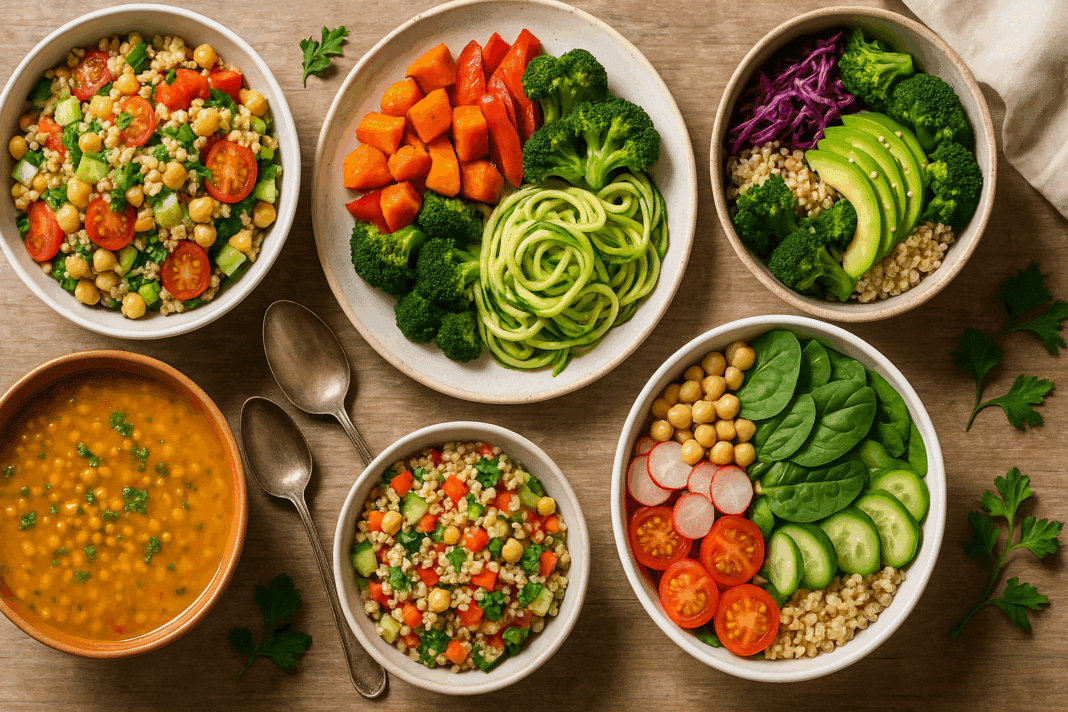
Eating well doesn’t have to mean following restrictive diets, skipping meals, or counting every bite. In fact, some of the most sustainable and enjoyable ways to nourish your body come from simplifying what’s on your plate—choosing meals that are rich in nutrients, lower in calories, and rooted in plants. That’s where vegetarian low calorie meals come into play. These meals are not only excellent for maintaining a healthy weight but also support energy, digestion, and long-term wellness. And contrary to common myths, they can be deeply flavorful, satisfying, and easy to prepare.
In recent years, both health experts and everyday individuals have increasingly turned to plant-based meals to reduce chronic disease risk, enhance digestion, and increase daily energy. But within the broad spectrum of plant-based eating, a more focused approach—centered on the concept of the low calorie veggie meal—has emerged as a powerful way to align taste with health goals. By emphasizing whole ingredients, balanced nutrition, and calorie-conscious cooking, this approach delivers on both wellness and satisfaction.
You may also like: Smart, Simple Recipes for a Balanced Diet: Expert-Backed Healthy Food Dishes to Support Everyday Wellness

Rethinking Calories: Why Quality Matters More Than Quantity
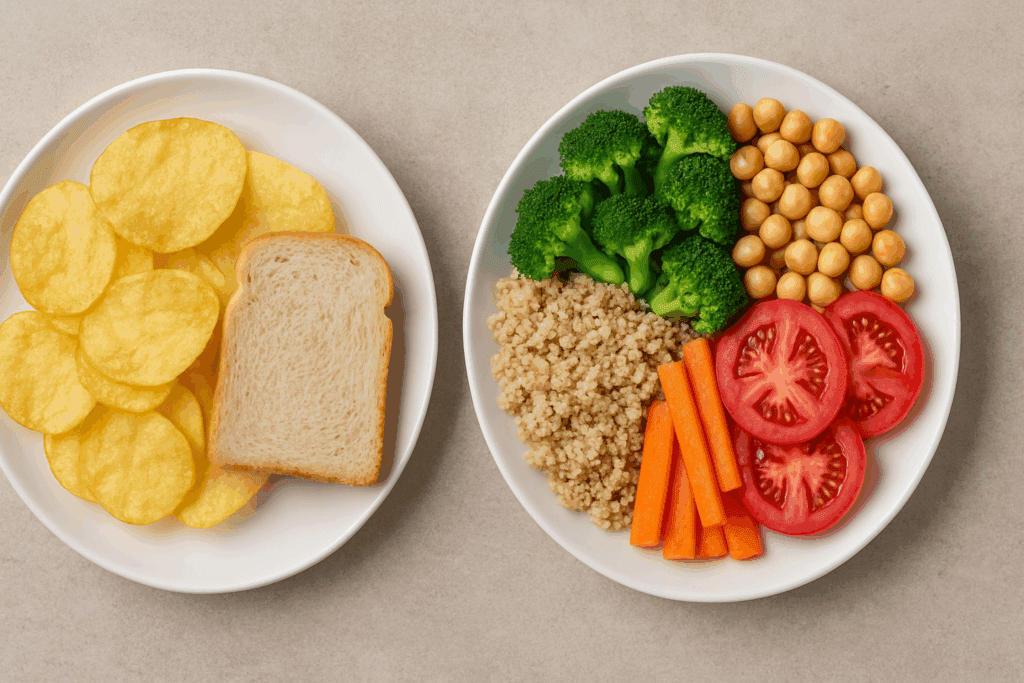
Calories are commonly viewed as the main measure of a meal’s health value. But the truth is, not all calories are created equal. While it’s true that excess calories can lead to weight gain, focusing solely on calorie counting can overshadow the importance of food quality. A vegetarian low calorie approach prioritizes not just eating less, but eating better. It emphasizes foods that provide maximum nutrients with minimal calories—what dietitians refer to as nutrient-dense foods.
For example, 300 calories of mixed vegetables, quinoa, and chickpeas offers significantly more vitamins, minerals, fiber, and plant protein than 300 calories of chips or white bread. A low calorie veggie meal built with these principles keeps you fuller for longer and fuels your body with the micronutrients it truly needs. Nutrient density helps regulate blood sugar, maintain energy levels, and support vital functions like hormone production and immune response.
What makes this especially appealing is that plant-based foods naturally tend to have fewer calories than meat- and fat-heavy meals. Leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are foundational components of a vegetarian low calorie diet and can be enjoyed in large portions without overloading on calories. This makes it easier to create satisfying meals that support healthy weight without the need for excessive restriction or complicated tracking.

Building the Ideal Low Calorie Veggie Meal
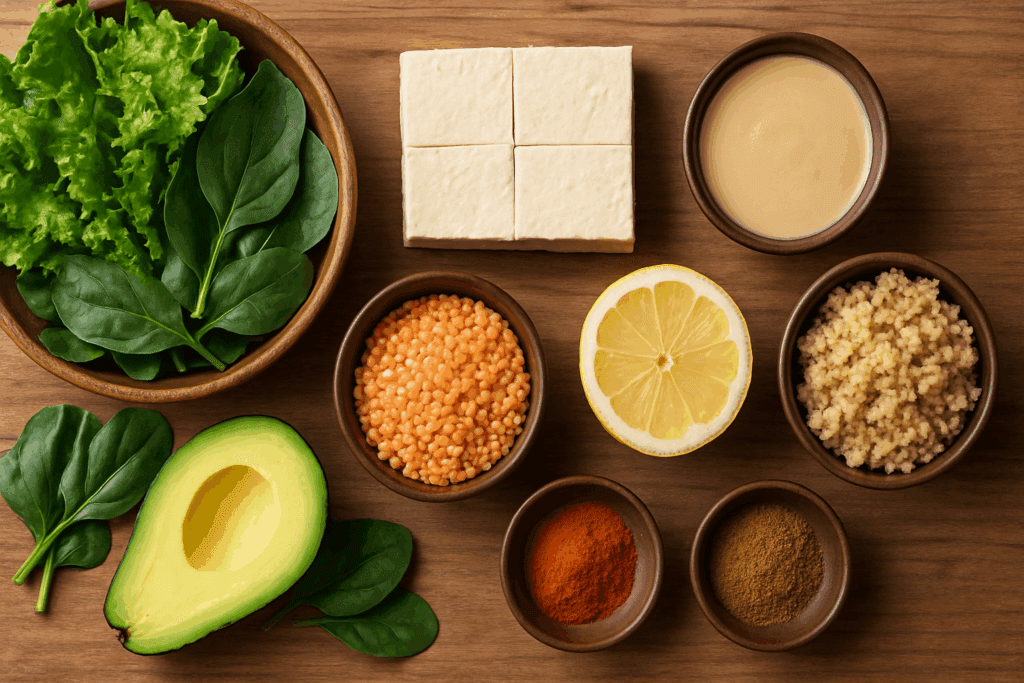
Creating a low calorie veggie meal that’s both balanced and delicious involves more than just tossing vegetables on a plate. The goal is to combine fiber-rich vegetables, plant-based proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates into one cohesive, flavorful dish. The process begins with a strong foundation of vegetables—think leafy greens, zucchini, bell peppers, mushrooms, and cauliflower. These offer volume, texture, and essential vitamins without adding much to the calorie count.
Next, include a solid source of plant protein. Lentils, tofu, black beans, tempeh, and quinoa are all excellent options. Protein helps curb hunger and supports muscle maintenance, especially important if you’re following an active lifestyle or trying to lose weight. Including a healthy fat—like a spoonful of tahini, a few slices of avocado, or a sprinkle of hemp seeds—not only enhances flavor but also promotes satiety and aids in nutrient absorption, particularly fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
The finishing touch is seasoning and variety. Spices like turmeric, cumin, smoked paprika, and chili powder can transform simple ingredients into crave-worthy meals. Citrus juice, vinegar, and fresh herbs add brightness without additional calories. A simple veggie stir-fry with tofu and bok choy, a roasted cauliflower and lentil bowl, or a zucchini noodle dish with tomato and basil are all prime examples of meals that are low in calories, high in nutrients, and incredibly satisfying.
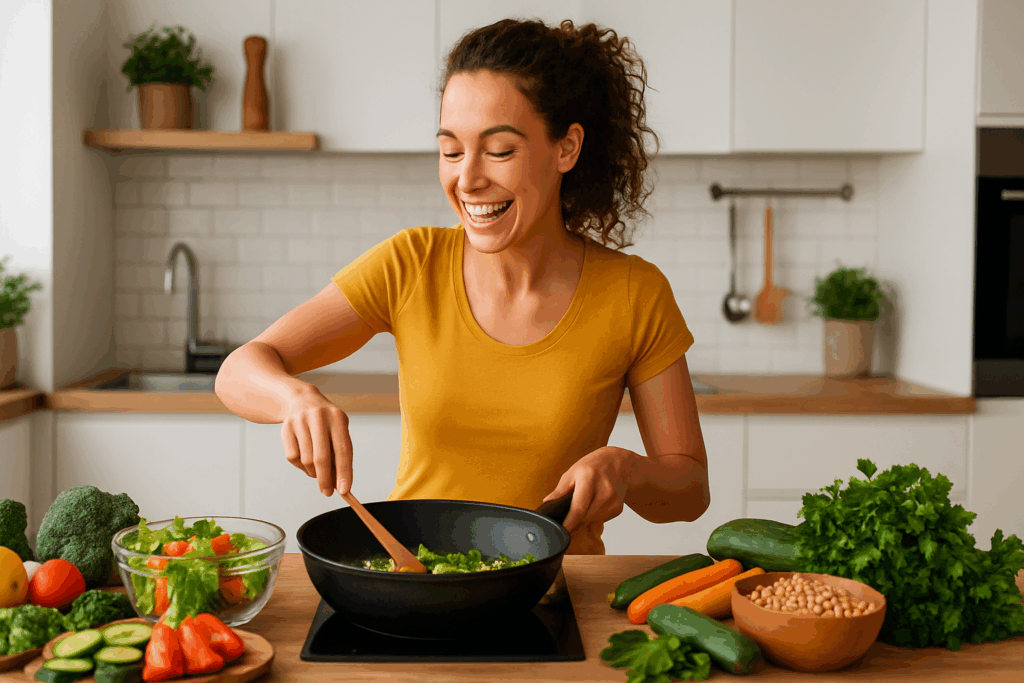

Real Benefits of Eating Vegetarian and Low Calorie
Choosing vegetarian low calorie meals isn’t just a dietary preference—it’s a lifestyle decision that comes with significant health rewards. Research has shown that people who follow plant-based diets tend to have lower body mass indexes, improved blood pressure, and reduced risks of heart disease, certain cancers, and type 2 diabetes. This is due in large part to the high fiber and antioxidant content found in whole plant foods, which help combat inflammation and oxidative stress.
Weight management is another key benefit. Because low calorie veggie meals are high in fiber and water content, they promote fullness without excess calories. This means you can eat until you feel satisfied without derailing your goals. It also makes portion control more intuitive and less stressful, which can help prevent disordered eating patterns. Additionally, the complex carbohydrates found in vegetables, legumes, and whole grains provide a steady source of energy, avoiding the spikes and crashes associated with sugary or highly processed foods.
These meals also support digestive health. Fiber feeds the beneficial bacteria in your gut microbiome, which plays a role in everything from immunity to mood regulation. And for those concerned about nutrient intake, a well-planned vegetarian low calorie diet can provide all the essential nutrients your body needs. From plant-based iron and calcium to omega-3s and B vitamins, thoughtful food choices can ensure you’re meeting your daily nutritional requirements.
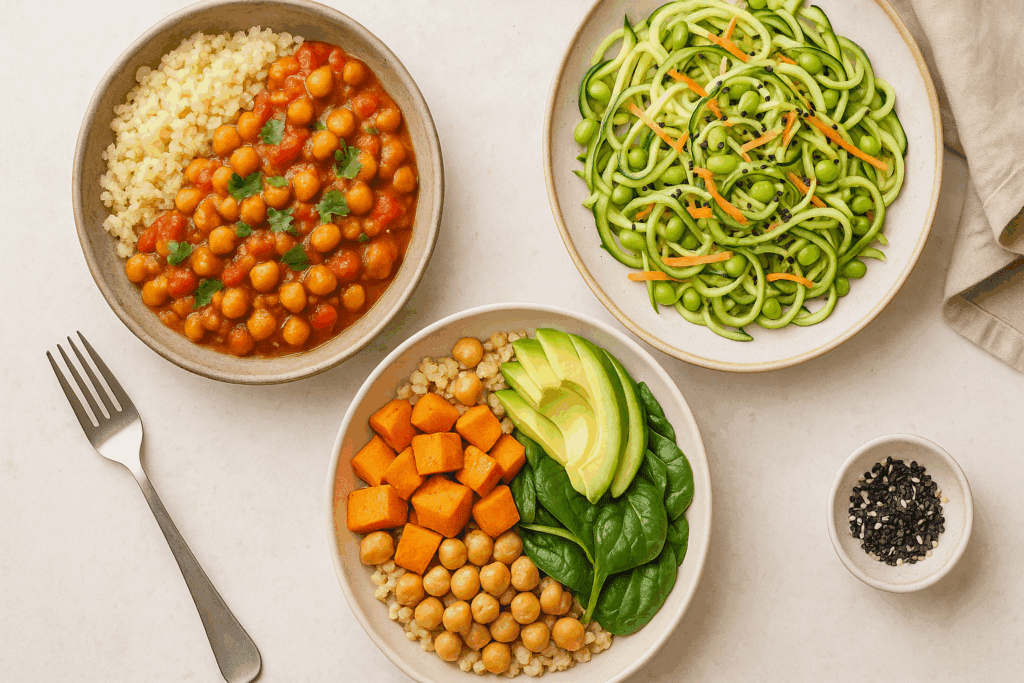

Meal Ideas That Taste Great and Keep You Full
One of the best parts about embracing a vegetarian low calorie lifestyle is discovering how diverse and delicious the meals can be. From globally inspired flavors to comfort food made lighter, the possibilities are endless. Take, for example, a Moroccan-inspired chickpea stew with tomatoes, carrots, and warm spices. It’s deeply satisfying, rich in plant protein, and only about 350 calories per serving. Or try a grain bowl with roasted sweet potatoes, kale, black beans, and a drizzle of lime-tahini dressing—filling, flavorful, and full of texture.
For lunch, a zucchini noodle salad tossed with edamame, avocado, and sesame seeds delivers a refreshing crunch with healthy fats and protein. Another simple but nourishing option is a lentil and spinach soup served with a side of whole grain crackers. Even classic dishes like pasta can be reinvented using spiralized veggies or whole wheat noodles, paired with sautéed greens and a homemade tomato or pesto sauce.
These examples show that low calorie veggie meals can be exciting and indulgent in all the right ways. The key is using whole, fresh ingredients and learning how to build flavor without relying on high-calorie additives like heavy creams or processed sauces. Over time, your palate will naturally shift toward lighter, cleaner tastes, making healthy eating feel less like a chore and more like a daily treat.
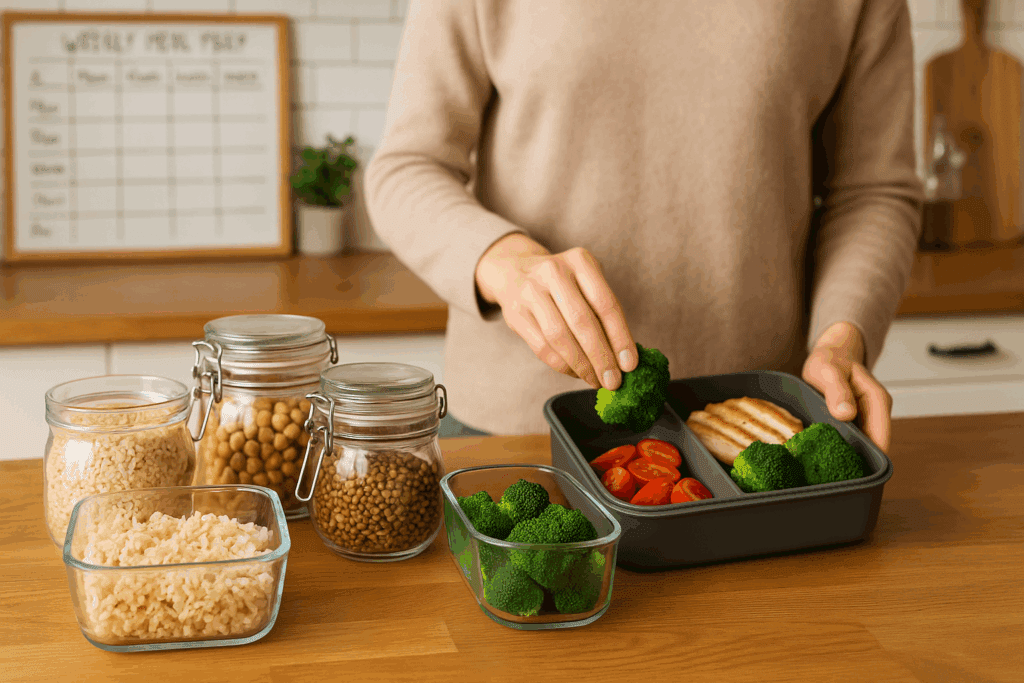

Expert Tips for Long-Term Success
Sustainability is what makes a healthy lifestyle truly effective, and success with vegetarian low calorie meals depends on creating routines that work for you. One of the most useful strategies is meal prepping—setting aside a couple of hours each week to batch-cook ingredients like grains, beans, and roasted vegetables. These staples can be mixed and matched into different meals, saving time and ensuring you always have healthy options on hand.
Keeping your kitchen stocked with essentials like canned legumes, frozen vegetables, whole grains, and flavorful spices makes it easy to throw together meals without overthinking. Investing in quality containers for storing leftovers can also help you pack lunches or freeze portions for busier days. And if you’re dining out or grabbing something on the go, look for veggie-forward options with simple ingredients and clear nutritional labels.
Another expert tip is to focus on how food makes you feel rather than solely on the numbers. Pay attention to how different meals affect your mood, energy levels, digestion, and sleep. This mindfulness can reinforce your healthy habits and help you stay in tune with your body’s needs. The more you prioritize meals that nourish and energize you, the easier it becomes to maintain a low calorie vegetarian lifestyle without falling back on old patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions: Vegetarian Low Calorie Meals
1. Can a vegetarian low calorie lifestyle support high-performance athletes or active individuals?
Absolutely. Although low calorie diets are often associated with weight loss or sedentary lifestyles, a well-planned vegetarian low calorie approach can support athletes when meals are structured for nutrient density and strategic fueling. Endurance athletes, for example, may rely on low calorie veggie meal options post-workout to replenish nutrients while maintaining a lean body composition. The key is emphasizing protein-rich plant foods like lentils, tempeh, and quinoa, along with smart carbohydrates like sweet potatoes and whole grains to fuel performance. Supplementation with nutrients like B12 and iron may be required, but plant-based athletes can thrive with careful planning, especially when energy needs are met through quality rather than quantity. Many elite plant-based athletes—including ultramarathoners and Olympians—credit their stamina and recovery to the anti-inflammatory nature of vegetarian diets, even when calorie-controlled.
2. How can vegetarian low calorie meals help regulate appetite and emotional eating patterns?
One of the often-overlooked benefits of a vegetarian low calorie approach is its potential impact on satiety hormones and emotional eating behaviors. Fiber-rich foods found in these meals help slow digestion and regulate blood sugar, which plays a crucial role in controlling ghrelin and leptin—the hormones responsible for hunger and fullness. Additionally, low calorie veggie meal plans tend to reduce blood sugar spikes, minimizing cravings that often trigger impulsive snacking or overeating in response to stress or boredom. The act of preparing fresh, whole foods also promotes mindful eating habits, which is a key behavioral tool in managing emotional eating cycles. Over time, consistent consumption of such meals may help rewire reward pathways in the brain, reducing dependence on calorie-dense, ultra-processed comfort foods.
3. Are there any long-term cognitive benefits associated with low calorie veggie meal patterns?
Yes, emerging research indicates that vegetarian low calorie diets may play a neuroprotective role as part of a brain-healthy lifestyle. Low calorie veggie meals rich in antioxidants, polyphenols, and plant-derived omega-3s—like those found in flaxseeds and walnuts—can help reduce neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are linked to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. Furthermore, diets that are high in vegetables and legumes are associated with better memory, executive function, and mental clarity in older adults. A steady intake of micronutrients like folate, magnesium, and vitamin E—commonly found in low calorie vegetarian foods—also contributes to neural health. These findings suggest that beyond weight management, such diets could offer protective benefits for long-term cognitive performance.
4. What are some unexpected social or psychological benefits of adopting a vegetarian low calorie diet?
The lifestyle shift that comes with preparing and enjoying low calorie veggie meals can foster a deeper connection with food and community. Many individuals report enhanced self-efficacy and pride in cooking meals from scratch using whole ingredients. Additionally, engaging with local farmers’ markets or vegetarian meal groups can help build a sense of social belonging, which plays an important role in mental well-being. Psychologically, knowing that your dietary choices support not only personal health but also environmental and ethical values can provide a strong sense of purpose and alignment. Over time, these emotional and social reinforcements become part of a positive feedback loop, encouraging consistency and reducing reliance on unhealthy convenience foods.
5. How can families with children adopt low calorie veggie meal strategies without compromising on taste or variety?
Children are often perceived as picky eaters, but introducing vegetarian low calorie meals early can help shape more adventurous and balanced palates. The trick is to emphasize variety, texture, and visual appeal—think colorful stir-fries, build-your-own veggie tacos, or homemade veggie nuggets with fun dipping sauces. Involving kids in the cooking process also increases their interest and willingness to try new plant-based foods. Nutritionally, such meals can still meet developmental needs when planned to include calcium-rich greens, fortified plant milks, legumes, and whole grains. Importantly, low calorie doesn’t mean low satisfaction—meals can be designed to be both fun and filling, proving that healthy choices can also be family-friendly and enjoyable.
6. How do low calorie veggie meals affect gut microbiota and digestive health over time?
A sustained pattern of consuming vegetarian low calorie meals can significantly enhance gut microbiota diversity, which is a critical factor in digestive and overall health. The high fiber content in these meals serves as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a balanced internal ecosystem. Diverse vegetables, legumes, and fermented plant foods like kimchi and tempeh further enrich the gut microbiome, which in turn supports immune function, mood regulation, and nutrient absorption. Over time, individuals may experience reduced bloating, improved regularity, and even decreased inflammation in the gut lining. Unlike low-fiber weight loss diets, the low calorie veggie meal approach fosters gut health in a sustainable, supportive way.
7. Are vegetarian low calorie meal plans adaptable for people managing chronic illnesses like PCOS or hypothyroidism?
Yes, with guidance, a vegetarian low calorie meal plan can be tailored to support individuals with chronic conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hypothyroidism. For PCOS, meals rich in anti-inflammatory ingredients—like leafy greens, flaxseeds, and berries—can help regulate insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance. In cases of hypothyroidism, special attention should be given to iodine, selenium, and zinc intake, which can be managed through a combination of seaweed, Brazil nuts, and legumes. Low calorie veggie meals can reduce the systemic inflammation often associated with these conditions, and when personalized, may improve symptom management. Consultation with a registered dietitian is recommended for optimal nutrient calibration, but plant-based diets offer a flexible framework for chronic illness support.
8. What are some practical strategies for maintaining a vegetarian low calorie lifestyle while traveling or dining out?
Travel and restaurant dining can pose challenges, but with a few smart strategies, maintaining a vegetarian low calorie approach is entirely feasible. Start by researching plant-forward restaurants or cafes ahead of time, and opt for menu items that emphasize vegetables, legumes, and grains rather than creamy sauces or fried elements. Requesting steamed or grilled vegetables, dressing on the side, or a double portion of greens can turn almost any dish into a low calorie veggie meal. Packable snacks like roasted chickpeas, raw nuts, or dried edamame also make a big difference when healthy options are limited. Ultimately, flexibility and preparation are key—when you approach travel as an opportunity to explore regional produce and local vegetarian dishes, it enhances the experience rather than restricts it.
9. How is the vegetarian low calorie trend evolving in the food industry, and what innovations are emerging?
The food industry is rapidly adapting to meet consumer demand for healthier, plant-based options, and the vegetarian low calorie movement is at the heart of this evolution. We’re seeing a rise in minimally processed meal kits that emphasize clean ingredients and portion control, as well as innovative plant-based proteins made from lentils, chickpeas, and fungi. Food tech companies are also developing calorie-smart meat alternatives and low-calorie pasta substitutes using ingredients like kelp, hearts of palm, and konjac root. Restaurants are becoming more mindful of plant-forward menu options that cater to health-conscious consumers, often featuring calorie information and customizable vegetarian dishes. These developments reflect a broader societal shift toward sustainable, health-oriented eating—and vegetarian low calorie foods are playing a leading role in shaping that future.
10. What mindset shifts are most helpful when transitioning to a vegetarian low calorie lifestyle?
Perhaps the most transformative aspect of embracing a vegetarian low calorie way of eating is the mindset shift from restriction to abundance. Instead of focusing on what you’re avoiding, it’s more empowering to concentrate on all the new foods, flavors, and culinary skills you’re gaining. Understanding that every low calorie veggie meal is an investment in your long-term energy, clarity, and wellness can help reinforce motivation. It’s also helpful to adopt a flexible mindset—perfection isn’t required, and occasional indulgences don’t undo overall progress. The focus should be on progress, not rigidity, and recognizing that health is built through sustainable, enjoyable habits. When plant-based, calorie-conscious meals are framed as tools for vitality rather than limitations, they become much easier—and more rewarding—to sustain.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Vegetarian Low Calorie Living
Making the switch to a vegetarian low calorie lifestyle is a smart and empowering choice—one that supports not only your physical health but also your emotional well-being and long-term quality of life. These meals are far from restrictive. In fact, they offer a refreshing sense of abundance: plates filled with colorful vegetables, hearty legumes, and wholesome grains that provide essential nutrients in every bite.
A well-designed low calorie veggie meal fuels your body, satisfies your hunger, and gives you the tools to prevent disease, manage weight, and feel better every day. From quick stir-fries to slow-cooked stews, from vibrant salads to warm grain bowls, there’s no shortage of satisfying, delicious, and health-promoting meals you can enjoy on this journey. It’s not about eating less—it’s about eating smart, with intention and joy.
Whether you’re new to plant-based eating or looking to fine-tune your approach, the path forward is full of possibilities. With each smart, intentional meal you prepare, you’re investing in a healthier, more vibrant you. Let your plate reflect your goals, your values, and your commitment to living well—and know that vegetarian low calorie meals are one of the most accessible, effective, and enjoyable ways to do just that.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
plant-based meal ideas, healthy vegetarian recipes, calorie-conscious eating, plant-based nutrition tips, low calorie meal prep, weight loss vegetarian recipes, plant-based diet benefits, fiber rich vegetarian meals, whole food plant diet, vegetarian lifestyle tips, heart healthy vegetarian meals, clean eating for vegetarians, nutrient-dense plant foods, gut health and plant foods, anti-inflammatory vegetarian diet, vegetarian meals for energy, healthy eating habits, sustainable eating tips, balanced vegetarian meals, vegetarian food for wellness
Further Reading:
27 Vegetarian Dinners with 400 Calories or Less
94 Vegetarian Dinners You Need to Try
Low-calorie vegetarian recipes
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.

