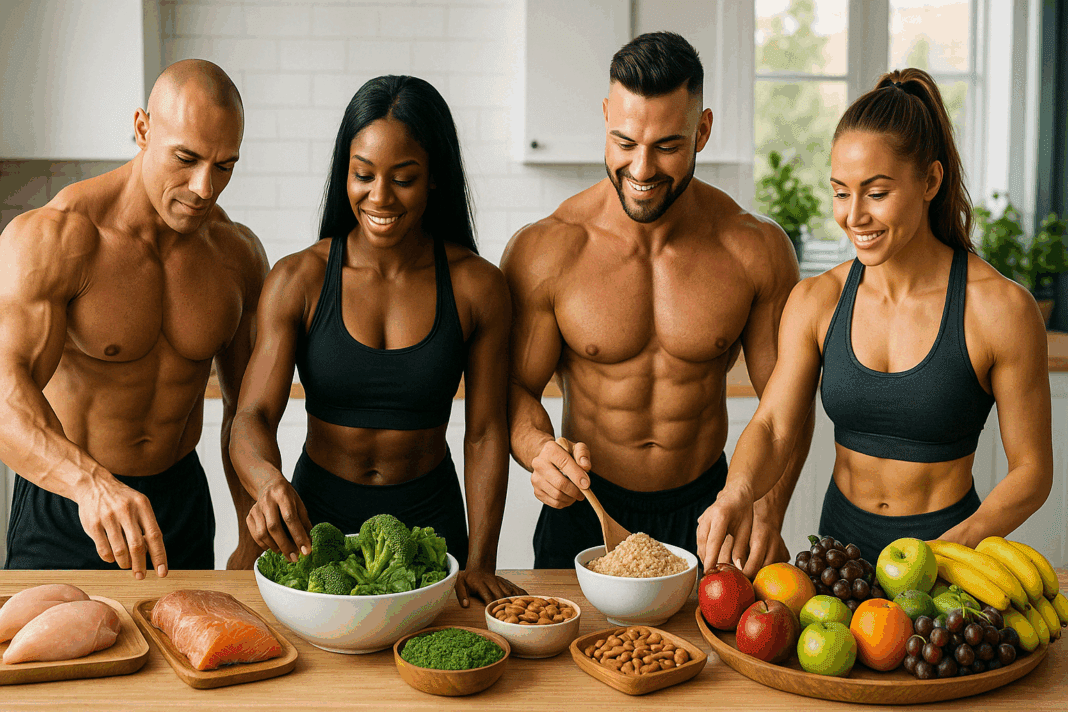
In the world of fitness and nutrition, one question echoes across gyms, forums, and coaching consultations: what do body builders eat to support strength, sculpt lean muscle, and maintain a balanced lifestyle? The answer, while rooted in science, is far from one-size-fits-all. In this comprehensive guide, we unpack the dietary strategies that bodybuilders use to fuel performance, optimize recovery, and sustain long-term health, aligning with mindful eating and healthier lifestyle principles.
You may also like: Smart Meal Prep for Weight Loss: Expert-Approved Lunch Ideas and Recipes to Stay on Track
While popular culture often focuses on extremes, sustainable bodybuilding nutrition relies on consistency, quality food choices, and strategic meal timing. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your strength journey, understanding the role of nutrition in bodybuilding is key. This guide explores not only what does a bodybuilder eat on a daily basis, but also how dietary needs vary between individuals, including insights into the best bodybuilding diet for women.
The Foundation of a Bodybuilding Diet: Macronutrient Mastery
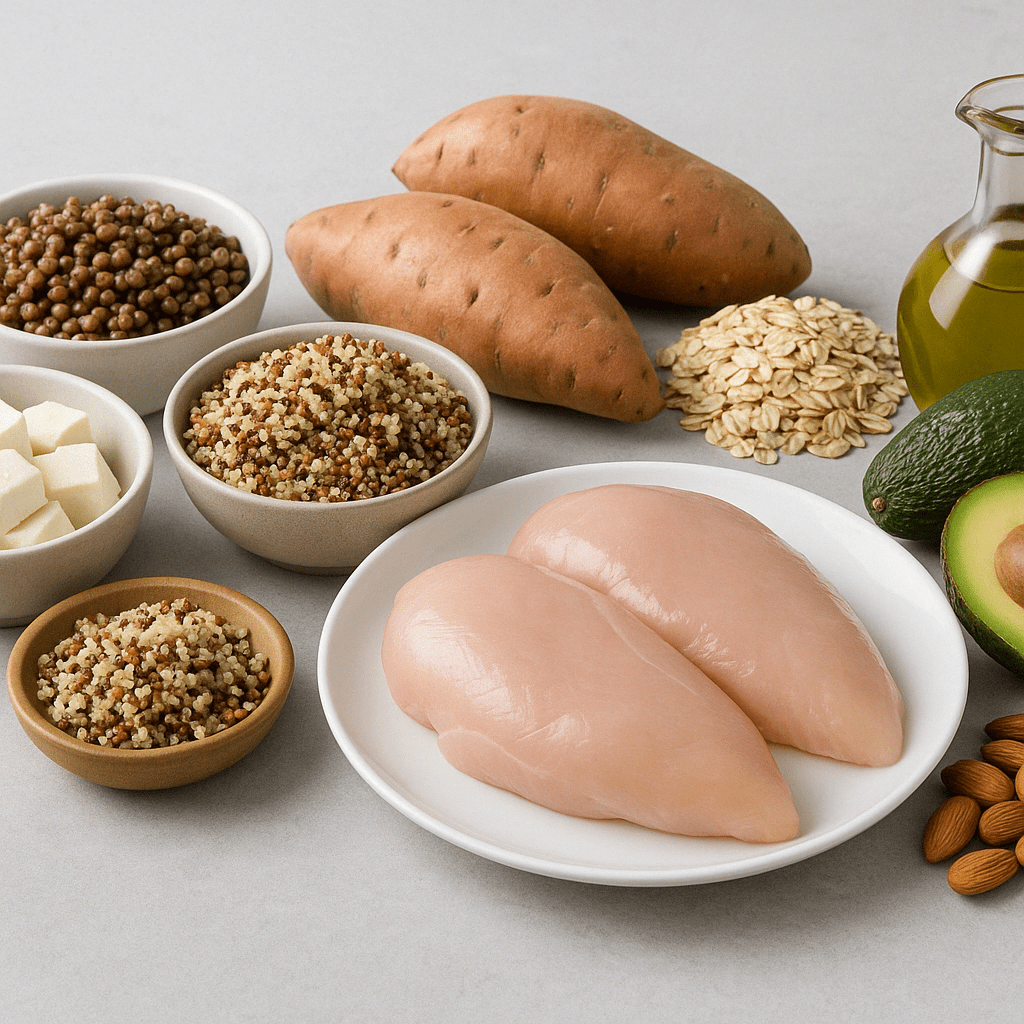
At the core of every successful bodybuilding plan is a strategic balance of macronutrients: protein, carbohydrates, and fat. Each plays a specific role in supporting hypertrophy, performance, and recovery. Protein, the most emphasized macronutrient in bodybuilding, is essential for muscle repair and growth. Most bodybuilders aim for 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, depending on training intensity, body composition goals, and individual metabolism.
Carbohydrates serve as the body’s primary energy source. For bodybuilders, carbs are not the enemy—they’re essential for fueling workouts, maintaining glycogen stores, and supporting muscle retention during calorie deficits. Complex carbohydrates like oats, sweet potatoes, legumes, and whole grains offer sustained energy and vital nutrients.
Dietary fat, often misunderstood, plays a crucial role in hormone regulation, brain health, and long-term satiety. Healthy fat sources—such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil—should be included in any balanced bodybuilding meal plan.

Meal Frequency and Timing: How Often Do Bodybuilders Eat?
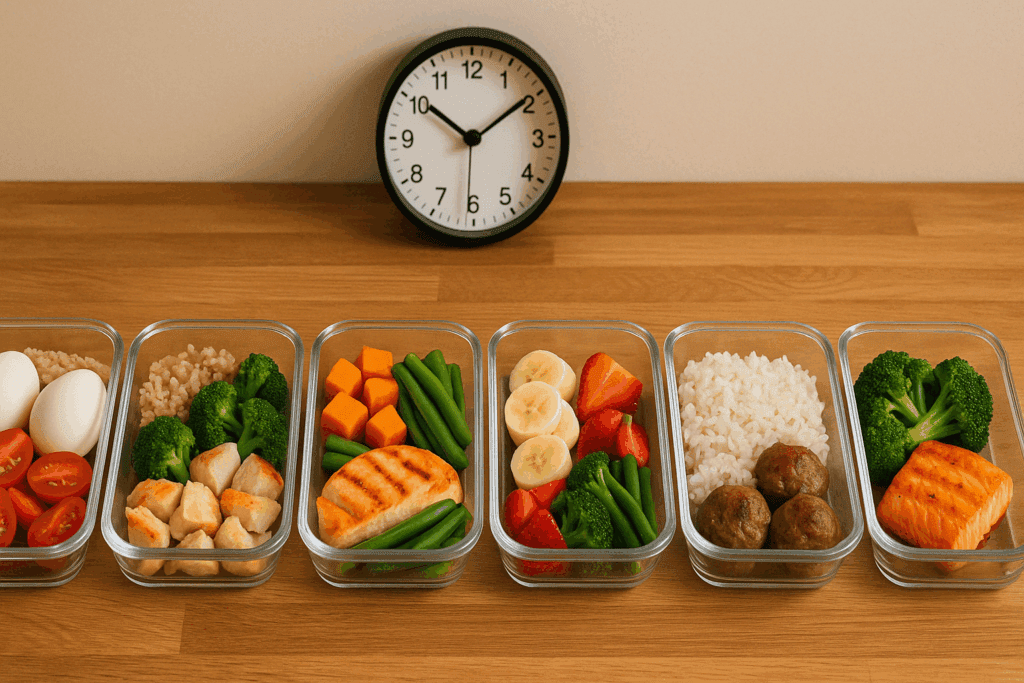
When asking the question body builder how many meals do you eat per day, the answer typically ranges between five and seven. Frequent meals ensure a steady supply of nutrients to muscles, help manage hunger, and support consistent energy levels. However, it’s not just about frequency—it’s about timing.
Strategic meal timing around workouts is one of the most impactful elements of a bodybuilding diet. Consuming a protein- and carb-rich meal 60 to 90 minutes before training can enhance performance, while a post-workout meal focused on protein and fast-digesting carbs can jumpstart recovery. While the classic six-meal-a-day approach remains popular, some athletes opt for variations such as intermittent fasting or fewer meals with larger portions, tailored to their training and lifestyle preferences.
Micronutrients Matter: Beyond the Big Three
While macronutrients dominate the bodybuilding conversation, micronutrients—vitamins and minerals—are equally critical. Nutrient deficiencies can impair muscle growth, slow recovery, and lead to long-term health issues. Calcium, magnesium, zinc, vitamin D, B-complex vitamins, and antioxidants like vitamins C and E support energy metabolism, immunity, and cellular repair.
For bodybuilders following plant-based or restrictive diets, careful planning ensures adequate intake of iron, vitamin B12, iodine, and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are essential for maintaining energy, supporting red blood cell production, and promoting inflammation control post-workout.
What Does a Bodybuilder Eat in a Day? Sample Smart Meals
A typical day for a bodybuilder might start with a protein-rich breakfast such as scrambled tofu or egg whites paired with oatmeal, chia seeds, and berries. Mid-morning snacks often include Greek yogurt with almonds or a protein shake with banana. Lunch might feature grilled chicken, quinoa, and mixed vegetables, while the afternoon snack could be a hummus wrap or cottage cheese with fruit. Dinner usually consists of lean protein, roasted vegetables, and a complex carb like brown rice or sweet potato.
Importantly, what bodybuilders eat also depends on their current goal—bulking, cutting, or maintenance. During a cutting phase, meals are lower in calories but still high in protein to preserve lean mass. Bulking meals are more calorie-dense, with increased carbs and healthy fats to support muscle gain.

The Female Perspective: Tailoring the Bodybuilding Diet for Women
When it comes to building strength and muscle, women have unique physiological considerations that impact nutrition. A bodybuilding diet for women must address hormonal fluctuations, energy availability, and nutrient timing with precision. While the foundational principles of high-protein, balanced meals apply to both sexes, women may require adjustments in total caloric intake and macronutrient ratios.
For example, during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, women may benefit from slightly higher carb intake to support energy and mood. Additionally, iron-rich foods become especially important for menstruating women. Incorporating sources such as lentils, spinach, pumpkin seeds, and fortified cereals can help maintain optimal iron levels.
Smart supplementation—particularly with calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and omega-3s—can further support bone health and hormone balance in active women. Women should also be mindful of body composition goals and avoid overly aggressive calorie restriction, which can impair muscle gains and disrupt metabolic function.
Balancing Performance and Sustainability: The Role of Whole Foods
Sustainability and long-term health are critical considerations in any bodybuilding diet. While supplements have a place, whole foods should form the backbone of a bodybuilder’s nutrition. Whole-food-based meals support gut health, provide phytonutrients, and deliver a balance of fiber and hydration that processed options often lack.
Meal prepping with whole ingredients—like roasted vegetables, beans, tofu, lean meats, whole grains, and healthy oils—makes it easier to stay on track and avoid the pitfalls of highly processed convenience foods. It also reinforces a mindful eating approach, where athletes are more attuned to hunger, fullness, and food quality.
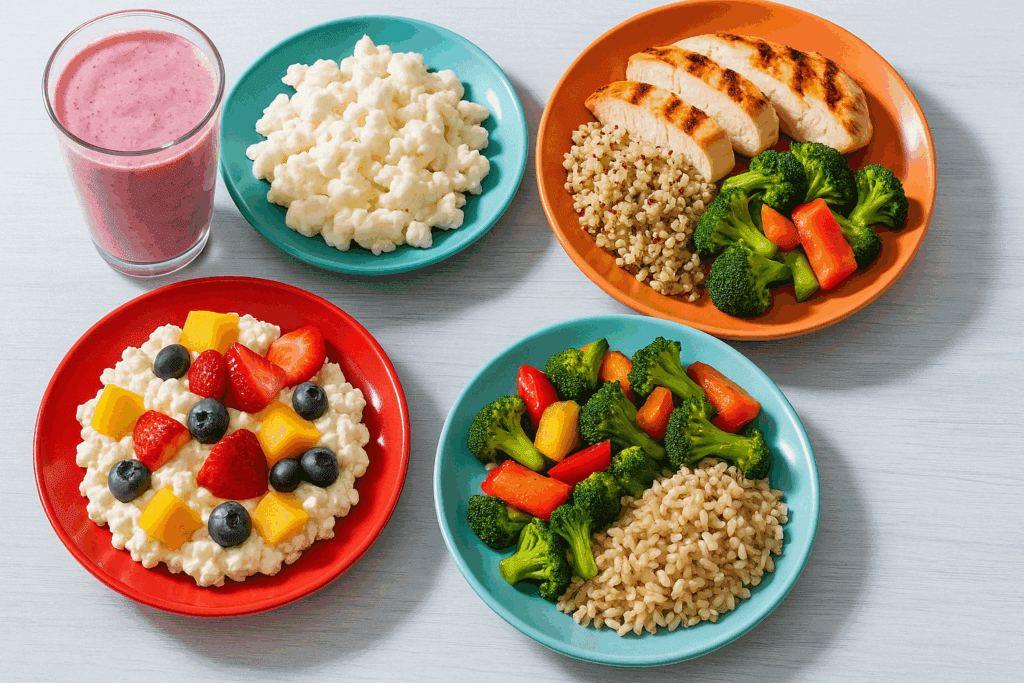
Is Keto a Good Diet for Bodybuilders? Comparing Keto and Low Carb Approaches
One of the most common debates in the strength training world is the comparison of the ketogenic diet vs low carb plans. Some bodybuilders experiment with keto or low-carb approaches to reduce body fat and improve insulin sensitivity. However, the answer to whether is keto a good diet for gaining muscle remains complex.
The ketogenic diet—a very low-carb, high-fat plan—forces the body to burn fat for fuel. While this can result in significant fat loss, especially during a cutting phase, it may compromise workout performance for some athletes due to limited glycogen availability. In contrast, low carb diet keto diet variations that allow moderate carb intake may better support endurance and strength.
A key distinction in the keto diet vs low carb diet debate lies in sustainability. Is a keto diet sustainable for long-term muscle building? For many, the restrictive nature of strict keto makes it difficult to maintain, particularly when training volume increases. Athletes who follow a more flexible low-carb plan, including high-fiber vegetables, legumes, and targeted carb timing, may experience better adherence and performance outcomes.
Understanding the differences between s keto low carb and more moderate carb strategies is essential for tailoring a personalized nutrition plan. For some, a cyclical keto diet—where carbs are reintroduced periodically—offers a compromise. Regardless of the approach, what matters most is nutrient density, adequate protein, and the ability to stick with the plan long term.
Is Keto No Carbs? The Truth About Carbs in Bodybuilding Diets
A common misconception is that the ketogenic diet means eliminating all carbohydrates. So, is keto no carbs in practice? Not exactly. Even the strictest keto diets include small amounts of carbs—typically around 20 to 50 grams per day—from non-starchy vegetables, nuts, seeds, and trace sources.
For bodybuilders, this distinction is critical. Total carb elimination can negatively affect performance, mood, and muscle preservation. Strategic carb intake—whether through a targeted keto diet or low-carb cycling—can support training demands while still allowing the body to use fat for fuel.
Those exploring low carb diet keto diet plans should remember that quality trumps quantity. Whole-food sources like leafy greens, berries, and legumes can fit into even reduced-carb plans while delivering essential fiber and antioxidants. This approach helps preserve lean mass and promotes metabolic flexibility.
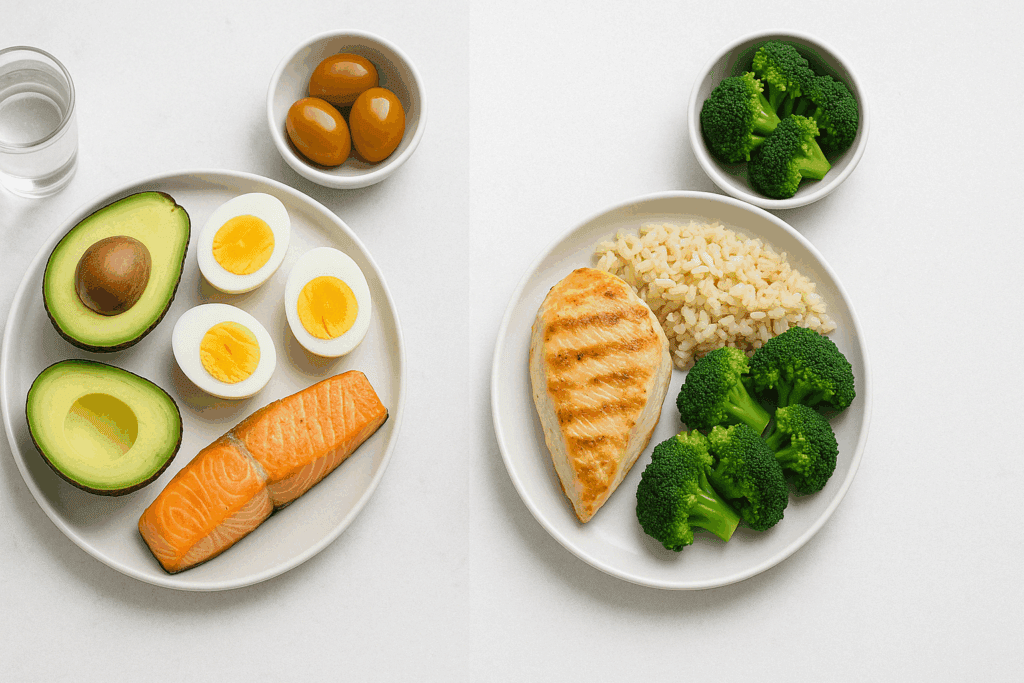
Frequently Asked Questions: Smart Bodybuilding Nutrition
1. How do bodybuilders adjust their diets during injury recovery periods?
Injury recovery is a crucial time when dietary needs shift, even for seasoned lifters. During recovery,bodybuilders focus on maintaining lean muscle without overloading on calories that can lead to fat gain due to reduced activity. Protein remains essential, but anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, berries, and leafy greens also become dietary staples. This is a time when what do body builders eat includes more collagen-rich broths, omega-3 fats from flax or walnuts, and micronutrients like zinc and vitamin C to support tissue healing. Understanding what does a bodybuilder eat when they’re not training intensively offers insight into how nutrition supports resilience, not just performance.
2. What role does gut health play in bodybuilding performance and recovery?
Gut health is an emerging pillar in athletic nutrition that is often overlooked. When considering whatdo body builders eat, many now include probiotic-rich foods such as fermented vegetables, kefir, or plant-based yogurts to enhance microbiome diversity. A healthy gut supports efficient nutrient absorption—vital when your body is under the stress of intense training. Chronic digestive inflammation can impair recovery, energy levels, and even sleep quality. For those following a bodybuilding diet for women, hormonal fluctuations can also influence digestion, making gut support even more critical.
3. Can bodybuilders maintain their physique on a fully plant-based diet?
Yes, but it requires thoughtful planning. What does a bodybuilder eat when following a plant-basedregimen? The meals include a wide variety of legumes, soy products, whole grains, seeds, and vegetables to ensure adequate protein and nutrient density. Plant-based athletes often rely on tools like nutritional yeast, pea protein, or hemp protein to boost intake. For women, a bodybuilding diet for women that is plant-based must pay extra attention to iron, B12, and calcium intake to maintain strength and hormonal balance. This approach proves that optimal physique and ethical eating can coexist with the right knowledge.
4. How does meal frequency affect hormone levels and metabolic health in bodybuilders?
The traditional six-meal-a-day strategy is not just about energy levels—it also has implications forhormones like insulin, cortisol, and ghrelin. When asking body builder how many meals do you eat, it’s clear that frequent feeding helps blunt cortisol spikes and prevent muscle catabolism. However, some bodybuilders are exploring intermittent fasting or time-restricted eating to optimize insulin sensitivity and digestive efficiency. For women, metabolic responses to fasting may vary based on menstrual cycle phases, making the bodybuilding diet for women uniquely nuanced. Ultimately, the impact of meal timing is both physiological and psychological.
5. What food strategies do competitive bodybuilders use to peak before a show?
Show prep involves extreme precision. What do body builders eat in the final week beforecompetition? Meals are meticulously planned to manipulate water retention, muscle fullness, and skin tightness. Carb-loading typically begins 48–72 hours prior to the event, favoring simple carbs like rice cakes, sweet potatoes, and low-fiber fruits. Sodium and water intake may also be adjusted under professional guidance. These practices differ dramatically from off-season habits and are never permanent. Understanding what does a bodybuilder eat in prep underscores the complexity of physique presentation.
6. How do bodybuilders manage cravings while cutting calories?
Cravings can derail progress, especially during fat loss phases. To manage them, what do bodybuilders eat to stay full includes high-volume, low-calorie foods like steamed vegetables, broth-based soups, and fibrous fruits. Sugar-free gelatin, frozen berries with Greek yogurt, and spiced herbal teas are popular go-to items. Strategically timing carb intake around workouts helps reduce energy dips that trigger emotional eating. For women navigating a bodybuilding diet for women, addressing cravings also involves recognizing the influence of the menstrual cycle and planning around it with foods that stabilize blood sugar and mood.
7. Are there psychological benefits to structured eating in bodybuilding?
Absolutely. The discipline required to follow a structured eating plan contributes to mental resilience,focus, and emotional regulation. Knowing exactly what do body builders eat throughout the day reduces decision fatigue and helps maintain consistency in training and recovery. The rhythm of meal prep and regular eating fosters a sense of control that can spill over into other areas of life. For women, the bodybuilding diet for women is often empowering, especially when it breaks free from diet culture and reframes food as fuel for strength and autonomy. Structured nutrition can thus be both a physical and emotional foundation.
8. How do travel and social events affect a bodybuilder’s nutrition plan?
Flexibility is key when routine is disrupted. Bodybuilders often travel with portable options like proteinpowders, nut butter packets, or pre-cooked rice and tofu to stay consistent. When dining out, what does a bodybuilder eat depends on the restaurant’s offerings—but grilled proteins, salad bars, and simple starches are generally safe bets. Planning ahead helps maintain macros without sacrificing enjoyment. For women especially, navigating social events while adhering to a bodybuilding diet for women requires communication, confidence, and compromise to uphold long-term goals.
9. What do advanced bodybuilders do differently with nutrition compared to beginners?
Advanced athletes track not only macronutrients but also meal timing, nutrient timing, hydration, andeven micronutrient absorption rates. When asked what do body builders eat at an elite level, the answer often includes customized supplementation, high-quality whole foods, and data-driven adjustments. They understand that digestion, stress, and sleep can influence how well nutrients are utilized. An experienced body builder how many meals do you eat is often followed by insights into insulin sensitivity, gut response, and anabolic signaling windows. For women, progressing from a basic to advanced bodybuilding diet for women means personalizing protocols to match evolving training intensity, life phase, and hormonal shifts.
10. How do bodybuilders maintain motivation to follow strict diets long-term?
Long-term adherence stems from deeper motivations than just aesthetics. Many athletes see nutritionas part of a broader philosophy of self-mastery, longevity, and personal growth. Knowing what do body builders eat is only part of the story—why they eat that way reveals a mindset rooted in purpose. Celebrating small wins, visualizing long-term goals, and staying connected to a community help sustain focus. For women especially, a bodybuilding diet for women that honors both performance and wellbeing creates a meaningful, sustainable path that evolves beyond the scale or stage.
The Bottom Line: What Do Body Builders Eat for Results and Longevity?
In navigating the question what do body builders eat to maximize their strength, lean mass, and wellness, the answer is grounded in thoughtful planning, nutrient-dense food, and individualized adjustments. From understanding how many meals bodybuilders eat per day to tailoring a bodybuilding diet for women, success lies in aligning food choices with goals, training demands, and personal lifestyle.
While macronutrients provide the framework, micronutrients, meal timing, and whole-food strategies bring it all together. Whether incorporating carbs strategically or exploring the nuances of the ketogenic diet vs low carb approaches, the smartest bodybuilders prioritize consistency, sustainability, and long-term health.
Is keto a good diet for everyone in the fitness community? Not necessarily. Is a keto diet sustainable for building mass? Only if it’s thoughtfully planned with adequate protein and strategic refeeding. Ultimately, the best diet is the one that supports your energy, performance, and recovery while promoting a healthier lifestyle that endures beyond the competitive season.
As you apply these expert-backed strategies to your own nutrition, remember: success in bodybuilding doesn’t come from fads or extremes—it comes from discipline, knowledge, and respect for your body’s needs. And whether you’re experimenting with s keto low carb approaches or building meals around whole plant foods, the most powerful gains come from a smart, science-backed foundation.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.

