflammatory markers. For individuals wondering if they can heal their heart naturally, managing inflammation is a foundational step.
Research increasingly points to the gut-heart connection as well. A healthy microbiome appears to influence systemic inflammation, lipid metabolism, and immune function. Fermented foods, fiber-rich vegetables, and prebiotics may support gut health and indirectly assist the heart’s recovery process. While this area is still emerging, it underscores the interconnectedness of body systems in the healing journey.
Can You Heal Your Heart After a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, represents a severe form of heart muscle damage, often resulting in the death of cardiac cells due to oxygen deprivation. The affected area is typically replaced by scar tissue, which lacks the contractile ability of healthy muscle. However, healing after a heart attack is not only possible—it is expected with proper care.
Cardiac remodeling refers to the structural and functional changes that occur in the heart following injury. While some remodeling is maladaptive, leading to worsening heart failure, appropriate intervention can guide this process toward more favorable outcomes. Exercise, medications like beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors, and lifestyle changes all contribute to better remodeling. Furthermore, new approaches involving stem cell therapy and regenerative medicine are being investigated for their potential to regenerate heart tissue, although these remain largely experimental.
The key takeaway is that even after significant damage, you can heal your heart to a meaningful degree. Healing doesn’t necessarily mean returning the heart to its pre-damage state but rather optimizing what function remains and preventing further decline. In many cases, people recover their quality of life, regain physical capacity, and continue to thrive post-injury.
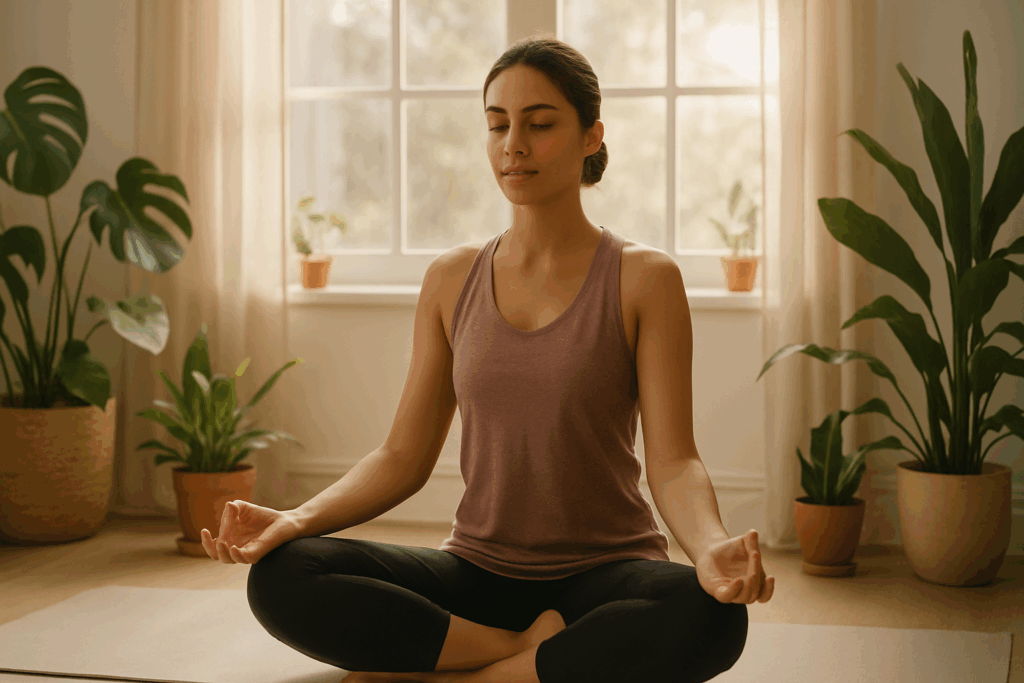

Integrating Mind-Body Practices to Enhance Recovery
Beyond the physical and nutritional aspects of recovery lies another powerful component: the mind. Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression have been shown to increase the risk of cardiovascular events and slow healing. The stress hormone cortisol can raise blood pressure, promote inflammation, and disrupt sleep, all of which are detrimental to heart health.
Mind-body practices such as meditation, yoga, tai chi, and breathwork have demonstrated positive effects on cardiovascular markers. These practices reduce sympathetic nervous system activity (“fight or flight”) and enhance parasympathetic tone (“rest and digest”), improving heart rate variability—a key measure of cardiac resilience. Engaging in mindfulness has even been shown to lower inflammatory cytokines and improve outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease.
Creating a recovery environment that addresses mental and emotional well-being is thus an essential part of how to repair heart muscle damage. Whether through formal therapy, community support, or daily mindfulness, nurturing psychological health enables the body’s intrinsic healing systems to function more effectively.
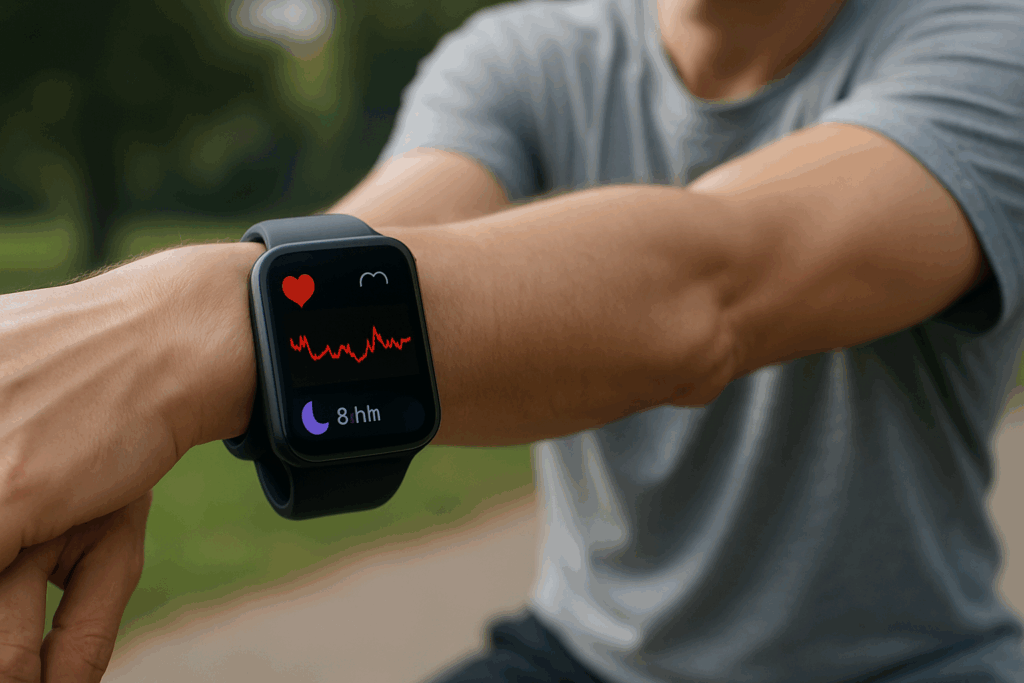

Advanced Tools: Wearables and Heart Health Monitoring
Technology is increasingly playing a role in personalized recovery. Wearable devices that monitor heart rate, variability, sleep patterns, and physical activity offer real-time feedback that can guide training intensity and recovery. For patients with prior heart muscle damage, this data provides insights into workload tolerance, helping avoid overexertion while maintaining progress.
Apps that track nutrition, hydration, and stress responses can also support the journey. Importantly, these tools should supplement, not replace, clinical care. Still, they offer individuals greater agency in their recovery—an empowering factor that aligns with the idea that you can heal your heart through informed self-management.
What Science Says About Natural Recovery Potential
Scientific consensus confirms that the heart has limited regenerative capacity, particularly in the adult human. However, studies in animals and select clinical trials have shown some ability for cardiomyocyte proliferation under certain conditions. The presence of cardiac progenitor cells and the possibility of reprogramming existing cells have opened doors in regenerative cardiology.
Additionally, lifestyle interventions remain the most accessible and evidence-supported ways to influence outcomes. Exercise has been shown to induce angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels—within the myocardium, which may improve perfusion and function. Nutritional strategies rich in polyunsaturated fats and low in added sugars can alter gene expression related to inflammation and oxidative stress.
Thus, while we may not yet have a complete blueprint for reversing all heart muscle damage, we do have tools to enhance function, preserve vitality, and even promote partial repair. When people ask, “can you heal your heart,” science responds with cautious optimism backed by practical, lifestyle-based interventions.

Healing as a Lifelong Process: Beyond Crisis Recovery
One of the most important concepts in this discussion is that healing is not a one-time event but a lifelong process. The habits and decisions made long after the acute phase of injury influence outcomes just as much as the early interventions. For example, someone who experienced heart damage in their 50s may still be making critical recovery gains well into their 60s and 70s by maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Consistency matters. Smarter training routines that evolve with age, seasonal dietary shifts that maintain anti-inflammatory intake, and ongoing emotional resilience practices all contribute to sustainable heart health. People often look for dramatic transformations, but the most meaningful progress tends to come quietly—through incremental improvements that add up over time. This is the quiet power of choosing to heal heart function through mindful, science-based living.
A New Definition of Heart Healing
Traditionally, the concept of healing has implied returning to a former state of wellness. However, in the context of heart muscle damage, healing may mean something broader. It could mean living with greater awareness, reducing future risks, and enhancing quality of life despite limitations. It might involve shifting identity—from someone who “survived” a heart event to someone who thrives through proactive health stewardship.
The goal is not perfection but resilience. Integrative cardiology is increasingly adopting this perspective, blending conventional treatments with lifestyle medicine to support the whole person. With each healthy meal, each walk in the park, each deep breath taken with intention, you signal to your body: we are healing. And that shift in narrative may be the most powerful tool of all.
Frequently Asked Questions: How to Repair Heart Muscle Damage Naturally
1. What are some lesser-known daily habits that can help heal heart muscle damage over time?
While exercise and diet are the foundation, subtle daily habits like morning light exposure, nasal breathing, and structured hydration patterns can complement your recovery. Natural circadian rhythm alignment helps regulate cortisol and melatonin, which indirectly support cardiac healing by improving sleep and reducing systemic inflammation. Nasal breathing during rest and exercise enhances nitric oxide production, a molecule that supports vascular health. Hydrating with mineral-rich water throughout the day maintains electrolyte balance, especially important when trying to heal heart muscle damage through physical activity. Over time, these smaller, mindful practices contribute to a broader framework in which you can heal your heart more effectively.
2. Can intermittent fasting support the body’s ability to repair heart muscle damage?
Emerging research suggests that intermittent fasting may enhance metabolic flexibility, reduce inflammation, and activate cellular repair processes like autophagy—all of which play a role in heart recovery. While more human studies are needed, animal models show promising links between fasting windows and reduced fibrosis after cardiac injury. If you’re wondering how to repair heart muscle damage without over-reliance on pharmaceuticals, integrating a medically supervised fasting protocol may be a complementary tool. However, those with existing cardiovascular conditions should consult a cardiologist or nutrition specialist before adopting this strategy. When done properly, intermittent fasting may create metabolic conditions that help the body heal heart tissues at a cellular level.
3. Are there emotional or psychological factors that affect the body’s ability to heal heart muscle damage?
Yes—emotional resilience plays a surprisingly direct role in cardiovascular recovery. Chronic emotional stress raises levels of cortisol and inflammatory cytokines that can interfere with the body’s attempt to heal heart muscle tissue. Conversely, practices that foster positive emotional states, like gratitude journaling, community engagement, or cognitive behavioral therapy, can enhance vagal tone and promote heart rate variability. These are not just mood boosters; they’re physiological interventions that align with the science of how to repair heart muscle damage from the inside out. Addressing the emotional body can be just as important as addressing the physical one.
4. How does muscle recovery in athletes differ from recovery in someone healing from heart muscle damage?
While both processes involve tissue repair, the stakes and strategies are vastly different. Athletes dealing with skeletal muscle damage often rely on rapid regeneration, protein synthesis, and performance-based rehab. In contrast, heart muscle recovery is far more delicate, as the heart has limited regenerative capacity. The question isn’t just can you heal your heart, but how can you support it in ways that preserve function without overtaxing it. Unlike an athlete’s approach, recovery after cardiac injury must be slower, more data-driven, and often supported by biofeedback tools that measure exertion thresholds and stress loads in real time.
5. What role do adaptogenic herbs play in supporting heart recovery?
Adaptogens like ashwagandha, rhodiola, and holy basil can modulate stress responses, reduce inflammation, and potentially stabilize cortisol—factors that influence cardiovascular repair. While they won’t directly regenerate heart tissue, they may contribute to an environment where healing becomes more feasible. When looking at how to repair heart muscle damage holistically, reducing stress hormones can create a metabolic and emotional setting conducive to cardiac improvement. Always pair adaptogen use with guidance from an integrative physician or herbalist. Used wisely, these herbs can be part of a supportive plan to help heal heart stress from within.
6. Can sauna therapy enhance the body’s ability to heal heart muscle damage?
Yes, particularly when used moderately and with medical clearance. Sauna therapy can improve circulation, lower blood pressure, and increase the production of heat shock proteins that protect cardiac tissue. Some studies suggest that frequent sauna use mimics the cardiovascular effects of moderate exercise, helping individuals who cannot yet engage in full-intensity workouts. When the goal is to heal heart muscle damage in a low-impact way, sauna therapy offers a passive but powerful avenue for increasing cardiovascular resilience. However, hydration and supervision are key to avoid placing additional stress on the body.
7. What are the most promising future treatments for natural heart repair?
Looking ahead, regenerative cardiology is exploring gene therapy, 3D bioprinting of heart tissue, and reprogramming of fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes. While these techniques are not yet mainstream, they hold great promise for patients who ask, “can you heal your heart beyond today’s limitations?” In the meantime, more accessible innovations like wearable ECG monitors, AI-driven recovery algorithms, and precision nutrition platforms are helping patients track subtle progress in real time. These tools blend technology and biology in ways that redefine how to repair heart muscle damage over the long term. As science progresses, the boundary between clinical intervention and daily lifestyle becomes more integrated than ever.
8. How can relationships and social connection influence heart healing?
Social support is one of the strongest predictors of heart health outcomes after a cardiac event. Isolation is associated with higher mortality rates in heart failure and post-heart attack patients, independent of other risk factors. Healing environments that include community, friendship, or family interaction promote oxytocin and other neurochemicals that reduce inflammation and lower blood pressure. When considering how to heal heart conditions naturally, social connection should be viewed not as a luxury but as a medical necessity. Joining a support group, spending time in emotionally safe environments, or even regular phone conversations can have a measurable impact on recovery.
9. What types of sleep patterns are best for someone trying to heal heart damage?
Deep, uninterrupted sleep facilitates parasympathetic dominance, tissue repair, and hormonal balance, all of which are essential to cardiac recovery. Poor sleep disrupts glucose metabolism, raises blood pressure, and elevates cortisol levels—conditions that undermine attempts to heal heart tissue. Establishing consistent bedtimes, reducing blue light exposure at night, and incorporating relaxing rituals like herbal teas or gentle stretches can significantly improve sleep quality. For individuals exploring how to repair heart muscle damage holistically, high-quality sleep is a pillar as critical as nutrition or exercise. Sleep apnea should also be ruled out, as it directly strains the heart.
10. Is it ever too late to try to heal your heart naturally after years of damage?
While early intervention is ideal, it is never too late to adopt heart-healing behaviors. Even in older adults with advanced cardiovascular disease, lifestyle interventions have shown measurable improvements in cardiac output, quality of life, and functional capacity. The body retains remarkable plasticity, and with the right support, you can heal your heart to a meaningful extent at virtually any stage. From diet to exercise to emotional renewal, each effort builds toward cumulative repair. Age should be a motivator—not a deterrent—when considering how to repair heart muscle damage and reclaim long-term health.
Conclusion: Yes, You Can Heal Your Heart with Smarter Training and Nutrition
The question at the heart of this conversation—can you heal your heart—is not simply a medical inquiry. It is a personal one, often born from fear, hope, and the desire to regain control over health. The answer is that while some structural damage may be permanent, the potential for healing exists in many powerful forms. By understanding how to repair heart muscle damage through evidence-based training, nutrient-dense eating, and inflammation management, you lay the foundation for true recovery.
Smart endurance and strength training tailored to your needs can stimulate positive remodeling, improve circulation, and build resilience. Anti-inflammatory, whole-food nutrition supports cellular function, reduces oxidative stress, and supplies the raw materials for repair. Emotional well-being, stress reduction, and lifestyle consistency further enhance the healing environment. Together, these elements answer the call to heal heart health with a resounding yes.
As we look ahead, scientific advancements may continue to refine our understanding of cardiac regeneration. But you don’t have to wait for a breakthrough to begin. You can take action today—with your next step, your next meal, your next breath. Because healing is already within reach, and your heart is listening.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
30 ways to Improve Your Heart Health Naturally