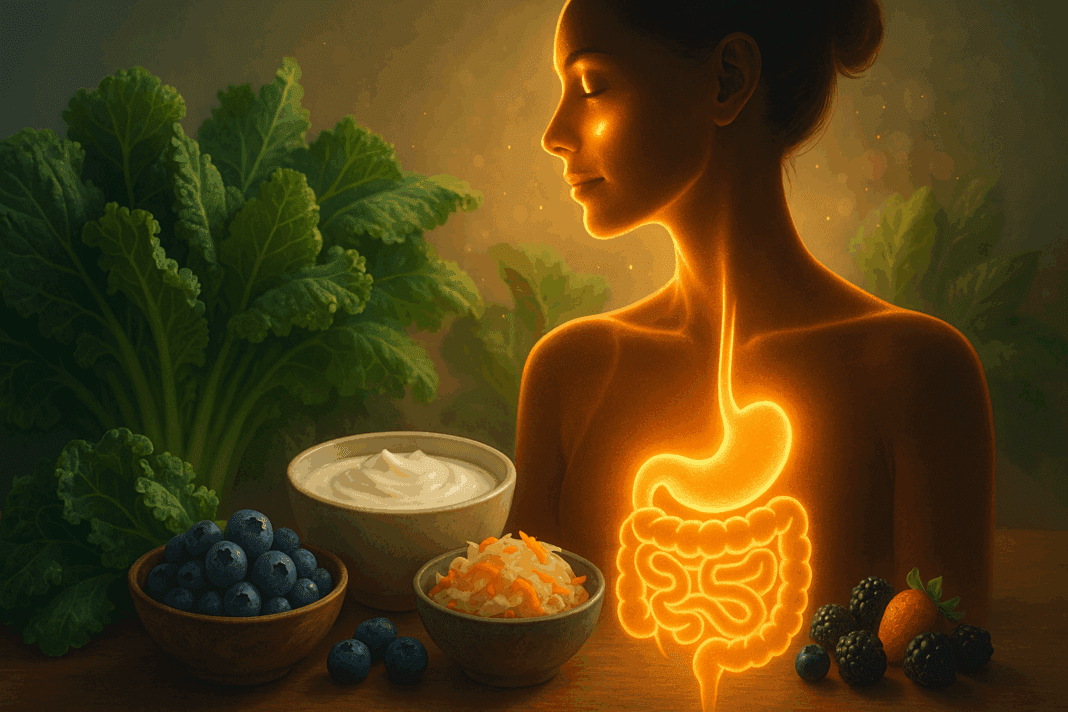
The relationship between diet and skin health is far more complex than many realize. While skincare products and topical treatments receive much of the attention in discussions about achieving a radiant complexion, emerging science has increasingly highlighted the powerful role of internal health—especially gut health—in shaping the appearance and resilience of our skin. For those seeking the best foods for clear skin, this search often leads to a deeper exploration of the gut-skin axis and the role of probiotics and holistic nutrition. This article takes a comprehensive dive into the intricate connection between the gastrointestinal system and skin clarity, offering research-based insights and practical strategies for dietary improvements that promote not only beautiful skin but also long-term digestive and overall wellness.
You may also like: The Ultimate Guide to Gut Healthy Meals: Best Meals for Gut Health and Nourishing Recipes You’ll Love
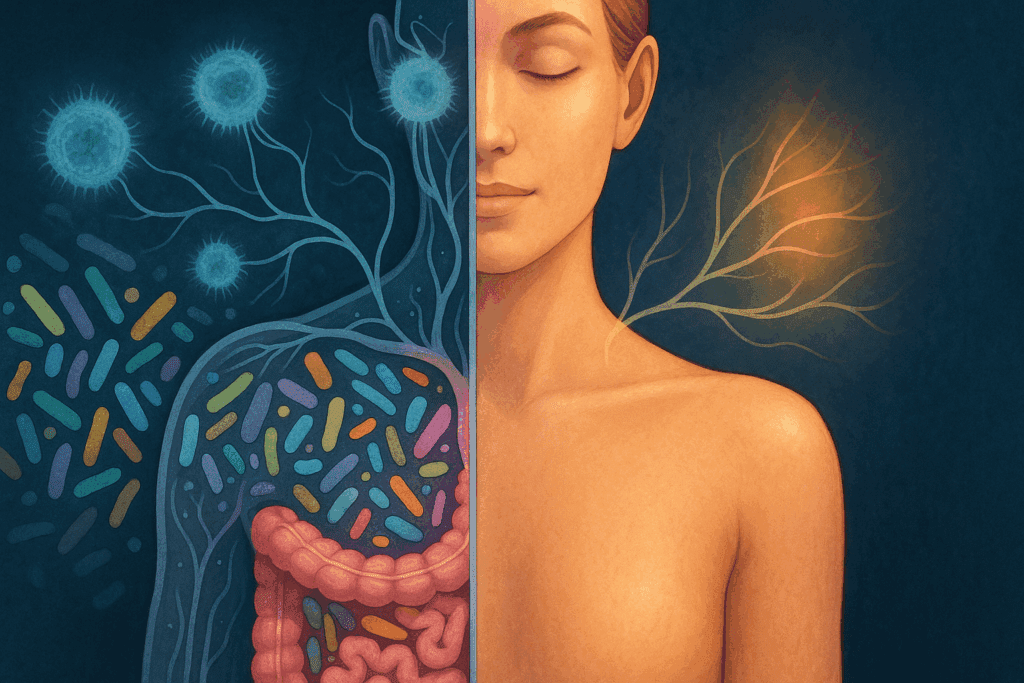
Understanding the Gut-Skin Axis: A Hidden Driver of Skin Health
The gut-skin axis refers to the bidirectional communication network between the gastrointestinal tract and the skin. This connection is facilitated by the immune system, hormones, neurotransmitters, and the gut microbiome. The gut microbiome, a vast ecosystem of trillions of microbes, plays a critical role in modulating inflammation, regulating immune responses, and producing essential nutrients. Disruption of this delicate ecosystem through stress, processed foods, antibiotics, or environmental toxins can contribute to chronic inflammation and systemic imbalances that manifest as skin concerns, including acne, eczema, psoriasis, and dullness.
Scientific studies have shown that individuals with imbalanced gut flora often exhibit higher rates of inflammatory skin conditions. For instance, one study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology found that patients with acne vulgaris were significantly more likely to exhibit gastrointestinal symptoms, suggesting a clear link between gut dysfunction and skin pathology. This growing body of research supports the need to address gut health as part of any comprehensive strategy for achieving clear and glowing skin.

Why Probiotic and Prebiotic Nutrition Matters for Clearer Skin
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support a healthy gut microbiome, while prebiotics are dietary fibers that feed these bacteria. Together, they contribute to a balanced gut environment, enhancing digestive efficiency and supporting immune function. Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated that probiotic supplementation can reduce skin inflammation, lower oxidative stress, and improve hydration and elasticity.
The most notable probiotics include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, which have been found to regulate immune responses and mitigate inflammatory processes that trigger acne and rosacea. These strains also enhance the skin barrier function by increasing ceramide production, which prevents moisture loss and irritation. When supported by prebiotic-rich foods like garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, and bananas, these probiotics thrive and multiply, amplifying their skin-supporting benefits.
Incorporating fermented foods such as kefir, sauerkraut, miso, and kimchi into the diet can provide a natural source of probiotics. These foods not only aid digestion but also deliver active cultures directly to the gut. For those struggling with persistent breakouts or dry, irritated skin, exploring probiotic therapy and gut-focused nutrition may lead to significant improvements.
Best Foods for Clear Skin Backed by Science
To understand which are the best foods for clear skin, we must look beyond surface-level trends and focus on evidence-based nutritional strategies. Anti-inflammatory foods, rich in antioxidants, essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, are foundational to healthy skin. Among the top contenders are fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats help reduce inflammation, maintain skin elasticity, and prevent dryness.
Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in vitamins A, C, and K, all of which support collagen production, cell regeneration, and wound healing. Vitamin C, in particular, is crucial for preventing oxidative stress, which contributes to skin aging. Berries, including blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, provide polyphenols and flavonoids that combat free radicals and promote an even skin tone.
Nuts and seeds like almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, and chia seeds are excellent sources of vitamin E and selenium, both known to support skin repair and reduce UV damage. Avocados supply monounsaturated fats and glutathione, a powerful antioxidant associated with skin brightening and detoxification. These examples represent just a portion of the many foods that are good for your skin and can be integrated into a clear skin diet.

How Digestive Health Influences Skin Inflammation and Acne
Acne and other inflammatory skin conditions often reflect underlying gastrointestinal disturbances. One of the main culprits is intestinal permeability, also known as “leaky gut,” where the gut lining becomes compromised, allowing endotoxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream. This triggers an immune response that can result in widespread inflammation, including in the skin.
Furthermore, digestive disorders like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are increasingly linked to skin issues. Individuals with SIBO often experience nutrient malabsorption, particularly of zinc, B vitamins, and essential fatty acids—all of which are vital for skin integrity and repair. Addressing these gut issues through targeted nutrition, supplementation, and sometimes antimicrobial protocols can substantially improve skin conditions.
To foster a gut environment that minimizes inflammation, it’s essential to avoid foods that disrupt gut flora, such as processed sugars, refined carbohydrates, and artificial additives. Instead, embracing a diverse, plant-rich diet complemented by fermented foods and fiber can lay the foundation for both digestive comfort and improved skin health.

Eating Healthy for Skin: The Importance of Nutrient Density
While calorie control and macronutrient balance are essential for overall health, when it comes to eating healthy for skin, the nutrient density of food matters most. Nutrient-dense foods provide a higher concentration of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals per calorie. These compounds are critical for regulating skin cell turnover, enhancing collagen synthesis, and maintaining moisture retention.
Foods to eat for clear skin should be chosen not only for their individual nutrients but also for their synergistic effects. For example, pairing vitamin C-rich citrus fruits with iron-containing leafy greens can improve iron absorption, supporting oxygen delivery to skin cells. Similarly, consuming healthy fats with fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K ensures proper utilization and benefits for skin structure.
Whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide zinc and B vitamins while stabilizing blood sugar levels, which is essential for reducing acne flare-ups. Beans and legumes are another valuable source of fiber and protein, offering prebiotic support and helping to regulate hormonal activity linked to skin breakouts.
Integrating these healthy skin foods into daily meals fosters a more stable and radiant complexion. By prioritizing colorful, fresh, and minimally processed foods, individuals can support their skin from within and enjoy lasting results without reliance on cosmetic products alone.
Best Foods for Clear Skin: Gut-Healthy Ingredients That Nourish Your Glow
When it comes to assembling a daily diet that delivers visible skin improvements, selecting the best foods for clear skin that also promote gut health is essential. Greek yogurt, for instance, provides both protein and probiotics, supporting digestion and enhancing skin elasticity. Sweet potatoes, rich in beta-carotene, convert to vitamin A in the body and help regulate oil production and skin tone.
Green tea is another powerful addition, containing epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a potent antioxidant that reduces inflammation and protects against UV-induced skin damage. Tomatoes deliver lycopene, a carotenoid associated with improved skin texture and reduced sensitivity to the sun. Broccoli offers a diverse array of nutrients including vitamin C, lutein, and sulforaphane, which may protect against environmental damage and oxidative stress.
These foods not only fit within a clear skin diet but also enhance microbial balance and digestive integrity. Choosing meals that integrate these elements on a regular basis provides a sustainable way to support both inner and outer health. As a bonus, many of these foods also support weight management, cardiovascular wellness, and mental clarity, reinforcing the holistic benefits of dietary transformation.
Clear Skin Diet: Avoiding Foods That Aggravate Gut and Skin
Just as some foods are celebrated for their skin-supportive properties, others are known to undermine gut integrity and trigger skin issues. High glycemic index (GI) foods, including white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels. This, in turn, increases sebum production and inflammation, both of which are central to acne development.
Dairy products, particularly those that are not fermented, have also been linked to acne and hormonal imbalances. While the evidence is mixed, some studies suggest that dairy may influence insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a hormone that stimulates oil gland activity and contributes to clogged pores. For individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy sensitivity, eliminating milk, cheese, and ice cream can lead to noticeable skin improvements.
Other dietary offenders include alcohol, which disrupts gut flora and dehydrates the skin; processed meats, which introduce inflammatory compounds; and artificial sweeteners, which may interfere with microbial diversity. While complete elimination is not always necessary, reducing intake and replacing these items with nutrient-rich alternatives can be a game-changer.
A diet for good skin is as much about what you avoid as what you include. Awareness of food sensitivities, inflammatory triggers, and blood sugar dynamics empowers individuals to make informed dietary decisions that nurture the skin from within.
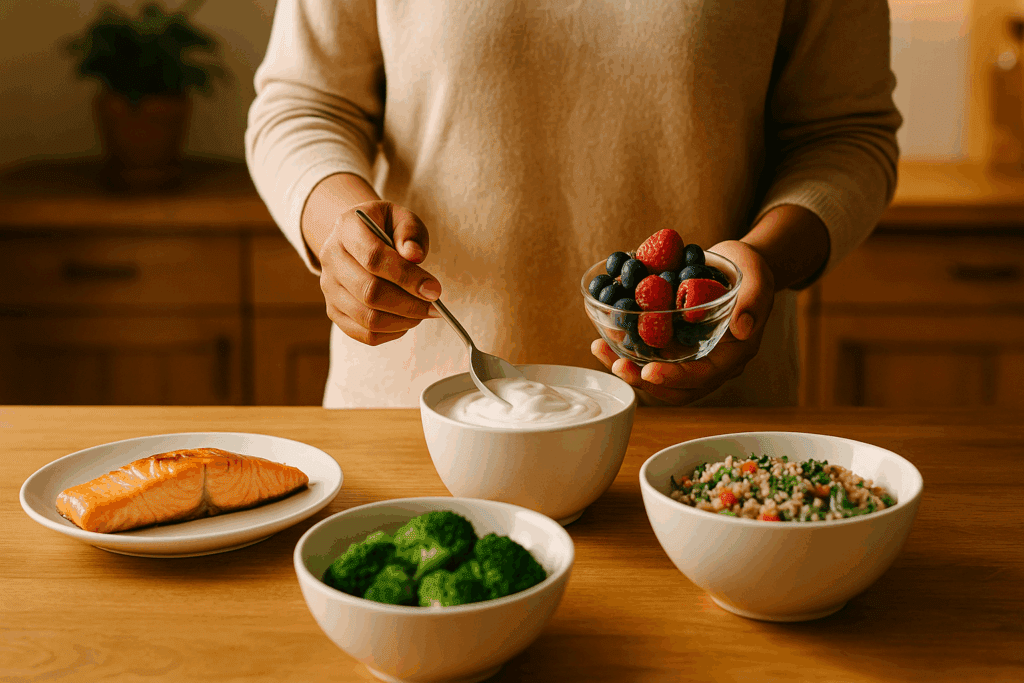
Foods That Are Good for Your Skin: A Holistic Supplement Approach
In addition to whole foods, certain supplements can complement a clear skin diet and address common nutrient gaps. Omega-3 supplements derived from fish oil or algae are known to reduce inflammation and improve skin hydration. Zinc supplements support wound healing and regulate oil production, especially for individuals with acne-prone skin.
Probiotic supplements containing strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium longum have been shown to improve both gut function and skin outcomes. Vitamin D, often deficient in modern populations, plays a critical role in immune regulation and may help reduce skin sensitivity and irritation.
Collagen peptides, derived from marine or bovine sources, are also gaining popularity for their role in supporting skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles. While the body produces collagen naturally, production declines with age, making supplementation a valuable strategy for maintaining youthful skin. When combined with vitamin C and hyaluronic acid, collagen supplements can offer synergistic benefits.
Holistic supplementation should be approached thoughtfully, ideally under the guidance of a healthcare professional. The goal is to enhance dietary patterns, not replace them, and to focus on bioavailable forms of nutrients that support both gut flora and skin integrity.
Best Foods for Clear Skin to Eat Every Day: Real-Life Applications
Creating sustainable habits around food for skin health involves practical meal planning and mindfulness. A balanced breakfast might include Greek yogurt topped with berries and chia seeds, offering a trifecta of probiotics, antioxidants, and healthy fats. For lunch, a quinoa salad with leafy greens, avocado, chickpeas, and olive oil delivers fiber, protein, and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Dinner could feature grilled salmon with roasted sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli, providing essential fatty acids, beta-carotene, and detox-supportive sulfur compounds. Snacks like carrot sticks with hummus, pumpkin seeds, or a small square of dark chocolate ensure steady nutrient intake throughout the day. Beverages such as green tea, lemon water, and bone broth hydrate and nourish the gut lining.
Integrating these foods for great skin into everyday routines does not require rigid dieting. Rather, it involves intentional choices that align with individual preferences and lifestyle demands. Over time, these habits can lead to clearer, more resilient skin and a deeper sense of vitality.
What to Eat for Better Skin: Seasonal and Cultural Diversity
One of the most enriching aspects of eating for clear skin is the opportunity to explore diverse cuisines and seasonal ingredients. In Mediterranean diets, for example, staples like olive oil, legumes, whole grains, and fresh vegetables support skin health and gut function. Traditional Japanese meals rich in miso, seaweed, and fermented soy offer both probiotics and anti-aging nutrients.
Incorporating seasonal produce ensures freshness and variety, which promotes microbial diversity and prevents dietary monotony. Summer fruits like watermelon and cucumber hydrate the skin, while winter squash and beets provide immune support during colder months. Adapting your diet for better skin according to local availability and culinary traditions can enhance both enjoyment and outcomes.
Cultural diversity in food choices also supports emotional well-being and social connection, both of which influence hormonal balance and skin clarity. Eating with mindfulness and gratitude amplifies digestive efficiency and fosters a holistic approach to health that transcends aesthetic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions: Best Foods for Clear Skin and Gut Health
How does gut health influence skin hydration and elasticity?
While inflammation is a commonly discussed link between gut health and skin conditions, its impact on hydration and elasticity is equally significant. The gut plays a central role in nutrient absorption, particularly of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins, which directly influence collagen synthesis and moisture retention in the skin. When the gut lining is compromised due to dysbiosis or leaky gut syndrome, nutrient absorption is hindered, leading to dryness, sagging, and premature wrinkles. Moreover, a healthy gut microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that regulate pH balance and help maintain the integrity of the skin barrier. A well-balanced microbial environment fosters the retention of hyaluronic acid in the skin, offering long-term hydration and a plumper appearance.
Are the best foods for clear skin different for men and women?
While the foundational principles of eating healthy for skin are largely consistent across genders, there are hormonal and metabolic differences that slightly shift the ideal diet. For instance, men may benefit from higher zinc intake, commonly found in pumpkin seeds and oysters, to regulate sebum production and support testosterone balance. Women, especially during hormonal shifts like menstruation or menopause, may experience more cyclical acne and benefit from flaxseeds, which contain lignans that modulate estrogen levels. Both genders require a diet for better skin rich in antioxidants, but women might place more emphasis on iron- and folate-rich foods such as lentils and spinach to compensate for monthly losses. Thus, while the best foods for skin health overlap, subtle hormonal nuances can inform personalized dietary choices.
What role do sleep and circadian rhythm play in the gut-skin connection?
Circadian rhythms govern not only sleep cycles but also the functioning of the gut and skin. Poor sleep disrupts gut microbiota diversity, leading to increased gut permeability and inflammation, which can manifest as skin flare-ups or dullness. During deep sleep, the body performs vital detoxification and repair processes, including skin cell regeneration and collagen synthesis. Foods for clear skin should ideally be consumed in alignment with circadian patterns—light meals in the evening support digestion and prevent overnight inflammation. Prioritizing sleep hygiene, such as dimming lights before bed and limiting sugar intake at night, enhances both gut and skin health by allowing restorative hormonal processes to unfold naturally.
Can fermented foods replace probiotic supplements in a clear skin diet?
Fermented foods like kimchi, kefir, and tempeh are excellent sources of live bacteria that support gut flora, but their bacterial strains and potency can vary widely. While these foods for great skin offer additional enzymes, vitamins, and bioactive peptides that supplements lack, they may not always provide the therapeutic doses needed for clinical improvements in certain skin conditions. Probiotic supplements offer standardized strains with specific benefits, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus for eczema or Bifidobacterium longum for acne-related inflammation. Ideally, fermented foods and supplements should complement one another, with the former enriching daily nutrition and the latter targeting specific gut or skin issues. For individuals on antibiotics or dealing with chronic gut imbalance, supplementation may be more effective initially.
How does emotional well-being affect a clear skin diet’s success?
Stress and emotional health can significantly undermine the benefits of even the best foods for clear skin. Chronic stress alters gut motility and reduces mucosal immunity, allowing pathogenic bacteria to flourish and impair nutrient absorption. Emotional distress also influences eating behaviors, often leading to consumption of high-sugar or ultra-processed comfort foods that aggravate both gut and skin. Practicing mindfulness around eating, incorporating adaptogens like ashwagandha, and engaging in restorative activities like yoga or walking can reinforce the gut-skin axis. Therefore, while food for nice skin is important, its efficacy is enhanced when paired with emotional resilience and mental wellness strategies.
What are some underrated healthy skin foods with gut-supporting benefits?
Beyond well-known options like berries and avocados, several underrated foods to eat for clear skin also nourish the gut. Jerusalem artichokes and dandelion greens are rich in inulin, a potent prebiotic that feeds beneficial gut bacteria. Seaweed varieties such as wakame and nori contain iodine and antioxidants, supporting both thyroid function and microbial diversity. Black garlic, aged to enhance its antioxidant profile, offers antimicrobial properties that benefit both digestive and skin health. Buckwheat, though often overlooked, is gluten-free and high in rutin, which strengthens blood vessels and reduces redness in sensitive skin. These lesser-known additions make powerful allies in a comprehensive clear skin diet.
Why is diversity in your diet crucial when eating for clear skin?
Relying too heavily on a limited set of foods, even if they are among the best foods for clear skin, can reduce microbiome diversity and compromise skin benefits over time. Each plant-based ingredient feeds different strains of gut bacteria, and greater microbial diversity is associated with reduced inflammation and improved skin resilience. Rotating your food for skin intake—such as varying leafy greens or swapping grains weekly—ensures a broader spectrum of nutrients and reduces the risk of developing food intolerances. A varied diet also minimizes overexposure to potential anti-nutrients or allergens, such as oxalates in spinach or lectins in legumes. Cultivating this variety supports a more robust gut ecosystem, which in turn reflects in healthier, more luminous skin.
How does alcohol consumption disrupt a diet for good skin?
Alcohol acts as a dual disruptor, impairing both gut barrier integrity and skin hydration. It diminishes microbial diversity, promotes the growth of harmful bacteria, and compromises liver function—all of which contribute to systemic inflammation and dull, puffy skin. Alcohol also depletes nutrients critical for food for skin health, including B vitamins, zinc, and magnesium. While moderate consumption may not entirely negate the benefits of healthy skin foods, regular or excessive intake introduces oxidative stress that accelerates aging. Replacing alcohol with kombucha or herbal elixirs enriched with adaptogens and probiotics offers a supportive alternative within a clear skin diet.
Can travel or frequent lifestyle changes impact the gut-skin connection?
Yes, frequent changes in environment, time zones, and dietary patterns can cause fluctuations in gut microbiota, leading to temporary skin issues like dryness, breakouts, or sensitivity. Disrupted routines often reduce access to whole foods and increase dependence on processed options, weakening the foundation of eating healthy for skin. Jet lag and irregular sleep patterns further aggravate gut imbalance by altering digestive enzyme cycles and immune activity. To mitigate these effects, travel with shelf-stable probiotics, fiber-rich snacks like chia seed packs, and herbal teas known to soothe the gut, such as chamomile or peppermint. Maintaining a few consistent food for skin staples while adapting locally available produce can help sustain microbial and skin balance.
How do aging and hormonal shifts redefine the best foods for clear skin?
As we age, changes in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and testosterone, influence both sebum production and collagen synthesis. The skin becomes thinner, less elastic, and more prone to dryness, making dietary interventions even more essential. Foods that are good for your skin during younger years, like those high in antioxidants, remain important, but you may also need to emphasize bone broth, collagen peptides, and vitamin K2-rich foods like natto for enhanced repair and elasticity. Menopausal women might find flaxseed and soy more beneficial due to their phytoestrogen content, which helps counter hormonal skin thinning. Thus, while the best foods for skin stay largely consistent, adjustments should be made over time to accommodate evolving biological needs.
Conclusion: Unlocking Clearer Skin Through the Gut-Skin Connection
The journey to radiant skin begins deep within the gut, where trillions of microbes interact with every aspect of health. By focusing on the best foods for clear skin—including probiotics, antioxidant-rich produce, healthy fats, and prebiotic fibers—we activate the body’s innate capacity for healing and renewal. The foods we choose daily are not merely fuel but also powerful agents of transformation that influence how we look, feel, and age.
Understanding the gut-skin axis allows us to take a root-cause approach to skin challenges rather than simply masking symptoms. By embracing a clear skin diet grounded in whole, nutrient-dense, and gut-friendly foods, we pave the way for lasting beauty and resilience. Eating healthy for skin is not a trend but a long-term investment in self-care that reflects the integration of science, culture, and conscious living.
Through small yet consistent choices—from sipping green tea to enjoying a colorful salad—we nourish our microbiome, balance our hormones, and fortify our skin barrier. The result is not only a clearer complexion but also a healthier, more vibrant version of ourselves. Let your plate be your prescription, and let every bite bring you closer to the luminous skin you deserve.
Further Reading:
The 11 Best Foods for Healthy Skin