A well-balanced diet is the cornerstone of good health, but not all nutrients are created equal when it comes to promoting digestive wellness. Among the most critical elements for a thriving gut are protein and fiber foods. These nutritional powerhouses work synergistically to support gut microbiota, improve digestion, and bolster long-term metabolic and immune health. As more people look for natural strategies to enhance wellness through diet, understanding the role of a high protein high fiber diet becomes essential. In this comprehensive guide, we explore how protein and fiber can transform your digestive health, offer sustainable weight management, and provide a path to lasting well-being.
You may also like: The Ultimate Guide to Gut Healthy Meals: Best Meals for Gut Health and Nourishing Recipes You’ll Love
Understanding the Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Health
The human gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that form the gut microbiome, a dynamic ecosystem that influences everything from digestion to mood. The microbiome consists of bacteria, fungi, and other microbes that play a vital role in breaking down food, synthesizing vitamins, and regulating the immune system. A balanced gut microbiome promotes nutrient absorption and prevents the overgrowth of harmful bacteria. In contrast, dysbiosis—an imbalance of gut flora—can contribute to inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, and even mental health disorders.
Fiber plays a particularly vital role in feeding beneficial bacteria. When fermentable fibers reach the colon, they serve as prebiotics that fuel gut flora. This fermentation process produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which help maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining and reduce inflammation. Meanwhile, protein provides the amino acids necessary for repairing gut tissue and supporting enzyme function. The combination of these nutrients makes a high protein and fiber diet foundational to digestive and overall health.
The Science Behind Protein and Fiber Synergy
While each nutrient offers unique benefits, the interaction between protein and fiber creates a synergistic effect that amplifies their health-promoting properties. Fiber slows the digestion of protein, promoting satiety and steady energy levels. This can help prevent insulin spikes and support metabolic balance. Additionally, combining protein with fiber-rich foods can reduce the glycemic impact of meals, which is especially beneficial for individuals managing blood sugar.
Moreover, consuming adequate protein ensures the body can repair and maintain muscle mass, which is important for metabolic rate and physical performance. Fiber, especially soluble fiber, binds to bile acids in the intestine, helping regulate cholesterol and support heart health. Together, these nutrients can optimize digestive function and foster a favorable gut environment. As emerging research continues to highlight the benefits of this dietary combination, adopting a diet rich in protein and fiber foods becomes increasingly compelling.
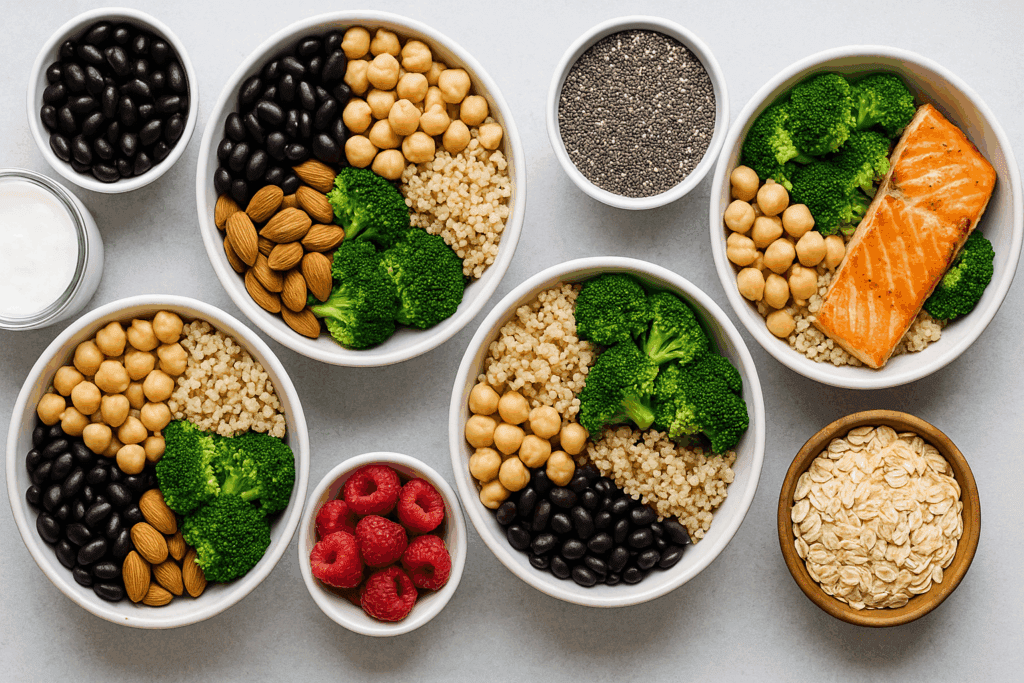

Top Protein and Fiber Foods for Weight Loss and Gut Wellness
One of the most effective ways to promote both gut health and sustainable weight management is by prioritizing protein and fiber foods for weight loss. Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are rich in both macronutrients, making them ideal for promoting satiety and supporting gut flora. These foods are also rich in resistant starch, which ferments in the colon and feeds beneficial bacteria.
Another excellent option is quinoa, a complete plant-based protein that also offers ample fiber. Nuts and seeds, including chia seeds, flaxseeds, and almonds, deliver healthy fats alongside protein and fiber, making them a versatile addition to any meal. Greek yogurt and kefir provide high-quality protein and beneficial probiotics, enhancing microbial diversity in the gut. When paired with fruits like raspberries or pears, these dairy options become even more potent allies in digestive health.
Whole grains such as oats, barley, and farro also contribute to a high protein high fiber diet. These grains are digested slowly, helping regulate appetite and blood sugar levels. For those who consume animal products, lean poultry, eggs, and fish like salmon can complement fiber-rich side dishes such as roasted vegetables or lentil salads to create balanced, gut-friendly meals.
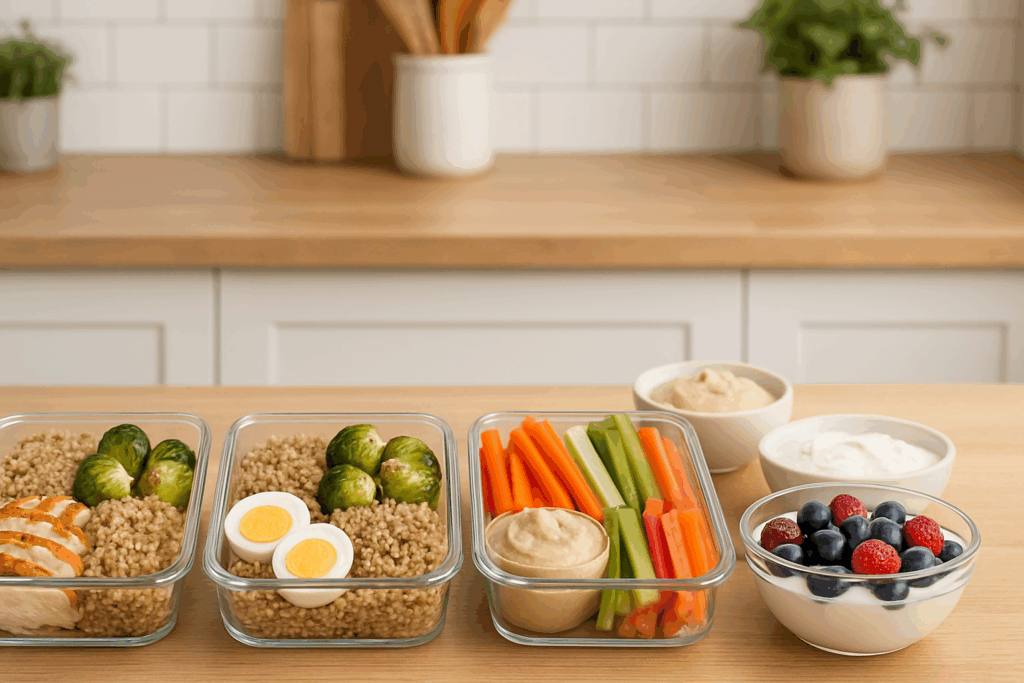

Building a High Protein High Fiber Diet for Lasting Energy
Crafting meals around high protein and fiber diet principles can lead to more stable energy levels and reduced cravings. Starting the day with a breakfast that includes eggs, whole grain toast, and avocado provides a solid foundation of protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Midday meals can feature protein-rich salads with beans, seeds, and leafy greens, while dinner might include grilled chicken or tofu with a side of quinoa and roasted Brussels sprouts.
Snacking smart is also key to maintaining consistent energy and supporting digestion. Instead of reaching for processed foods, choose options like hummus with vegetable sticks, Greek yogurt with flaxseed, or a smoothie with protein powder and berries. These snacks offer not only protein and fiber but also phytonutrients and antioxidants that further enhance gut health.
Hydration plays a vital role in fiber digestion. Without adequate water, fiber can cause bloating or constipation. Drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day ensures that fiber moves smoothly through the digestive tract and supports regular bowel movements. This holistic approach to nutrition helps ensure that every aspect of digestion is optimized, contributing to lasting wellness.
How Foods High in Protein and Fiber Influence Gut Flora
The impact of foods high in protein and fiber extends beyond digestion to the intricate community of microbes living in the gut. A diet that includes a diverse range of fiber sources fosters microbial diversity, which is a hallmark of a healthy microbiome. Each type of fiber supports different species of bacteria, helping maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Proteins, particularly those from plant sources, contribute specific amino acids that gut bacteria can metabolize into bioactive compounds. These compounds can influence gut barrier integrity and inflammatory responses. For example, tryptophan from protein-rich foods can be converted by gut microbes into metabolites that affect serotonin production, linking digestive health with emotional well-being.
However, the quality of protein matters. Excessive consumption of red or processed meats, especially when paired with low fiber intake, can promote the growth of harmful bacteria. This underscores the importance of combining protein with ample fiber and focusing on lean, minimally processed sources. By nourishing beneficial bacteria and limiting harmful strains, foods full of protein and fiber lay the foundation for a resilient and balanced gut.
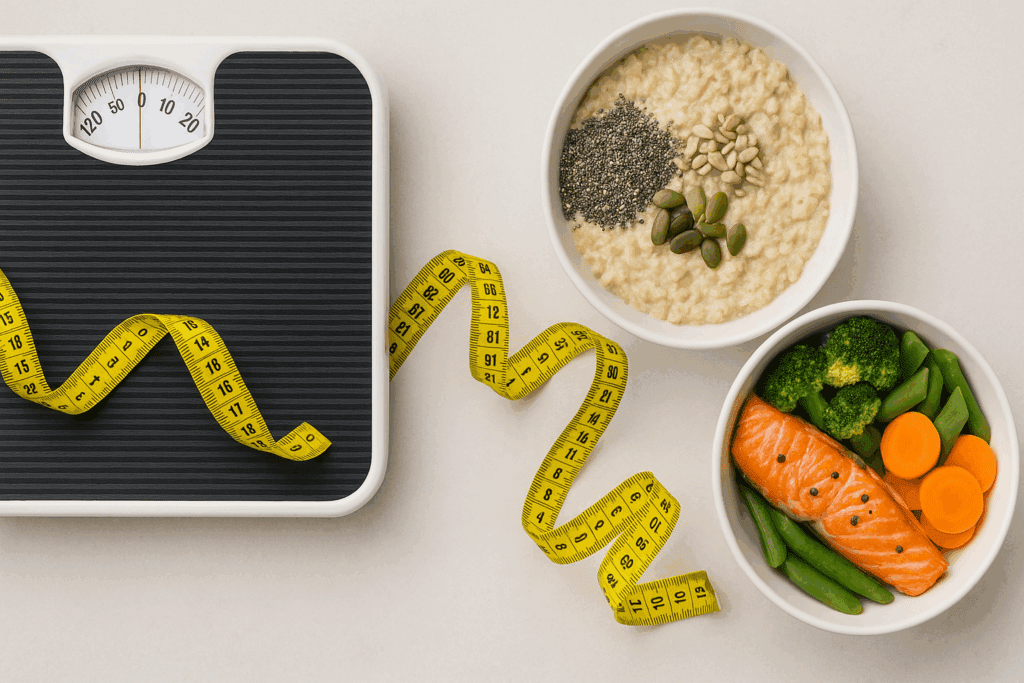

Protein and Fiber Foods for Weight Loss and Metabolic Balance
Weight loss is often framed in terms of calories in versus calories out, but the quality of those calories is equally important. Protein and fiber foods for weight loss help shift the focus from restriction to nourishment. These foods enhance satiety, reduce hunger hormones like ghrelin, and support muscle retention during caloric deficits.
High protein high fiber meals slow gastric emptying, prolonging the feeling of fullness and reducing the likelihood of overeating. This effect is particularly helpful for those managing blood sugar levels or dealing with insulin resistance. Additionally, maintaining lean body mass through adequate protein intake boosts basal metabolic rate, making it easier to sustain weight loss over time.
Fiber also plays a key role in regulating fat metabolism. Soluble fiber binds to dietary fats in the digestive tract, limiting their absorption and promoting excretion. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool, supporting regular elimination and reducing the reabsorption of certain toxins. Together, these functions support metabolic detoxification and long-term health.
The Role of Holistic Supplements in Supporting a High Protein and Fiber Diet
While whole foods should always be the foundation of any diet, supplements can offer targeted support, especially when dietary intake is lacking. Plant-based protein powders derived from peas, hemp, or rice can help individuals meet their protein needs without excess saturated fat or additives. These supplements are particularly helpful for vegetarians, vegans, or individuals with limited appetite.
Fiber supplements such as psyllium husk or inulin can fill gaps in fiber intake and support bowel regularity. However, it’s important to introduce these gradually and accompany them with sufficient water to prevent discomfort. Digestive enzyme supplements may also be beneficial for individuals with compromised digestion, helping break down protein and fiber more efficiently.
Probiotic supplements can further enhance gut health by introducing beneficial bacteria strains that work synergistically with dietary fiber. When selecting a probiotic, choose one that includes clinically studied strains like Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium and check for third-party testing. These supplements, when combined with a diet rich in protein and fiber foods, create a robust framework for gut and metabolic health.

Incorporating Protein and Fiber Foods into a Gut-Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a gut-healthy lifestyle goes beyond isolated food choices and involves cultivating habits that consistently support digestion and overall vitality. Meal planning and preparation are powerful strategies for ensuring daily intake of high protein high fiber meals. By preparing legumes, whole grains, and protein-rich ingredients in advance, it becomes easier to create balanced meals even during busy weeks.
Mindful eating is another important practice. Taking time to chew thoroughly and savor meals allows digestive enzymes to activate and improves nutrient absorption. This mindfulness also enhances awareness of hunger and fullness cues, reducing the likelihood of overeating or digestive distress.
Stress management, adequate sleep, and physical activity all interact with gut health. Chronic stress can alter gut permeability and microbial balance, while sleep disturbances can disrupt hormone regulation related to appetite and digestion. Exercise supports healthy transit time and promotes a favorable microbial profile. Together, these lifestyle elements reinforce the benefits of a high protein and fiber diet.
Why Protein and Fiber Foods Are Essential for Long-Term Wellness
When evaluating the long-term benefits of any dietary pattern, sustainability and health outcomes are key indicators. Protein and fiber foods meet both criteria by offering lasting satiety, improved digestion, and broad nutritional coverage. These foods reduce the risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and colorectal cancer.
Unlike restrictive diets that are difficult to maintain, a high protein and fiber diet encourages the inclusion of diverse, nutrient-rich foods that support gut and systemic health. This inclusivity makes it easier to adhere to over the long term, enhancing both mental and physical well-being.
The dual action of protein and fiber in regulating appetite, supporting muscle maintenance, and feeding the microbiome makes them indispensable components of any wellness strategy. As more people seek evidence-based ways to improve their health through nutrition, integrating protein and fiber foods into daily life stands out as a transformative approach.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Protein and Fiber Foods for Gut Health and Wellness
How can I optimize a high protein high fiber diet for active lifestyles?
Athletes and physically active individuals have unique nutritional needs, particularly when it comes to sustaining energy, repairing muscle tissue, and supporting recovery. A high protein high fiber diet can be strategically adjusted by prioritizing nutrient timing and the quality of each food source. For example, pre-workout meals might emphasize easily digestible proteins like Greek yogurt and fruit, while post-workout meals should combine lean protein and complex carbohydrates such as grilled chicken with quinoa and vegetables to enhance muscle recovery and replenish glycogen stores. Additionally, fiber intake should be adjusted slightly around high-intensity training windows to avoid digestive discomfort. By integrating protein and fiber foods that also contain anti-inflammatory compounds, such as omega-3-rich chia seeds or turmeric-spiced legumes, active individuals can optimize both performance and gut health.
What are the best protein and fiber foods for weight loss during perimenopause?
During perimenopause, hormonal fluctuations can make weight management more challenging due to shifts in metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and appetite regulation. A high protein and fiber diet is particularly beneficial in this stage of life because it helps counteract hormonal weight gain by stabilizing blood sugar and enhancing satiety. Foods high in protein and fiber like edamame, tempeh, and berries can help mitigate cravings and improve gut hormone signaling. Soluble fibers, in particular, assist with estrogen metabolism by binding to excess hormones in the digestive tract. Including cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts, paired with protein-rich eggs or legumes, supports hormonal balance and encourages weight loss without deprivation. These targeted combinations promote long-term metabolic balance while addressing the unique needs of perimenopausal women.
How does a protein and fiber food plan influence mental health and emotional resilience?
The gut-brain axis is a two-way communication system between the digestive tract and the brain, and it plays a key role in emotional regulation and mental clarity. A diet abundant in protein and fiber foods supports this axis by nourishing gut bacteria that produce mood-stabilizing neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA. For instance, tryptophan-rich proteins such as turkey or pumpkin seeds, when consumed with fiber-rich foods like oats or apples, enhance serotonin synthesis. Moreover, consistent intake of a high protein and fiber diet helps prevent the blood sugar crashes that can contribute to mood swings, fatigue, and anxiety. Over time, a nourished microbiome can reduce systemic inflammation linked to depression and support more balanced emotional health. This psychological benefit is a powerful, often overlooked reason to prioritize foods full of protein and fiber.
Can a high protein and fiber diet reduce the risk of food intolerances and sensitivities?
Emerging research suggests that maintaining a diverse and well-fed microbiome through balanced dietary practices may help reduce the likelihood of developing new food intolerances. Fiber serves as a prebiotic, encouraging the growth of microbial species that protect the gut lining and reduce intestinal permeability. When this barrier is compromised, particles of undigested food can enter the bloodstream and trigger immune responses, contributing to sensitivities. Incorporating anti-inflammatory protein and fiber foods, such as wild salmon with roasted sweet potatoes or lentils with turmeric, reinforces the mucosal barrier and fosters immune tolerance. While genetic predispositions and environmental exposures also play roles, adopting a high protein high fiber diet can be a proactive strategy for supporting digestive resilience.
How do I adapt a high protein and fiber diet for plant-based living?
For those embracing vegetarian or vegan lifestyles, meeting protein and fiber goals requires a bit more planning but is entirely achievable. Plant-based diets naturally emphasize fiber through fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. To ensure sufficient protein intake, one can combine complementary protein sources such as rice and beans or hummus with whole grain pita to obtain all essential amino acids. Fortified plant-based milks and protein powders made from pea, hemp, or brown rice also enhance protein variety. Foods high in protein and fiber like tempeh, lentils, and quinoa form the cornerstone of plant-powered nutrition. These ingredients not only align with ethical and environmental goals but also contribute to vibrant gut health when consumed in diverse, whole-food forms.
Are there seasonal strategies to keep protein and fiber foods interesting year-round?
Absolutely. A common challenge with any dietary approach is monotony, but rotating seasonal produce and protein sources can keep meals engaging and nutritionally varied. In the spring, pair green peas and asparagus with hard-boiled eggs or seared tempeh. Summer invites lighter fare like grilled fish tacos with mango slaw and black beans, which are both festive and fiber-rich. Autumn lends itself to warm bowls featuring roasted root vegetables, farro, and slow-cooked lentils. Winter is ideal for hearty soups with barley, beans, and shredded chicken, spiced with warming herbs like cumin or rosemary. Each season provides an opportunity to explore new flavors while staying committed to a high protein and fiber diet.
What are the psychological barriers to adopting a high protein and fiber diet, and how can they be overcome?
Behavioral change often involves more than just knowledge—emotions, habits, and social influences can shape our food choices. Some individuals may associate protein and fiber foods with blandness or diet restrictions, creating resistance to adopting them. Others may struggle with time constraints or lack of cooking skills. Addressing these barriers involves reimagining what a high protein and fiber diet can look like: flavorful, culturally diverse, and accessible. Cooking classes, community-supported agriculture (CSA) boxes, or simple batch-cooking techniques can empower individuals to embrace this lifestyle. Framing the diet not as a sacrifice, but as a foundation for strength and clarity, helps shift the mindset and makes lasting change more achievable.
How do protein and fiber foods affect long-term immune function and inflammation?
A well-nourished gut microbiome is one of the body’s most powerful allies in preventing chronic inflammation and maintaining immune vigilance. Soluble fiber helps produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid with potent anti-inflammatory effects. Protein contributes to the synthesis of antibodies, immune enzymes, and repair mechanisms essential for recovery and resilience. Over time, consistently eating foods full of protein and fiber has been shown to reduce biomarkers associated with chronic diseases like cardiovascular conditions and autoimmune disorders. By minimizing systemic inflammation and fortifying immune responses, a high protein and fiber diet becomes a crucial pillar of preventative health.
Exploring Future Innovations in Protein and Fiber Food Formulation
As nutritional science and food technology evolve, exciting innovations are emerging that elevate the potential of protein and fiber foods. One area of growth is the development of personalized nutrition apps that use microbiome sequencing to tailor high protein and fiber diet recommendations to an individual’s unique gut composition. Additionally, advances in fermentation are enabling the creation of gut-friendly protein snacks that include prebiotic fibers and postbiotics for added health benefits. Lab-grown meats and plant-based protein alternatives are also being enhanced with natural fibers to support digestion. The future will likely see a surge in functional foods that offer targeted benefits for digestion, energy, and mood. As this field matures, consumers will gain even more tools to create nourishing, science-backed eating habits.
Protein and Fiber Food Combinations That Maximize Gut Health
Creating the most effective meals for digestive wellness involves combining ingredients that offer complementary nutritional properties. For instance, pairing wild rice with black beans creates a complete protein while supplying both soluble and insoluble fiber. Adding fermented vegetables like kimchi to a tofu stir-fry introduces probiotics that work synergistically with the fiber content. Even simple additions like lemon juice to lentil salads can enhance iron absorption, making the protein more bioavailable. By layering meals with thoughtfully chosen protein and fiber foods, individuals can amplify the health benefits and support microbiome diversity. These strategic pairings transform everyday meals into powerful tools for sustaining gut and metabolic health.
Conclusion: Elevate Gut Health and Wellness with Protein and Fiber Foods
In the evolving landscape of health and nutrition, the importance of gut health has never been clearer. From enhancing digestion to supporting immune function and emotional balance, the gut plays a central role in overall well-being. Embracing a dietary pattern rich in protein and fiber foods offers a powerful and sustainable pathway to nourish this vital system.
This guide has explored the intricate synergy between protein and fiber, the specific foods that deliver these nutrients, and the holistic lifestyle practices that amplify their effects. A high protein high fiber diet is not just a trend—it’s a science-backed approach to achieving and maintaining wellness. By focusing on foods high in protein and fiber, and by embracing the practical strategies laid out here, individuals can take proactive steps toward a healthier gut and a more vibrant life.
As you consider your own wellness journey, remember that small, consistent changes in your daily choices can yield profound results. Let protein and fiber be your allies in building a life marked by resilience, energy, and digestive harmony.
Further Reading:
7-Day High-Protein, High-Fiber Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan, Created by a Dietitian
Weight-loss Success Depends on Eating More Protein, Fiber while Limiting Calories, Study Finds
30-Day High-Protein, High-Fiber Meal Plan for Weight Loss, Created by a Dietitian

