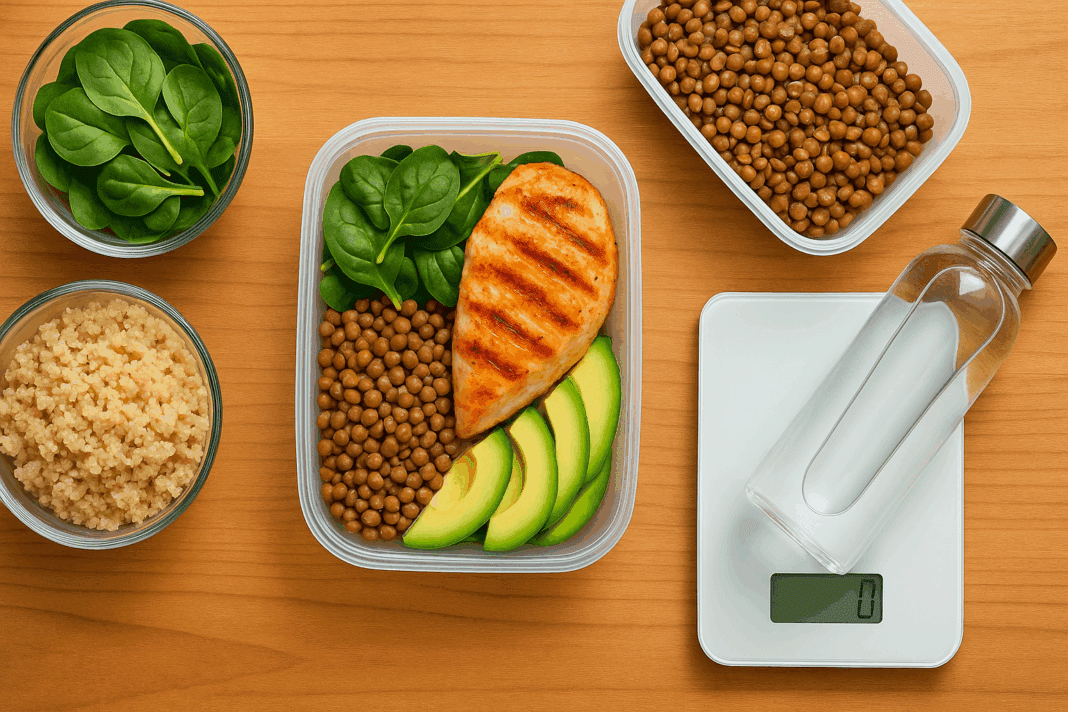In the pursuit of a healthier lifestyle, dietary choices are often the cornerstone of sustained success. For individuals looking to lose weight while preserving lean muscle mass and maintaining energy, the concept of smart fueling becomes crucial. Central to this strategy are low calorie high protein meals for weight loss, which offer a dual advantage: they reduce overall caloric intake while supplying the amino acids necessary for metabolic maintenance and muscle support. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the science, strategies, and real-world applications of high-protein, low-calorie diets that align with both weight management and long-term health.
You may also like: Smart Meal Prep Ideas for a Low Carb Diet: Sustainable Strategies for Weight Loss and Lasting Energy
Understanding the Metabolic Role of Protein in Weight Management
Protein serves as a multifunctional macronutrient with implications far beyond muscle repair. It influences satiety, thermogenesis, and metabolic rate, making it a powerful tool in the context of weight loss. When protein is consumed in higher proportions, it enhances the feeling of fullness, helping individuals naturally regulate their intake of other, more calorie-dense macronutrients like fats and carbohydrates. This is particularly significant in low calorie high protein meals for weight loss, where volume and satisfaction must compensate for reduced energy density.
Moreover, protein has a higher thermic effect of food (TEF) compared to fats or carbohydrates. This means the body expends more energy during its digestion and absorption, creating a metabolic edge for those prioritizing protein in their meals. For individuals choosing between diets, the question often arises: is keto a low carb diet, and how does that compare to a high-protein low-calorie approach? While both aim to manipulate macronutrient ratios for fat loss, the latter often emphasizes lean protein sources and sustainable caloric deficits without the potential side effects associated with very low-carb regimens.
Crafting High-Protein, Low-Calorie Meals: Principles and Ingredients
Designing meals that are both satisfying and aligned with calorie-conscious goals requires a strategic approach. Lean animal proteins such as skinless poultry, white fish, and egg whites are excellent staples. Plant-based options like lentils, tofu, tempeh, and seitan also provide substantial protein while offering added benefits such as fiber and phytonutrients.
Vegetables, particularly cruciferous and leafy greens, should form the bulk of any weight loss plate. These low-calorie, nutrient-dense foods add volume, aid digestion, and enhance satiety. Pairing them with moderate amounts of whole grains like quinoa or farro can provide a slow-digesting carbohydrate base that complements protein without compromising energy balance.
It’s worth noting that many people mistakenly equate ketogenic plans with universally high-protein models. However, the ketogenic diet vs low carb approach typically prioritizes fat over protein to maintain ketosis. In contrast, high-protein, low-calorie meal plans are more flexible and often better tolerated long-term, particularly for individuals who struggle with restrictive eating.
How Protein Recipes for Weight Loss Differ from Traditional Diet Meals
Traditional diet meals often rely on calorie counting without regard to macronutrient quality. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies and loss of lean mass. Protein recipes for weight loss, on the other hand, focus on maximizing nutrient density per calorie. This includes the thoughtful incorporation of herbs, spices, and cooking techniques that enhance flavor without adding hidden calories.
For example, a grilled chicken salad with balsamic vinegar and avocado provides not just protein but also healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. Similarly, a lentil and spinach stew spiced with turmeric and cumin delivers plant-based protein alongside anti-inflammatory compounds. These meals are not only more nourishing but also more satisfying, making adherence to a healthy eating plan easier over time.
The Science Behind Satiety and Energy Regulation
Research consistently demonstrates that protein-rich meals stimulate greater satiety than their carbohydrate-heavy counterparts. This effect is mediated by hormonal responses involving ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and peptide YY (a hormone that promotes fullness). High-protein, low-calorie meals can reduce ghrelin levels more effectively than meals dominated by simple carbs, helping to suppress appetite naturally.
Additionally, protein supports lean body mass during weight loss, which in turn sustains basal metabolic rate. This contrasts with low-protein calorie-restricted diets, which can lead to a decline in metabolic rate due to muscle loss. When considering options like the low carb diet keto diet comparison, it’s clear that while ketosis can reduce hunger for some individuals, it may not preserve muscle mass as effectively without adequate protein.
Meal Timing and Distribution of Protein Intake
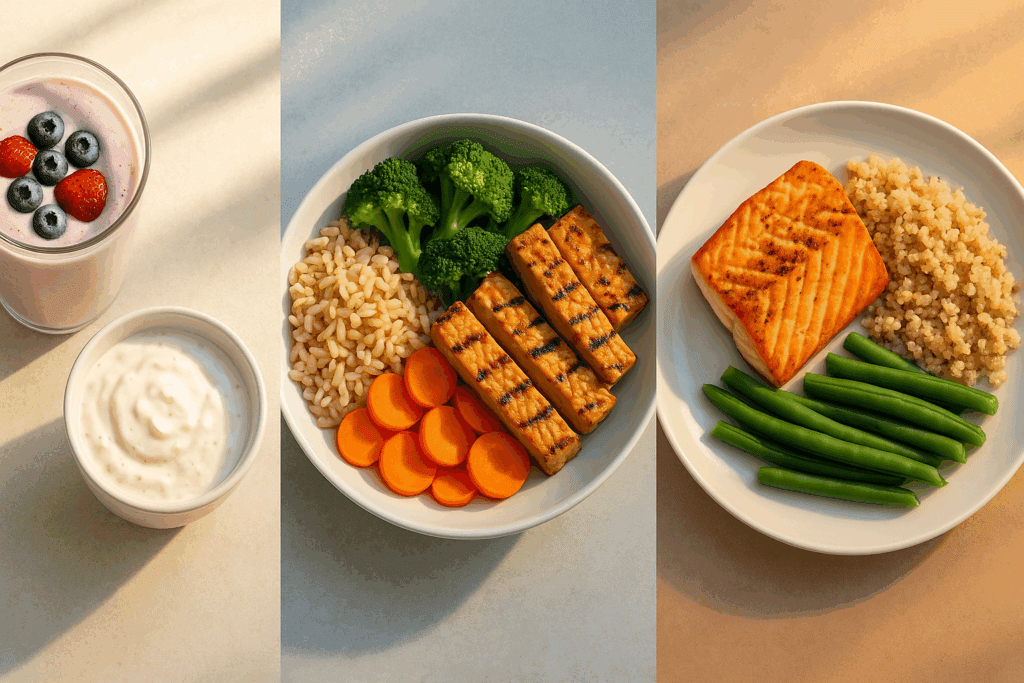
Emerging evidence suggests that distributing protein intake evenly throughout the day may enhance muscle synthesis and satiety. Rather than consuming the bulk of daily protein at dinner, including moderate protein portions in breakfast and lunch can optimize metabolic benefits. A breakfast smoothie with Greek yogurt and flaxseed, a lunch featuring grilled tempeh and roasted vegetables, and a dinner with baked salmon and quinoa provide a balanced template for daily intake.
This strategy aligns with findings from sports nutrition and aging research, where even protein distribution has been linked to better body composition outcomes. For those asking is keto a good diet, the answer often depends on individual tolerance and lifestyle. A high-protein, calorie-controlled plan may offer similar weight loss benefits with fewer restrictions and more nutritional balance.
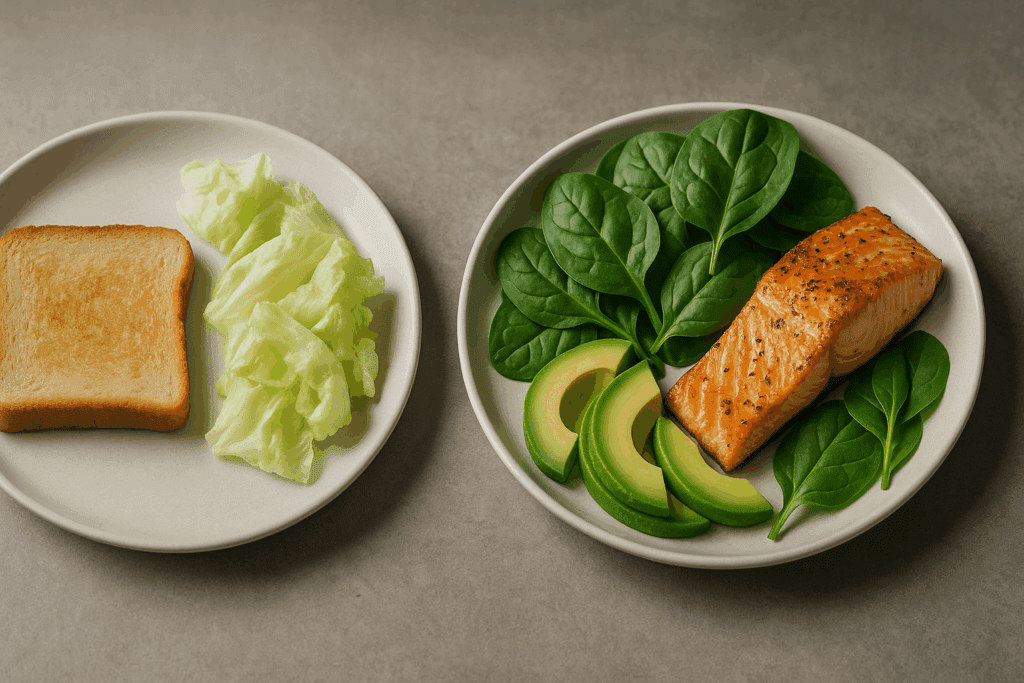
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Carbohydrates and Protein
A prevailing myth in weight loss culture is that carbohydrates must be severely restricted to achieve fat loss. This belief fuels the popularity of the ketogenic diet vs low carb comparison, often without context. While reducing refined carbs and sugars can be beneficial, complex carbohydrates from vegetables, legumes, and whole grains provide essential fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
What differentiates a sustainable plan is not the absolute exclusion of carbs but their integration with high-quality protein and healthy fats. Low calorie high protein meals for weight loss succeed when they are not just low in energy but also high in nutritional value. A quinoa and black bean bowl with avocado and lime vinaigrette, for instance, offers complete protein and balanced macronutrients while remaining calorie-conscious.
Is Keto No Carbs? Clarifying Dietary Terminology
One of the most common misconceptions is the idea that is keto no carbs. While the ketogenic diet is indeed very low in carbohydrates, it does not eliminate them entirely. The typical keto plan allows for about 20 to 50 grams of net carbs per day, primarily from non-starchy vegetables and nuts. This level is sufficient to maintain essential bodily functions and support limited glucose needs.
Understanding the difference between is keto a low carb diet and how it contrasts with moderate-carb, high-protein plans is vital. The former aims to induce a state of ketosis through fat predominance, while the latter uses protein to stabilize blood sugar and manage hunger. Both can be effective for weight loss, but the high-protein approach may offer greater flexibility and sustainability.

Personalizing Protein Needs Based on Activity and Goals
Not all protein needs are created equal. Athletes, older adults, and individuals with high physical demands may require more protein to maintain muscle and support recovery. The general guideline of 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight may suffice for sedentary individuals, but active populations often benefit from intakes ranging from 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram.
Customizing intake ensures that meals are not just low in calories but also tailored to physiological demand. This personalization is where protein recipes for weight loss truly shine—they can be adapted for different energy levels, fitness goals, and dietary preferences, whether plant-based or omnivorous. This adaptability also makes high-protein strategies more inclusive and accessible than one-size-fits-all ketogenic templates.
The Sustainability Question: Is a Keto Diet Sustainable Long-Term?
Sustainability is a critical consideration in any dietary plan. While some individuals thrive on strict low-carb regimens, others find the social, psychological, and nutritional limitations of ketosis burdensome over time. This raises the question: is a keto diet sustainable?
For many, the answer lies in the middle ground. High-protein, moderate-carb, low-calorie approaches provide structure without rigidity. They allow for a broader range of food choices, making them easier to follow in the long run. Moreover, they support metabolic health without drastically altering energy systems, making them ideal for both weight loss and maintenance phases.
Real-World Applications: Planning Meals for Everyday Success
Implementing a high-protein, low-calorie plan in daily life requires practical strategies. Meal prep, portion control, and ingredient awareness are foundational. Batch-cooking lean proteins, pre-chopping vegetables, and preparing sauces with Greek yogurt or tahini instead of cream-based dressings can simplify adherence.
Restaurants and takeout can also be navigated strategically. Opting for grilled rather than fried items, requesting dressings on the side, and focusing on protein and vegetable combinations are simple yet effective tactics. With consistency, these choices accumulate into long-term behavioral change that supports health.
When considering low calorie high protein meals for weight loss, it’s clear that success comes not from deprivation but from intentional, informed eating. With planning and persistence, these meals become not just a diet strategy but a sustainable lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions: High-Protein, Low-Calorie Strategies for Sustainable Weight Loss
What are some creative ways to add more protein to plant-based meals without increasing calories significantly?
Many people struggle with adding enough protein to their plant-based diets without inadvertently boosting calorie counts. A few smart strategies include using textured vegetable protein (TVP), which is low in calories but high in protein and absorbs flavors from sauces well. You can also incorporate spirulina into smoothies or soups for a concentrated protein punch. Fermented products like tempeh and miso not only enhance umami flavor but also contribute to gut health while keeping calories in check. These ingredients support the goal of creating low calorie high protein meals for weight loss while maintaining variety and taste.
How do low calorie high protein meals for weight loss impact hormonal balance, especially in women?
High-protein diets can positively influence hormone regulation, particularly those related to hunger and satiety such as ghrelin and leptin. In women, balancing these hormones can reduce cravings and help regulate menstrual cycles, especially when protein is distributed evenly across meals. However, very low-calorie diets can suppress estrogen production if maintained too long. It’s essential that women integrate protein recipes for weight loss in a way that prioritizes nutritional adequacy and not just caloric restriction. Choosing whole-food protein sources can also stabilize insulin and cortisol levels, which influence fat storage.
Can high-protein, low-calorie diets help with emotional eating or food addiction?
Yes, there is growing evidence that low calorie high protein meals for weight loss can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the emotional rollercoaster that often leads to binge eating. Foods rich in protein tend to curb hunger longer, which can help people avoid emotional triggers tied to hunger spikes. Additionally, consistent intake of amino acids like tryptophan supports serotonin production, which may improve mood regulation. Structured meal planning using protein recipes for weight loss creates routine and reduces impulsive eating behaviors. Many behavioral nutritionists recommend protein-centric eating as part of a holistic strategy for emotional eating management.
Are there any side effects of eating high-protein diets long-term?
While generally safe for healthy individuals, consuming extremely high-protein diets over extended periods may strain the kidneys in people with pre-existing kidney issues. It’s important to note that low calorie high protein meals for weight loss can still be balanced by incorporating fiber-rich vegetables and adequate hydration to support kidney function. Overemphasis on animal proteins without diversity may also reduce intake of key phytonutrients, especially in omnivorous diets. Rotating protein recipes for weight loss that include legumes, tofu, and nuts can help mitigate this concern. A varied and well-rounded protein intake is key to long-term sustainability and health.
What are the best protein-rich snacks for people trying to lose weight on the go?
Convenience is often a barrier to healthy eating, but there are numerous portable, protein-rich options. Hard-boiled eggs, cottage cheese packs, roasted chickpeas, and turkey roll-ups are simple, low calorie high protein meals for weight loss that require minimal prep. For plant-based eaters, edamame, protein bars made with pea or brown rice protein, and nut butter packets are excellent choices. Choosing snacks that combine protein with fiber or healthy fats extends satiety. Regular inclusion of such protein recipes for weight loss into your daily routine can curb cravings between meals and support a calorie deficit.
How do protein needs change as we age, and how does this affect weight management strategies?
As we age, our bodies become less efficient at synthesizing muscle protein, making higher protein intake essential to preserve lean mass. For individuals over 50, experts recommend increasing protein consumption by about 30%, particularly when engaging in resistance training. Low calorie high protein meals for weight loss remain important, but the emphasis shifts slightly toward muscle preservation rather than just fat loss. Integrating protein recipes for weight loss that include calcium-rich sources like sardines or fortified tofu also supports bone health. Protein becomes not only a tool for weight management but a cornerstone of aging well.
What role does food psychology play in sticking to a high-protein, low-calorie diet?
Cognitive patterns greatly influence dietary success. When meals are framed positively—as nourishing and satisfying—adherence improves. High-protein diets can contribute to this mindset by naturally increasing feelings of fullness and reducing the perceived need for indulgent snacks. Visualization strategies, such as imagining low calorie high protein meals for weight loss as fuel rather than restriction, also enhance compliance. People are more likely to succeed when they view protein recipes for weight loss as enjoyable rituals rather than dietary chores. Language, perception, and meal aesthetics all play a role in behavioral change.
How can one maintain variety in a high-protein, low-calorie diet without getting bored?
Variety is a common challenge in any targeted nutrition plan, but it can be addressed through international cuisines and creative ingredient swaps. For example, use Moroccan spices with lentils, Vietnamese herbs with tofu, or Greek yogurt as a base for Indian-inspired marinades. Flavor innovation transforms low calorie high protein meals for weight loss into something exciting rather than monotonous. Try rotating between different preparation methods—grilling, roasting, steaming, or raw blends. Curating global protein recipes for weight loss not only expands your palate but enhances micronutrient diversity as well.
Can high-protein diets improve sleep quality and recovery after exercise?
Absolutely. Protein supports the production of melatonin and serotonin—both critical to sleep regulation. Including protein-rich snacks in the evening, such as cottage cheese or a small turkey wrap, can improve sleep latency and recovery. Athletes benefit particularly from low calorie high protein meals for weight loss that support muscle repair overnight. Adding magnesium-rich foods like pumpkin seeds or dark leafy greens enhances this effect. When structured intentionally, protein recipes for weight loss can double as performance and recovery tools.
What innovations are emerging in the world of protein-focused diets?
The landscape of protein innovation is rapidly evolving, particularly in the area of plant-based proteins and lab-grown alternatives. New sources like mycoprotein (from fungi), mung bean protein, and precision-fermented whey are making waves. These offer exciting possibilities for creating low calorie high protein meals for weight loss with reduced environmental impact. Future protein recipes for weight loss may feature entirely novel sources that mimic meat’s texture and bioavailability without the ecological footprint. The intersection of sustainability, technology, and nutrition promises to redefine how we meet our dietary protein needs.
Reflecting on the Benefits of Protein-Powered Weight Loss
The journey toward sustainable weight loss and improved health is deeply personal, yet universally impacted by the quality of food choices. High-protein, low-calorie meals offer a path forward that respects both metabolic science and everyday practicality. By emphasizing satiety, nutrient density, and metabolic support, these meals do more than just cut calories—they empower individuals to thrive.
In the comparison of the keto diet vs low carb diet, and debates like is keto a good diet or is keto no carbs, the takeaway is that success depends not on rigid rules but on alignment with individual needs and preferences. For many, protein-centric, calorie-controlled approaches strike this balance beautifully.
Protein recipes for weight loss are more than a trend—they are a reflection of nutritional evolution that prioritizes whole foods, balanced macros, and sustainable habits. Whether you’re meal prepping at home or choosing from a menu, remembering the power of smart fuel can keep your goals in focus and your health on track.
Further Reading:
High Protein, Low-Calorie Recipes
29 Day High-Protein Dinner Plan for Weight Loss
30 High-Protein Meals That Are Just As Easy To Whip Up As They Are Delicious