In today’s fast-paced world, cognitive performance is more essential than ever. Whether you’re a student, a working professional, or simply trying to stay sharp into your later years, maintaining mental clarity and sustained concentration has become a key to success. While brain-training apps and mindfulness practices often receive considerable attention, a foundational but frequently overlooked factor is nutrition. The food we consume has a profound and measurable impact on cognitive function. This article explores how diet affects focus, evaluates the best brain foods for boosting alertness, and outlines dietary strategies for sustained mental clarity.
You may also like: Plant Based Diet vs Standard American Diet: What the Latest Studies Reveal About Long-Term Health Outcomes
The Connection Between Nutrition and Brain Function
The human brain, despite representing only about 2% of our body weight, consumes around 20% of the body’s energy. This disproportionate demand for energy highlights the brain’s sensitivity to nutrient supply. Essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, antioxidants, and amino acids play integral roles in neurotransmitter production, synaptic plasticity, and neuroprotection. It is through these mechanisms that nutrition and brain function become deeply intertwined.
Studies have demonstrated that dietary patterns can influence the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. For instance, diets rich in saturated fats and refined sugars have been linked to impaired memory and learning ability, while nutrient-dense, plant-based diets are associated with better overall cognitive performance. Therefore, it is increasingly recognized that adopting the best diet for focus is not just beneficial in the long term but has immediate implications for daily mental performance.
How Does Diet Affect Focus and Alertness?
The link between diet and mental sharpness can often be observed in everyday experiences. A high-sugar breakfast may lead to a temporary burst of energy followed by a mid-morning crash and reduced concentration. In contrast, a balanced meal with complex carbohydrates, fiber, and healthy fats provides a slow and steady energy release, supporting sustained attention and reducing irritability.
When considering whether diet helps with your alertness, it is important to explore how different macronutrients and micronutrients interact with the brain. Carbohydrates, for example, influence the availability of glucose, the brain’s primary fuel source. However, not all carbohydrates are created equal. Whole grains provide a steady supply of glucose, while refined sugars can lead to erratic spikes and crashes. Proteins, on the other hand, supply amino acids like tyrosine and tryptophan, which are precursors to dopamine and serotonin—neurotransmitters that regulate mood and focus.
Moreover, fats are crucial, particularly omega-3 fatty acids found in flaxseeds, walnuts, and chia seeds. These essential fats support the integrity of neuronal membranes and have been associated with improvements in memory and cognitive function. By integrating these brain healing foods into a daily diet, individuals may experience tangible enhancements in their cognitive performance and emotional balance.

The Science Behind Brain Healing Foods
The term “brain healing foods” refers to nutrient-rich foods that support brain repair, neurogenesis, and protection against cognitive decline. These foods contain compounds that mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation—two major contributors to neural aging and damage. Antioxidants, found in abundance in berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables, neutralize free radicals that can damage brain cells.
In addition to antioxidants, polyphenols found in foods like blueberries, green tea, and dark chocolate have been shown to enhance brain function by promoting blood flow to the brain and stimulating the growth of new neurons. Curcumin, a compound found in turmeric, exhibits neuroprotective properties and has been studied for its role in delaying or preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
Plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as hemp seeds and algae oil, are also vital. These fats are involved in maintaining the fluidity of cell membranes and facilitating communication between brain cells. As part of a whole-food, plant-based diet, these nutrients contribute to a brain environment that is resilient and capable of recovering from daily stressors.
Best Brain Foods for Cognitive Performance
When seeking the best brain foods to support focus and concentration, several plant-based options consistently emerge as nutritional powerhouses. Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collards are rich in folate and vitamin K, both associated with slower cognitive decline. Berries, particularly blueberries, are known for their high antioxidant content and have been linked to improvements in memory and learning.
Avocados provide healthy monounsaturated fats, which improve blood flow to the brain, enhancing cognitive functions. Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds, offer a blend of vitamin E, zinc, and essential fatty acids, making them ideal brain food snacks. Legumes, including lentils and black beans, are another excellent source of plant-based protein and fiber, contributing to stable blood sugar levels and prolonged mental energy.
Whole grains such as oats, brown rice, and quinoa provide the slow-digesting carbohydrates necessary for consistent brain fuel. These foods are not only nutrient-dense but also help maintain satiety, reducing the temptation to reach for sugary snacks that can impair concentration. Incorporating these ingredients into daily meals ensures a steady intake of compounds that enhance mental clarity and cognitive resilience.

The Role of Hydration and Micronutrients
While the macronutrient composition of a diet is critical, micronutrients and hydration should not be overlooked. Even mild dehydration can result in impaired cognitive function, fatigue, and decreased alertness. Water is essential for maintaining the balance of electrolytes that facilitate nerve transmission and brain cell communication.
Key micronutrients like iron, magnesium, and zinc are also vital for brain health. Iron deficiency can lead to reduced oxygen delivery to the brain, resulting in fatigue and diminished concentration. Magnesium plays a role in nerve signaling and stress regulation, while zinc is involved in memory formation and neural signaling. Plant-based sources of these nutrients include pumpkin seeds, legumes, dark leafy greens, and fortified cereals.
B vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the maintenance of brain structure. Although B12 is typically found in animal products, plant-based individuals can obtain it through fortified foods or supplementation. A comprehensive focus on micronutrient intake helps ensure that the brain receives all the tools it needs to function optimally.
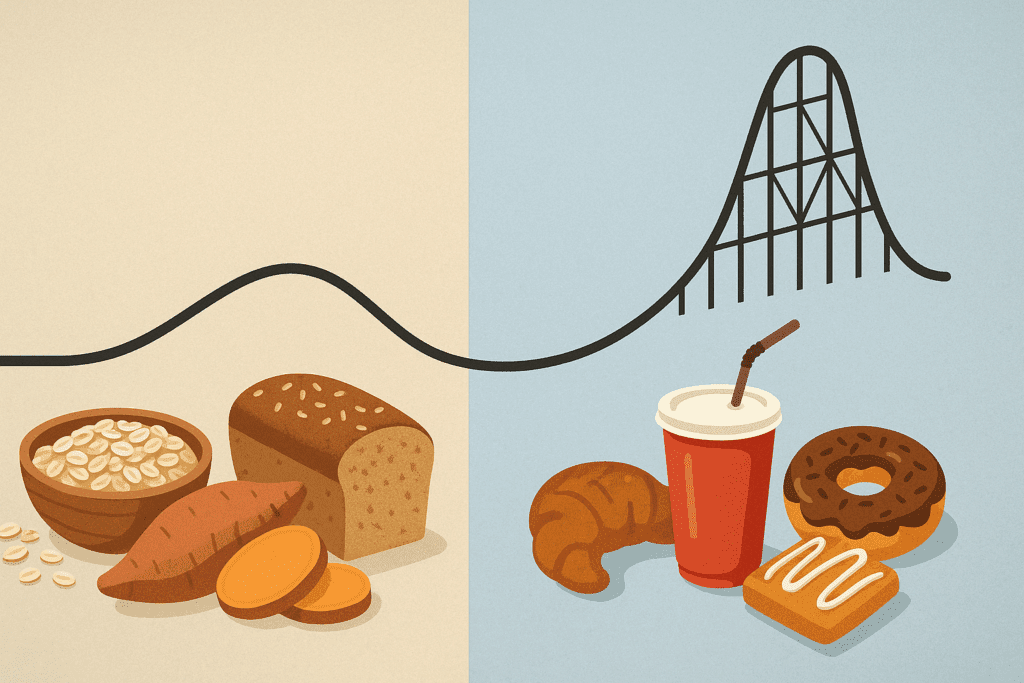
How Blood Sugar Stability Affects Focus
Blood sugar fluctuations are among the most immediate dietary factors that affect focus and concentration. When blood glucose levels spike rapidly due to high-sugar foods, the body responds with a surge of insulin, followed by a sharp drop in blood sugar. This sequence often leads to symptoms of fatigue, irritability, and reduced mental clarity.
Choosing foods with a low glycemic index helps stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent these cognitive crashes. Complex carbohydrates, such as those found in oats, sweet potatoes, and whole grains, digest slowly and provide a steady energy supply. Pairing these with healthy fats and proteins further slows absorption and extends the period of satiety and alertness.
For individuals wondering, “Does diet help with your alertness?” the evidence strongly supports a link between consistent blood sugar regulation and improved cognitive function. Maintaining a dietary pattern that avoids refined sugars and includes balanced meals throughout the day is one of the simplest yet most effective strategies for enhancing mental performance.
Best Diet for Focus: Plant-Based Strategies
A growing body of research supports the role of plant-based diets in improving brain function. Diets such as the Mediterranean, DASH, and MIND diets—all of which emphasize plant-based foods—have been associated with lower risks of cognitive decline. These dietary patterns prioritize fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains while minimizing processed foods and saturated fats.
A plant-based approach naturally incorporates many of the best brain foods, offering a rich source of antioxidants, fiber, and phytochemicals. These compounds collectively reduce systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are implicated in diminished brain function. Additionally, the high fiber content of plant-based foods supports gut health, which recent studies have linked to cognitive health through the gut-brain axis.
Importantly, a well-structured plant-based diet is entirely capable of providing all the nutrients necessary for optimal cognitive performance. With mindful inclusion of fortified foods or supplements for nutrients like B12, plant-based eaters can support brain health while also reducing their risk of chronic diseases that impair cognitive function over time.
Brain Food Snacks for Midday Focus
Snacking can either support or sabotage concentration, depending on the quality of the food choices. Brain food snacks that balance healthy fats, protein, and complex carbohydrates are particularly effective at boosting mental energy and sustaining focus between meals. Nuts and seeds, for example, offer a quick and portable source of essential nutrients that promote neurotransmitter production and brain cell repair.
A small serving of trail mix made with walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and dried blueberries delivers omega-3s, magnesium, zinc, and antioxidants in one convenient package. Hummus paired with raw vegetables like carrots or bell peppers provides protein and fiber, while the vegetables offer vitamins that support brain health. Smoothies made with plant-based milk, spinach, flaxseeds, and berries are another excellent option, delivering a concentrated dose of brain-supportive nutrients in an easily digestible form.
For those who need to maintain steady cognitive performance throughout the day, incorporating these kinds of snacks can help bridge the gap between meals without relying on processed or sugary alternatives. Regularly consuming brain food snacks ensures a continual supply of energy and essential compounds that keep the mind sharp and focused.
Foods That Improve Concentration in Academic and Work Settings
In academic and professional environments, the ability to maintain concentration can significantly influence performance. Certain foods have been shown to enhance working memory, decision-making, and overall mental stamina. Dark chocolate, for example, contains flavonoids and small amounts of caffeine, which together enhance blood flow to the brain and stimulate alertness.
Bananas provide a quick source of glucose paired with potassium and vitamin B6, supporting nerve function and serotonin production. Edamame offers a plant-based source of complete protein, iron, and choline—an essential nutrient for brain development and memory. These foods, when incorporated regularly, become allies in sustaining mental effort and improving task efficiency.
Understanding which foods improve concentration allows individuals to strategically plan their meals and snacks around periods of high cognitive demand. Whether preparing for an exam, a presentation, or a demanding project, consuming the right foods beforehand can provide a measurable boost in mental acuity and endurance.
The Long-Term Impact of Diet on Cognitive Health
While the immediate effects of diet on focus are clear, the long-term implications are equally significant. Chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and nutrient deficiencies can all contribute to accelerated cognitive decline. A diet high in whole, plant-based foods not only supports daily focus but also protects against conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and age-related cognitive impairment.
Lifelong dietary habits play a critical role in determining the resilience of the brain over time. Diets rich in saturated fats and processed foods have been associated with structural changes in the brain, including reduced hippocampal volume—a region involved in memory. Conversely, diets emphasizing plant-based sources of nutrition foster neuroplasticity and protect against oxidative damage.
Investing in a dietary pattern that includes the best brain foods and avoids harmful ingredients is an essential part of a holistic strategy for cognitive longevity. By adopting these principles early and maintaining them consistently, individuals can significantly enhance their quality of life as they age.

Frequently Asked Questions: Diet and Mental Focus
What are some underrated plant-based foods that significantly boost focus?
While common choices like blueberries and walnuts often headline discussions on the best brain foods, some underrated options deserve equal attention. Seaweed, for example, is rich in iodine, a trace mineral essential for optimal thyroid function, which indirectly supports brain metabolism and mental sharpness. Fermented foods such as kimchi and sauerkraut also aid focus by supporting gut health, a major component of the gut-brain axis. These options demonstrate how deeply nutrition and brain function are connected, often in ways overlooked by mainstream dietary advice. Exploring lesser-known foods in the best diet for focus opens new opportunities to enhance cognition naturally.
Does intermittent fasting influence concentration or alertness levels?
Emerging research suggests intermittent fasting may positively influence cognitive clarity by promoting brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports neuron health. In the short term, fasting can increase levels of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter associated with heightened alertness and improved focus. However, the impact can vary depending on an individual’s existing nutritional status and metabolic flexibility. Those considering fasting should ensure that their eating windows include plenty of brain healing foods to sustain long-term cognitive benefits. This strategy is most effective when aligned with a focus on foods that improve concentration rather than used as a standalone solution.
Can diet changes support cognitive rehabilitation after brain injury?
Yes, dietary interventions are increasingly being explored in cognitive rehabilitation protocols. After a brain injury, the body’s demand for antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds rises dramatically. Including brain healing foods such as turmeric, flaxseed, and dark leafy greens may aid in neuronal repair and reduce oxidative stress. While not a substitute for clinical treatment, these foods enhance recovery efforts by improving the internal environment needed for neuroplasticity. This perspective expands how we understand nutrition and brain function in a clinical, recovery-focused context.
How do brain food snacks help during long workdays or study sessions?
Brain food snacks play a pivotal role in maintaining steady cognitive performance throughout extended periods of mental exertion. Unlike processed snacks that offer brief energy spikes, options like apple slices with almond butter or trail mix with pumpkin seeds provide a combination of slow-digesting carbohydrates and healthy fats. This nutritional synergy helps stabilize blood sugar levels, which is essential for maintaining focus and energy. Incorporating these into a daily routine supports the best diet for focus by bridging nutritional gaps between meals. Moreover, choosing snacks that align with foods that improve concentration adds another layer of strategic advantage to your workday.
Does diet help with your alertness during periods of high stress or burnout?
Absolutely—in times of high stress or mental fatigue, the right dietary choices can help buffer the physiological toll on the brain. High-magnesium foods like leafy greens, avocado, and quinoa help regulate cortisol levels and support a calmer nervous system. Additionally, omega-3-rich foods have been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, indirectly improving alertness and decision-making capacity. The question of “does diet help with your alertness” becomes particularly relevant when chronic stress is involved, as nutritional support can prevent long-term cognitive exhaustion. Therefore, using diet strategically during stressful periods is not just beneficial but essential.
What social or environmental factors influence dietary impact on focus?
Social settings and food accessibility heavily influence the success of any diet aimed at improving concentration. For example, workplace cultures that prioritize convenience over nutrition may inadvertently encourage choices that disrupt focus, such as sugary snacks or fast food. In contrast, communal eating environments that emphasize plant-based meals tend to support consumption of the best brain foods naturally. Environmental factors like exposure to pollutants or chronic noise can also increase oxidative stress, making brain healing foods even more crucial. Recognizing these contextual influences is vital for applying the best diet for focus in a sustainable way.
Are there specific foods that enhance long-term vs. short-term concentration?
Indeed, the duration of cognitive enhancement depends on the type of nutrients consumed. For short-term focus, foods like matcha, dark chocolate, or bananas provide quick-acting effects due to caffeine, theobromine, or simple sugars. In contrast, long-term mental clarity benefits more from consistent intake of nutrients like omega-3s, polyphenols, and B vitamins. These compounds found in whole grains, legumes, and leafy greens gradually improve neural efficiency and reduce inflammation. Choosing the right balance of immediate and lasting support is key when evaluating foods that improve concentration across various timelines.
How does sleep quality interact with the effects of brain-focused diets?
Sleep and diet are deeply interdependent when it comes to cognitive performance. Poor sleep can reduce insulin sensitivity, leading to erratic energy levels and poor food choices that compromise focus. Conversely, consuming brain food snacks with magnesium and tryptophan in the evening may improve sleep quality, which in turn enhances mental clarity the next day. The bidirectional nature of sleep and diet demonstrates how nutrition and brain function are continuously interacting. Paying attention to evening meals can be just as important as breakfast when aiming to follow the best diet for focus.
Is there a difference in how diet affects focus across different age groups?
Yes, age significantly modulates how diet influences mental performance. In younger individuals, diets high in refined sugar can disrupt neurodevelopment and attention regulation. Meanwhile, older adults may experience sharper benefits from brain healing foods due to the increased vulnerability of aging neurons to oxidative damage. Adolescents often benefit from brain food snacks that support stable glucose levels, while seniors may require higher levels of antioxidants and healthy fats. Understanding how does diet affect focus at various life stages allows for more tailored and effective nutritional strategies.
What emerging research could change how we view diet and mental clarity?
Emerging fields like nutritional psychiatry and microbiome research are revolutionizing our understanding of diet and cognition. Scientists are now exploring how fermented foods and prebiotics influence neurotransmitter synthesis via the gut-brain axis. Personalized nutrition based on genetic and microbiome profiles may soon offer precise dietary recommendations for focus and emotional balance. Studies are also beginning to examine how cumulative exposure to brain healing foods over decades affects epigenetic expression related to cognitive decline. These advances are reshaping not only how we answer “how does diet affect focus,” but also how we approach dietary interventions for long-term brain health.
Conclusion: Elevating Mental Clarity Through Smart Nutrition
In exploring how diet affects focus, one thing becomes abundantly clear: nutrition is not just a background player in cognitive health but a central pillar. From determining how alert you feel throughout the day to influencing long-term brain resilience, the food choices you make directly impact how your brain performs. By prioritizing foods that improve concentration, incorporating strategic brain food snacks, and following the best diet for focus—particularly one rooted in whole, plant-based nutrition—you can cultivate a sharper, more balanced mind.
Integrating brain healing foods such as leafy greens, berries, seeds, and whole grains into your daily meals isn’t merely about improving memory or boosting mental stamina in the short term. It is a long-term investment in the health, agility, and adaptability of your brain. Whether you’re seeking improved productivity, better mood regulation, or protection against age-related decline, the science-backed connection between nutrition and brain function provides a powerful incentive to make thoughtful, informed dietary choices.
Ultimately, the question isn’t just “Does diet help with your alertness?” but rather, “How can you use diet as a strategic tool to unlock your brain’s full potential?” With each well-chosen bite, you’re not only nourishing your body but also setting the stage for greater focus, resilience, and cognitive clarity in all areas of life.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
Slideshow: Brain Foods That Help You Concentrate
Foods linked to better brainpower
Nutritional psychiatry: Your brain on food
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.

