Chocolate cravings strike with surprising intensity. For many people, they’re more than just a fleeting thought—they’re an emotional and physiological experience tied to comfort, reward, and even stress relief. While a small indulgence is perfectly healthy from time to time, frequent or overpowering cravings can make it difficult to maintain a balanced diet or meet personal wellness goals. That’s why understanding the biology behind chocolate cravings and learning what to eat when you crave chocolate can empower healthier habits.
This article explores the psychology and physiology of chocolate cravings, discusses nutrient-based strategies for satisfying those urges, and offers expert-approved tips on how to stop chocolate cravings without deprivation. It also includes practical, sustainable advice on how can I stop craving chocolate in a way that supports long-term health and mindful eating.
You may also like: Why Am I Craving Sweets All of a Sudden? Expert-Backed Reasons and How to Stop Sugar Cravings Naturally
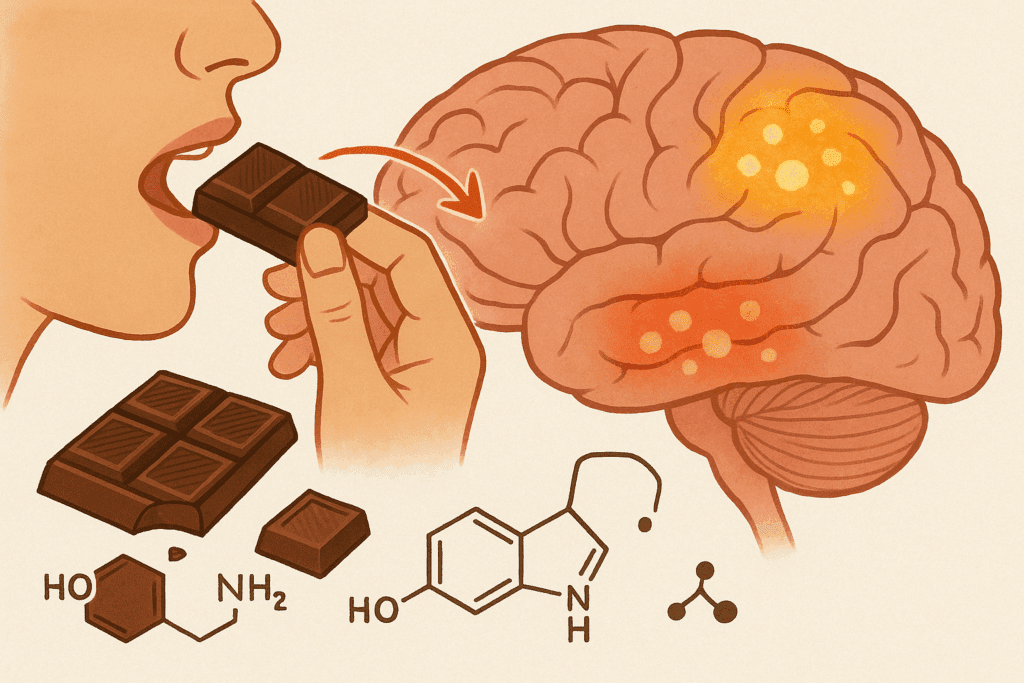
Why Chocolate? Understanding the Root of Cravings
To understand how to respond to chocolate cravings, it’s important to understand what drives them. Chocolate is not just a sweet treat—it’s a complex food containing sugar, fat, and naturally occurring psychoactive compounds like theobromine, caffeine, and phenylethylamine. These substances can influence neurotransmitter activity in the brain, particularly dopamine and serotonin, which are closely tied to feelings of pleasure and reward.
When we eat chocolate, especially varieties with higher sugar and fat content, it often triggers a dopamine release that temporarily improves mood. This is why many people associate chocolate with comfort, stress relief, or emotional regulation. Cravings for chocolate may also emerge during hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during the menstrual cycle, or due to low blood sugar levels, sleep deprivation, or nutrient deficiencies—particularly magnesium.
Understanding that these cravings are biologically and emotionally motivated—not a lack of willpower—can foster a more compassionate and effective approach to managing them.
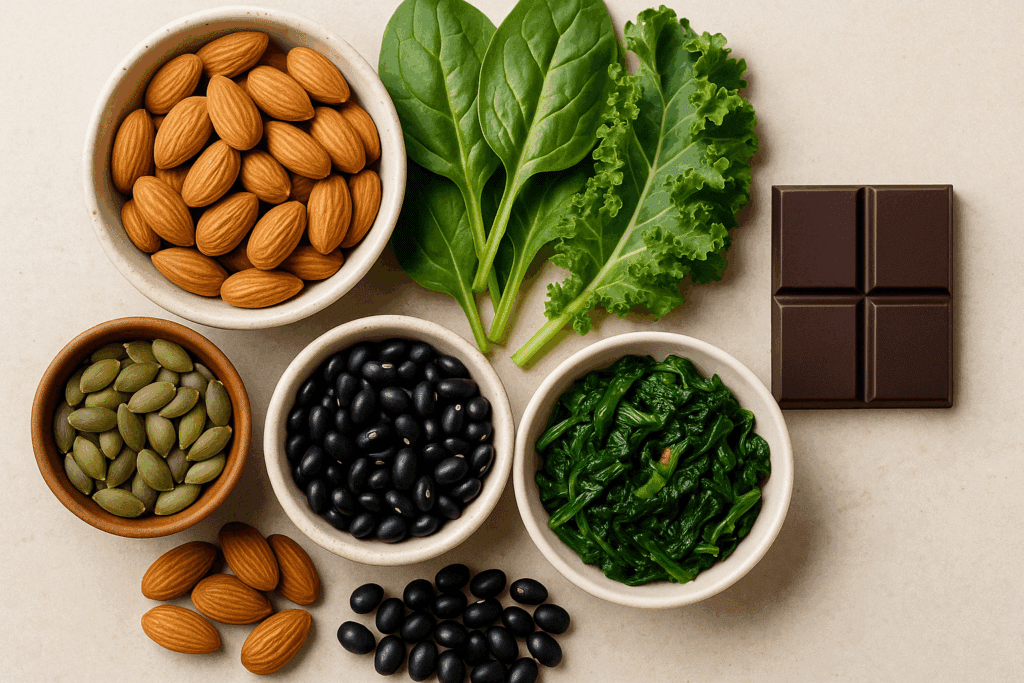

Nutrient Deficiencies That Fuel Chocolate Cravings
There’s a growing body of evidence suggesting that cravings for specific foods may sometimes indicate underlying nutrient deficiencies. Chocolate, especially dark chocolate, is rich in magnesium—a mineral involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the human body. If your body is low on magnesium, you might find yourself drawn to chocolate more frequently.
Magnesium isn’t the only nutrient at play. Low levels of zinc, B vitamins, and even iron can also contribute to persistent cravings. Because chocolate provides small amounts of each, the body might associate it as a quick fix. However, depending on chocolate to meet nutritional needs is inefficient and can lead to excess calorie consumption and blood sugar spikes.
When you find yourself wondering what to eat when you crave chocolate, choosing foods rich in magnesium—like pumpkin seeds, almonds, black beans, and leafy greens—may naturally reduce the craving. These whole foods support neurological function and may help restore balance without overindulgence.

Emotional Eating and the Chocolate Connection
Emotional eating is one of the most overlooked contributors to chocolate cravings. During moments of stress, sadness, boredom, or fatigue, turning to chocolate is often an unconscious strategy to self-soothe. It offers a sensory and emotional escape, providing a momentary feeling of happiness or satisfaction.
Addressing emotional eating requires mindfulness and compassion. Rather than forcing yourself to simply “resist,” it’s more effective to develop an awareness of your emotional triggers and build new coping mechanisms that don’t rely on food. This might include journaling, deep breathing exercises, calling a friend, or engaging in a hobby. When you ask yourself how can I stop craving chocolate, consider whether the craving is physical or emotional. That distinction can change the way you respond—and support healthier patterns in the long run.
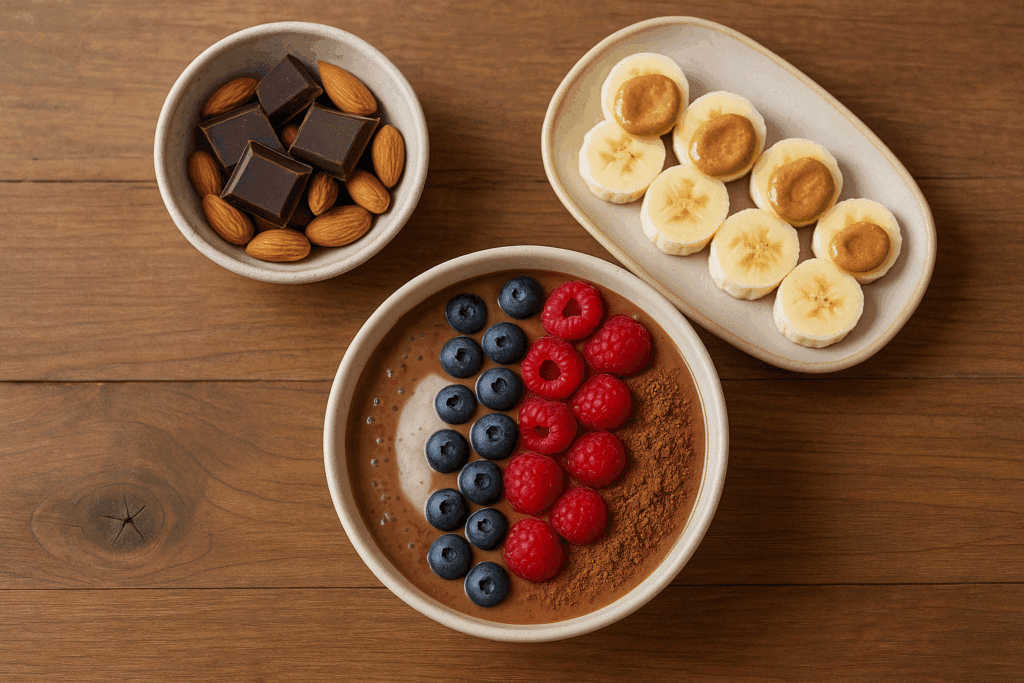

What to Eat When You Crave Chocolate: Smarter Substitutions
One of the most effective strategies for managing chocolate cravings is knowing what alternatives can satisfy your taste buds without derailing your nutrition goals. If your craving is rooted in taste and texture, there are plenty of nutrient-rich, lower-sugar options that can fulfill that need.
A great example is a small square of 85% dark chocolate paired with a handful of almonds or walnuts. This combination delivers the flavor you’re after, along with fiber, healthy fats, and protein that help stabilize blood sugar and prolong satiety. For those looking for non-chocolate alternatives, try banana slices topped with almond butter and a dusting of cacao powder—a flavor-rich option with the nutritional advantage of potassium and healthy fat.
Frozen berries blended with a splash of unsweetened plant milk and a teaspoon of cocoa can also create a smoothie bowl that hits all the right notes. Knowing what to eat when you crave chocolate helps redirect those urges into nutrient-dense choices that are both satisfying and sustainable.
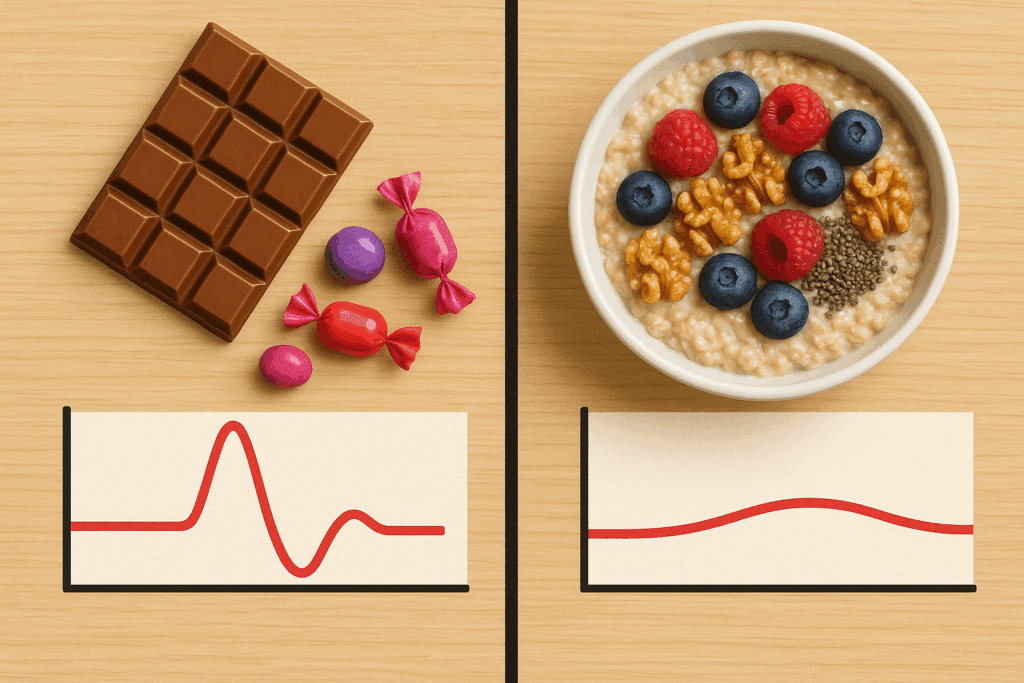
The Role of Blood Sugar in Chocolate Cravings
Unstable blood sugar is a significant contributor to intense cravings for sweets, including chocolate. When we consume refined carbohydrates or sugary snacks, they cause a rapid spike in blood glucose followed by a sharp drop—what’s commonly referred to as a “sugar crash.” During this dip, the brain signals a need for more quick energy, leading to heightened cravings for sweet, fast-acting carbohydrates like chocolate.
To break this cycle, it’s important to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. This means prioritizing balanced meals that include fiber, protein, and healthy fats. For instance, a breakfast of steel-cut oats with chia seeds, walnuts, and berries offers a slow-digesting source of energy that can help prevent mid-morning chocolate cravings.
If you find yourself consistently reaching for chocolate in the afternoon, it may be time to evaluate the nutritional quality of your lunch. Learning how to stop chocolate cravings often starts with blood sugar management—and that begins with well-balanced meals, not quick fixes.
Stress, Sleep, and Cravings: The Hormonal Link
Cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, is intricately linked to food cravings. Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which can stimulate appetite and prompt cravings for energy-dense foods—especially those high in sugar and fat. This physiological response is a survival mechanism, but in modern life, it often works against us.
Lack of sleep is another major factor. Sleep deprivation impacts the hormones ghrelin and leptin, which regulate hunger and satiety. When these hormones are thrown off balance, people tend to crave calorie-dense comfort foods like chocolate to compensate for low energy and mood disturbances.
To address the question of how can I stop craving chocolate, one must consider lifestyle factors like stress and sleep. Prioritizing quality sleep, creating boundaries around work and rest, and practicing stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation can dramatically reduce the intensity and frequency of cravings.
The Psychology of Restriction: Why Avoidance Backfires
While it may seem logical to simply eliminate chocolate from your diet to avoid temptation, strict restriction can actually intensify cravings. Psychological studies show that the more we try to suppress a thought or desire, the stronger it becomes—a phenomenon known as the “ironic process theory.” In the case of chocolate, the more you tell yourself you can’t have it, the more you may want it.
This is why many nutritionists and psychologists recommend a strategy of mindful inclusion. Rather than banning chocolate altogether, allow yourself to enjoy it in controlled portions. Savoring one or two squares of dark chocolate after a meal, for example, can satisfy your craving without leading to a binge. It also helps deconstruct the idea of chocolate as a “forbidden food,” reducing its power over time.
In this way, learning how to stop chocolate cravings doesn’t mean resisting every temptation—it means understanding your patterns and creating a flexible, sustainable relationship with food.
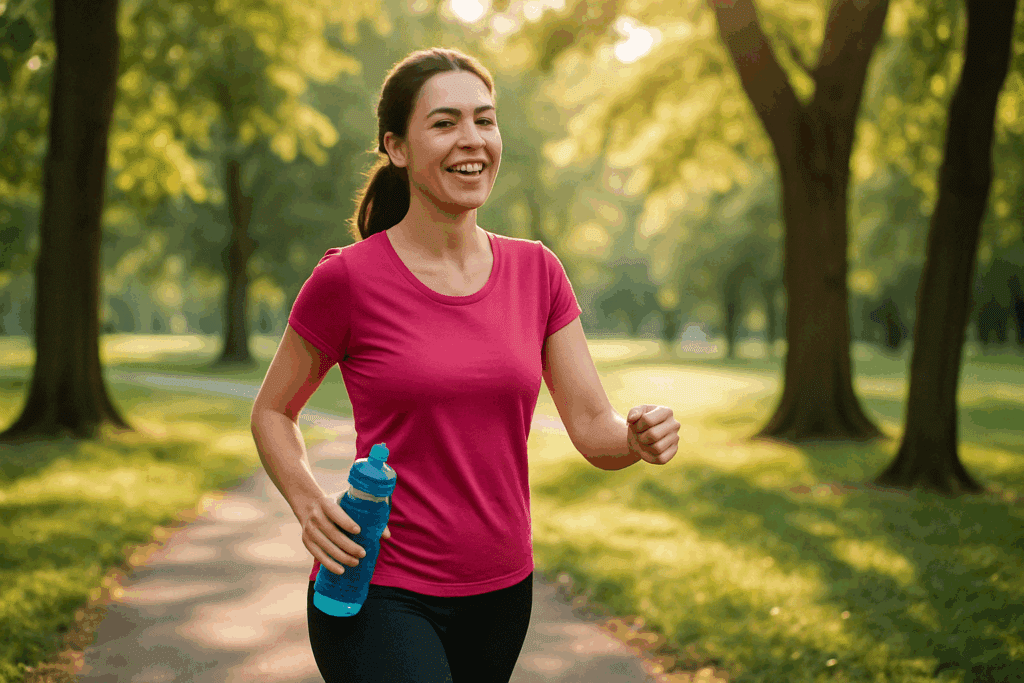

Building a Craving-Resistant Lifestyle
Beyond specific food swaps and stress management techniques, cultivating a lifestyle that naturally resists cravings is one of the most powerful long-term strategies. This includes eating meals at regular intervals, staying physically active, and making space for joy, purpose, and connection in daily life.
Regular physical activity plays a key role in regulating appetite and mood. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, boosts energy levels, and stimulates the production of endorphins—neurochemicals that naturally elevate mood. For many people, a brisk walk, a dance class, or even light stretching can diminish the desire to emotionally eat, particularly when craving chocolate due to boredom or low mood.
Hydration is also essential. Sometimes what feels like a chocolate craving is actually mild dehydration. Before reaching for a sweet treat, try drinking a glass of water and waiting ten minutes to see if the urge subsides. These small, consistent habits create a physiological and emotional environment where cravings have less control.

Expert Answers to “How Can I Stop Craving Chocolate?”
When someone asks, “how can I stop craving chocolate?”, it’s important to offer multi-dimensional guidance. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution because cravings arise from a complex interplay of factors—biological, emotional, nutritional, and psychological. Addressing only one dimension rarely leads to lasting change.
Nutritionists often start by helping clients build balanced meals and identify any micronutrient deficiencies. Psychologists might explore the emotional context in which cravings arise, such as loneliness or anxiety. Coaches may work on behavioral strategies, like using urge surfing (a mindfulness-based practice) to ride out the wave of craving without giving in.
Ultimately, the most effective strategies are those that combine nutritional insight with emotional awareness and lifestyle alignment. Empowering individuals with knowledge and practical tools fosters autonomy and resilience—not guilt or restriction.
How to Stop Chocolate Cravings with Mindful Eating
Mindful eating is one of the most research-supported methods for reducing food cravings, including those for chocolate. This approach emphasizes being fully present with your food—paying attention to flavors, textures, hunger cues, and satiety signals. It’s a way to turn off autopilot eating and reconnect with the body’s wisdom.
When you’re mindful, you’re more likely to ask meaningful questions like: Am I truly hungry, or am I trying to soothe an emotion? Is there a more nourishing option that would satisfy me just as much? Mindful eaters are also more likely to enjoy smaller amounts of chocolate without feeling the need to overconsume.
Practicing mindfulness can also help answer the question, what to eat when you crave chocolate, because it helps you pause and make a conscious choice rather than reacting impulsively. This doesn’t mean you never eat chocolate—it means you make room for it in a thoughtful, pleasurable, and health-supportive way.
Sugar Addiction vs. Craving: Knowing the Difference
It’s important to distinguish between a typical craving and a sign of potential sugar addiction. While occasional chocolate cravings are completely normal, persistent and compulsive consumption, despite negative consequences, may suggest a more complex issue. If you find yourself eating large quantities of chocolate in secret, feeling guilt or shame, or unable to stop even when you want to, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian with experience in food addiction.
Understanding how to stop chocolate cravings starts with recognizing their severity. For most people, lifestyle shifts, better nutrition, and emotional support will do the trick. But for others, professional help may be essential to regain control and develop healthier eating habits.
Satisfying Cravings Without Sabotage: A Realistic Path Forward
Being a chocolate lover doesn’t mean you’re doomed to struggle with cravings forever. In fact, many people find that once they adopt a balanced approach—one that includes nutrient-rich foods, emotional awareness, and flexible eating—they can enjoy chocolate mindfully without it becoming a problem.
Knowing what to eat when you crave chocolate is about more than substitution—it’s about nourishment, curiosity, and satisfaction. Whether it’s a magnesium-rich green smoothie, a mindful piece of dark chocolate, or simply pausing to reflect on your needs, these actions build self-trust. They help you shift from reaction to response, from guilt to grace.
Over time, these small choices create a new narrative—one where chocolate is not a villain, but a part of a full and flourishing life.
Frequently Asked Questions: How to Curb Chocolate Cravings Naturally
1. Can your environment influence chocolate cravings, and how can you manage that?
Absolutely. Environmental cues such as seeing chocolate ads, passing a bakery, or even watching a friend eat a chocolate dessert can trigger intense cravings, especially if you’re already feeling emotionally or physically depleted. One way to minimize this influence is to create a “craving-resistant environment.” Keep chocolate and ultra-processed sweets out of immediate reach at home or work, and instead stock up on healthier snacks that fulfill similar cravings. Knowing what to eat when you crave chocolate, such as a small portion of dark chocolate-covered almonds or fruit dipped in cacao yogurt, can help retrain your mind to seek satisfying but balanced options. The more your environment supports your goals, the easier it becomes to answer the question of how can I stop craving chocolate in the heat of the moment.
2. How do gut microbiota impact your chocolate cravings?
Recent research suggests a fascinating link between your gut microbiota and the foods you crave, including chocolate. Certain bacteria in the gut thrive on sugar and may “signal” the brain to prompt cravings for high-sugar items like milk chocolate. When you’re trying to figure out how to stop chocolate cravings, one of the most overlooked strategies is rebalancing your gut. Eating more prebiotic and probiotic foods—like fermented vegetables, unsweetened yogurt, and fiber-rich legumes—can help shift your microbiota composition, reducing signals that trigger sugar-seeking behavior. In this context, knowing what to eat when you crave chocolate might also include foods that support microbial diversity rather than merely replace the taste of chocolate.
3. Does hydration affect your desire for chocolate?
Yes, dehydration can be a hidden trigger for cravings, including those for chocolate. When your body lacks fluids, it may mistake thirst for hunger or a need for quick energy, prompting you to reach for sugary snacks. Before asking how can I stop craving chocolate, try drinking a full glass of water and waiting 10 to 15 minutes. Many people report that the craving either lessens or disappears altogether. Staying well-hydrated throughout the day not only supports your metabolism but also helps you recognize true hunger versus emotional or dehydration-driven signals, making it easier to determine what to eat when you crave chocolate more mindfully.
4. Are there seasonal or weather-related patterns in chocolate cravings?
Seasonal affective changes and weather shifts can play a subtle but significant role in food cravings. During colder, darker months, people often crave heavier, comforting foods, with chocolate being one of the most common. The lack of sunlight affects serotonin levels, which can intensify the urge to reach for sweets. To understand how to stop chocolate cravings in these periods, consider adding serotonin-supportive foods like bananas, oats, and turkey, along with vitamin D-rich sources, to your meals. These additions can help stabilize your mood and reduce the need for quick dopamine fixes, while still giving you flexibility in what to eat when you crave chocolate during winter slumps.
5. Can social situations make it harder to stop chocolate cravings?
Social influence is a powerful driver of eating behavior. If you’re at a party, in a break room, or at a gathering where chocolate desserts are front and center, your willpower may be undermined by social pressure or the desire to belong. One strategy for managing this is to bring your own healthier alternatives or plan ahead by eating a satisfying meal that leaves you less tempted. When you’re empowered with better knowledge of what to eat when you crave chocolate, you can make choices that honor both your health and social experiences. Social dynamics also add complexity to how can I stop craving chocolate, reminding us that cravings are not just biological but also social phenomena.
6. Can habit formation help reduce chocolate cravings long-term?
Yes, habit formation is a cornerstone of long-term craving reduction. Cravings often arise at the same times each day, such as mid-afternoon or late evening, becoming ritualized into your routine. One effective strategy for how to stop chocolate cravings is to replace that habitual behavior with a different, health-supportive one. For instance, taking a five-minute walk, doing breathwork, or sipping a cinnamon-spiced tea can act as a “pattern interrupter.” Over time, if your brain begins to associate that time of day with something other than eating chocolate, the craving loop weakens. Knowing how can I stop craving chocolate often comes down to consistent repetition of healthier habits that gradually replace older, less helpful ones.
7. What role does protein play in reducing chocolate cravings?
Protein has a profound impact on appetite regulation and satiety. Meals that are protein-rich help stabilize blood glucose levels and reduce the spikes and crashes that lead to cravings for sugar, including chocolate. If you’re trying to figure out what to eat when you crave chocolate, consider incorporating a protein source like Greek yogurt with cacao nibs, roasted chickpeas with cocoa seasoning, or a protein shake made with unsweetened cocoa and almond butter. These options support muscle repair and blood sugar balance while also satisfying that chocolate taste profile. Understanding how to stop chocolate cravings effectively includes recognizing protein as a strategic tool in your dietary arsenal.
8. Are there any herbs or natural supplements that reduce chocolate cravings?
Some natural supplements and herbs have shown potential in reducing sweet cravings. Chromium picolinate, for instance, may improve insulin sensitivity and help reduce cravings for sugar-rich foods like chocolate. Gymnema sylvestre is another herb traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine, known to dull the sweet taste receptors on the tongue, potentially making chocolate less appealing. These supplements should be used with guidance from a qualified health professional, especially if you are managing other conditions. If you’re exploring how to stop chocolate cravings, herbs and botanicals might offer supportive options—particularly when paired with consistent dietary practices and a strong understanding of what to eat when you crave chocolate from a whole-food perspective.
9. How do cultural and childhood associations affect chocolate cravings?
Cultural norms and early experiences can deeply influence your emotional relationship with chocolate. Many people associate chocolate with celebrations, love, or parental reward, creating a nostalgic and emotionally charged craving pattern. When those emotional imprints resurface during times of stress or fatigue, cravings may spike regardless of physical hunger. Addressing how can I stop craving chocolate in this context may require inner reflection, therapy, or journaling to reframe those associations. In parallel, developing new, comforting rituals—like warm herbal teas, scent-based self-care, or nature walks—can provide non-food emotional rewards. And in terms of what to eat when you crave chocolate, it helps to choose foods that replicate the sensory satisfaction without triggering old patterns tied to emotional eating.
10. Could mindfulness and intuitive eating actually retrain your cravings?
Yes, and the research supporting this is growing. Mindfulness-based eating practices help rewire the brain’s response to food cues by encouraging awareness, curiosity, and nonjudgmental observation. When you eat chocolate mindfully—slowing down, savoring each bite—you actually reduce the likelihood of overconsumption and increase satisfaction. Over time, you might find that the craving loses its urgency because the relationship with food has shifted from reactive to reflective. The practice of intuitive eating also promotes trust in the body’s signals, teaching you not just how to stop chocolate cravings in the moment, but how to prevent them from becoming disruptive long-term. As you deepen this practice, your choices around what to eat when you crave chocolate become rooted in wisdom, not impulse.
Conclusion: Creating a Healthy Relationship with Chocolate and Your Body
At the heart of every craving is a message. Sometimes it’s a call for comfort, sometimes it’s a request for nutrients, and sometimes it’s just a habit calling out for attention. By learning how to stop chocolate cravings naturally and compassionately, you begin to understand your body’s needs on a deeper level.
The answer to how can I stop craving chocolate isn’t found in restriction or guilt—it’s found in nourishment, mindfulness, and a flexible approach to food. And when you truly understand what to eat when you crave chocolate, you empower yourself with choices that satisfy both body and soul.
In the end, it’s not about avoiding chocolate—it’s about embracing a lifestyle that includes it wisely, lovingly, and in a way that supports your long-term health. By applying these science-backed, expert-approved strategies, you don’t just silence the craving—you transform it into an opportunity for deeper connection with yourself.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
A Dietitian’s 8 Favorite Ways to Satisfy Those Chocolate Cravings
Does My Chocolate Craving Mean Anything?
How to Overcome a Chocolate Addiction
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.

