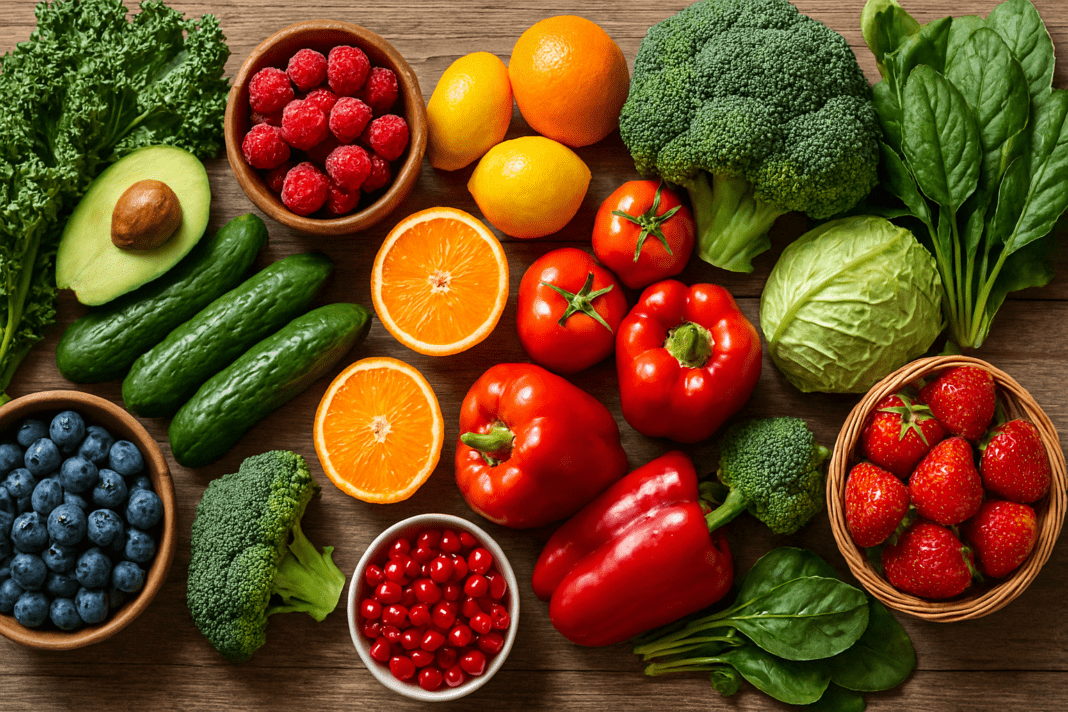
Understanding how to achieve sustainable weight loss remains one of the most frequently pursued goals in public health and individual wellness. As more individuals turn to natural, food-based strategies, the question arises: can fruits and vegetables truly support weight loss? The answer, supported by robust scientific evidence, is a resounding yes—when approached mindfully. For those exploring a whole-food, plant-based lifestyle or simply aiming to integrate more nutritious choices into their diet, identifying the best fruits and vegetables for weight loss is essential. Not only do these foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, but many also contain bioactive compounds that support metabolism and satiety, both crucial components in a successful weight loss strategy.
You may also like: Plant Based Diet vs Standard American Diet: What the Latest Studies Reveal About Long-Term Health Outcomes
Before diving into specifics, it’s worth recognizing the broader context: fruits and vegetables are low in energy density. This means they provide fewer calories per gram compared to calorie-dense processed foods. In turn, they allow people to eat satisfying portions while keeping overall calorie intake in check. Furthermore, their rich fiber content contributes to prolonged satiety, reduced hunger cravings, and improved digestion. For individuals wondering, “Is fruit good for weight loss?” or “Can eating fruit help you lose weight?” the evidence suggests that, when consumed as part of a balanced and mindful eating pattern, the answer is a definitive yes.

The Science Behind Weight Loss and Whole Plant Foods
Scientific studies consistently demonstrate that diets high in fruits and vegetables are associated with reduced body weight and decreased risk of obesity. This is not due to any magical property inherent in these foods but rather the synergistic effect of their low-calorie density, fiber content, phytochemicals, and water composition. When individuals focus on consuming more of the best fruits and veggies for weight loss, they naturally displace higher-calorie, nutrient-poor items from their diet.
Take, for instance, the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health’s analysis of diet patterns across thousands of individuals. Researchers found that people who increased their intake of fruits and non-starchy vegetables over time experienced less weight gain and, in many cases, actual weight loss. This research aligns with other findings that emphasize the metabolic benefits of fiber-rich foods. In particular, certain fruits good for fat loss, such as berries, apples, and citrus fruits, contain polyphenols and soluble fiber that can regulate blood sugar levels and support fat oxidation.
Among vegetables, the most promising for weight loss are those that are high in fiber but low in starch. These include leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower, and fibrous vegetables like celery and cucumber. When people ask, “What vegetables are good for weight loss?” or “What are the best veggies to eat to lose weight?” the answer lies in selecting those that offer both volume and nutritional density without contributing excessive calories.

Best Fruits to Eat for Weight Loss and Why They Work
Choosing the best fruits for weight loss involves more than just selecting low-calorie options. It’s also about understanding how different fruits interact with the body’s metabolic processes. For instance, apples and pears are not only low in calories but also high in pectin—a type of fiber that promotes satiety and slows gastric emptying. Studies have shown that participants who consumed apples regularly, as opposed to processed snacks of similar caloric value, experienced significant weight reductions.
Berries are another standout among fat burning fruits. Rich in antioxidants like anthocyanins and flavonoids, they help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. Their low glycemic index also means they cause minimal spikes in blood sugar levels, making them one of the healthiest fruits for weight loss. Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries can be incorporated into meals or enjoyed as standalone snacks, providing both flavor and functional benefits.
Citrus fruits—such as grapefruits, oranges, lemons, and limes—are also considered some of the best fruits to eat for weight loss. Grapefruit in particular has been shown to support weight loss when consumed before meals, possibly by reducing appetite and aiding in glucose metabolism. Additionally, the high water content in citrus fruits supports hydration, another factor that plays a role in fat metabolism and hunger regulation.
Bananas, often misunderstood in weight loss conversations due to their carbohydrate content, also deserve mention. When eaten in moderation, they offer resistant starch and potassium, aiding in digestive health and muscle function, especially important for those engaging in physical activity as part of their weight loss journey. For those who ask, “What are the fruits that make you lose weight?” the answer is not necessarily singular—rather, it’s the combination of nutrient density, fiber, and metabolic support that matters.
Vegetables That Promote Fat Loss and Satiety
While fruits get much of the spotlight, vegetables are equally vital in any evidence-based weight reduction plan. The best vegetables for weight loss typically fall into categories rich in fiber, water, and essential phytonutrients. Leafy greens—such as kale, spinach, arugula, and romaine—are virtually calorie-free but high in volume, making them excellent for increasing meal satisfaction without excess energy intake.
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage contain sulforaphane and other glucosinolates, compounds shown to support liver detoxification pathways and reduce systemic inflammation. These actions indirectly aid weight loss by promoting better hormonal balance and metabolic function. For those inquiring, “What are the best veggies to eat to lose weight?” cruciferous vegetables should be a central component of the answer.
Other notable vegetables include bell peppers, zucchini, cucumbers, and celery. These options are hydrating, crunchy, and naturally low in calories, making them ideal choices for snacking or incorporating into larger meals. Even when consumed in larger quantities, they contribute very little to daily caloric load while offering antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber that keep hunger at bay. These are exemplary weight reducing vegetables that deserve consistent inclusion in plant-based eating patterns.
It’s also important to discuss the role of legumes and starchy vegetables. While higher in calories and carbohydrates, foods like lentils, beans, and sweet potatoes provide substantial satiety due to their high fiber and protein content. For individuals seeking a more balanced approach that includes these items, portion control and timing (such as after exercise) can help optimize their benefits while still promoting weight loss.
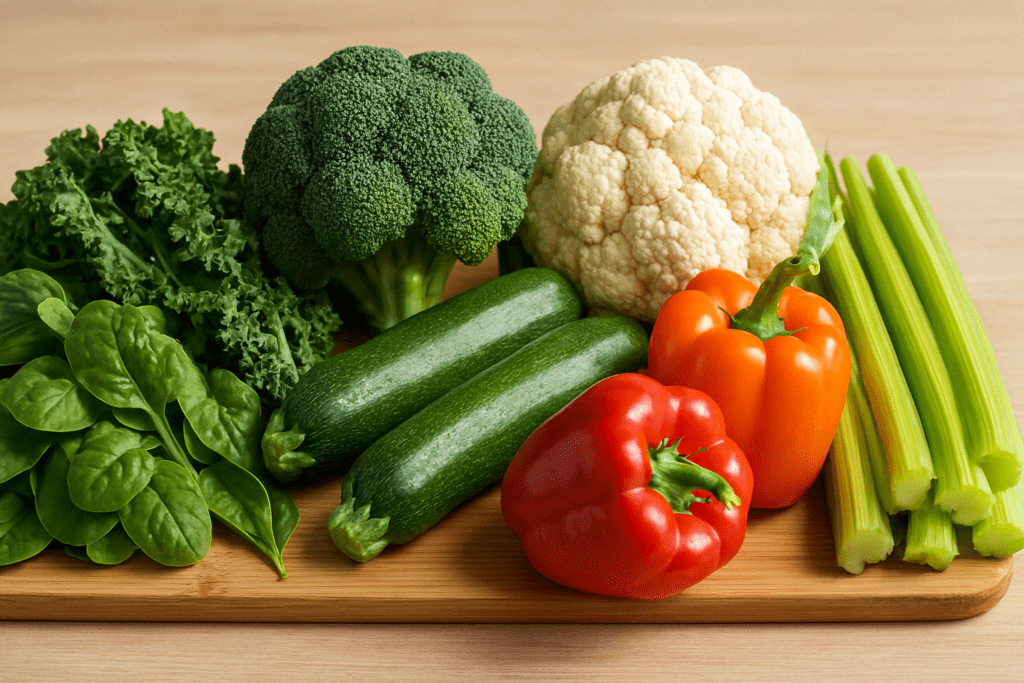

How Fiber from Fruits and Vegetables Enhances Weight Management
One of the primary mechanisms by which fruits and vegetables support weight loss is through their fiber content. Dietary fiber slows the rate of digestion, enhances feelings of fullness, and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, apples, berries, and citrus fruits, forms a gel-like substance in the gut that prolongs satiety and delays gastric emptying. This has direct implications for reducing calorie intake over the course of the day.
Insoluble fiber, present in vegetables like kale, carrots, and broccoli, adds bulk to the diet, promoting healthy bowel function and contributing to a sense of fullness. By supporting healthy digestion and minimizing constipation, these foods encourage a more efficient metabolism and may reduce abdominal bloating—a common concern during weight loss efforts.
Furthermore, fiber supports the gut microbiome. A healthy gut population enhances nutrient absorption and may influence weight through the production of short-chain fatty acids that regulate fat storage. For those wondering, “Can fruit help you lose weight?” or “Does fruit help you lose weight?” understanding the fiber connection is essential. It’s not just the caloric profile of fruit that matters—it’s also the structural properties of fiber that create lasting satiety and promote a healthy, sustainable eating pattern.
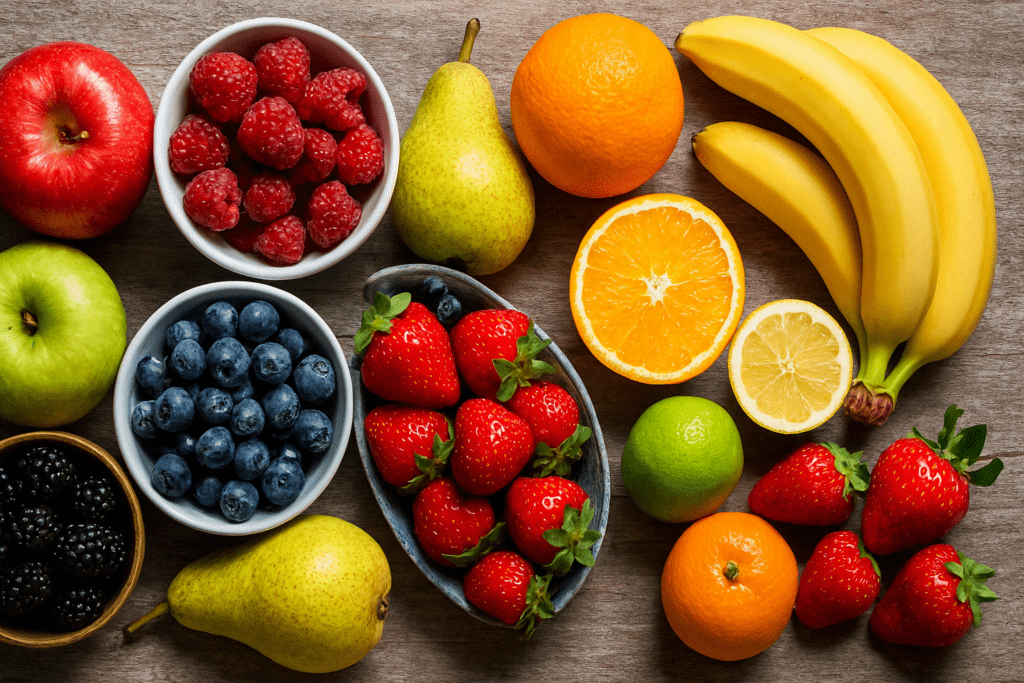

Addressing Common Myths: Can You Lose Weight Eating Fruit?
Many people encounter confusion around fruit consumption during weight loss, often fueled by fears about sugar content. However, it’s crucial to distinguish between the natural sugars found in whole fruits and the refined sugars present in processed foods. Whole fruits come packaged with fiber, water, and micronutrients that slow the absorption of sugars and moderate the body’s glycemic response.
Clinical research shows that moderate fruit intake is not associated with weight gain. In fact, increased fruit consumption has been linked to greater weight loss outcomes over time. This is especially true when fruit is used to replace calorie-dense snacks or desserts. For example, choosing an apple instead of a pastry provides fewer calories, more fiber, and longer-lasting satiety.
Concerns around fruits like bananas, grapes, or mangos are often exaggerated. While these fruits contain more natural sugars, they are still beneficial when included mindfully in the diet. The key lies in portion control and pairing—combining fruits with a small amount of healthy fat or protein can further blunt blood sugar spikes and improve satiety.
Ultimately, the question “Can u lose weight eating fruit?” must be answered with nuance. Yes, fruit for weight loss can be highly effective—but not in isolation. It should be part of a balanced, whole-food dietary pattern that includes a range of plant-based ingredients. Fruits that help in weight loss are not magical but are powerful when leveraged strategically within a broader context of lifestyle change.
Practical Strategies for Incorporating Weight Loss-Friendly Produce
Making fruits and vegetables a core part of one’s diet requires intention and planning, particularly for those transitioning from a more processed or animal-based pattern of eating. One effective approach is meal prepping, which ensures that vegetables are always readily available in the refrigerator and can be quickly added to meals. Roasting large batches of cruciferous vegetables or preparing mason jar salads filled with leafy greens and chopped produce helps support consistency.
Snacking habits can also be transformed by replacing chips and sugary snacks with carrot sticks, bell pepper slices, or apple wedges paired with almond butter. These changes, though seemingly small, have a cumulative effect over time. For anyone wondering about the best fruits and vegetables for weight loss, these habits offer a framework for real-world application that aligns with both nutritional science and behavioral psychology.
Smoothies are another practical vehicle for integrating nutrient-dense fruits. Combining spinach, frozen berries, a banana, and a tablespoon of chia seeds creates a filling, fiber-rich breakfast or post-workout meal. These combinations deliver fat burning fruits in a way that supports weight management while satisfying sweet cravings.
Dining out or ordering in doesn’t have to derail progress either. Choosing plant-forward options such as veggie bowls, grain salads, or stir-fries ensures that healthy fruits for weight loss and vegetables are still center stage. Making a habit of filling half your plate with non-starchy vegetables at every meal is a simple yet powerful tool for managing energy intake without feeling deprived.

Frequently Asked Questions: Fruits and Vegetables for Weight Loss
What makes certain fruits more effective for fat loss than others?
Fruits vary widely in their sugar, fiber, and phytochemical content, all of which influence their impact on weight management. The best fruits for weight loss are typically those that are lower in sugar, high in fiber, and rich in bioactive compounds like polyphenols. These characteristics help regulate insulin, curb hunger, and support metabolic function. Fat burning fruits such as berries, apples, and grapefruits work synergistically with the body to promote fat oxidation without adding excessive calories. When selecting fruits to lose weight, consider those with a lower glycemic index and high nutrient density to ensure long-term satiety and minimal blood sugar disruption.
How do vegetables contribute to long-term weight maintenance beyond calorie reduction?
Beyond their low-calorie content, the best vegetables for weight loss also provide prebiotic fiber that feeds beneficial gut bacteria. This microbial diversity can positively influence metabolic health, inflammation, and even cravings. Cruciferous vegetables, in particular, support detoxification processes in the liver, which can indirectly support fat loss by improving hormonal balance. Weight reducing vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts also promote thermogenesis, slightly increasing the energy cost of digestion. Incorporating these vegetables consistently can create an internal environment that favors healthy weight maintenance over time.
Can eating fruit really lead to measurable fat loss despite its sugar content?
Yes, and the key lies in the structure of whole fruit. Unlike refined sugars, the natural sugars in fruit are bound to fiber, slowing their absorption and preventing blood sugar spikes. When individuals ask, “Can eating fruit help you lose weight?” it’s crucial to highlight this distinction. In fact, several clinical studies have shown that those who consume more healthy fruits for weight loss, particularly those high in fiber, experience more sustainable fat loss. Fruit for weight loss becomes even more effective when used to replace processed snacks or desserts.
Is there a difference between fruits that help in weight loss and those that maintain energy during a calorie deficit?
Absolutely. While some fruits good for fat loss are optimized for reducing appetite and boosting metabolism, others provide sustained energy, making them suitable for pre-workout or afternoon consumption. Bananas, for instance, may not be the best fruit for losing weight in a calorie-restricted sense, but their potassium and resistant starch make them excellent for endurance and recovery. Meanwhile, the best fruits for diet variety include citrus, kiwi, and melon, which offer hydration and micronutrient support during caloric deficits. Tailoring fruit choices to your energy demands can improve both adherence and performance during a weight loss phase.
Which vegetables should I avoid if I’m aiming for rapid weight loss?
While no vegetable is inherently “bad,” some may be less effective in the early stages of weight loss due to their higher starch or caloric content. Vegetables like corn, peas, and white potatoes, though nutritious, are more calorie-dense and may not deliver the same satiety per calorie as leafy greens or cruciferous vegetables. For those wondering what vegetables are good for weight loss, focusing on non-starchy, water-rich vegetables is ideal. These options are often the best greens to eat to lose weight, helping reduce total energy intake while still providing critical nutrients. It’s not about restriction but rather about prioritizing foods that support your current goals.
How do fruits and vegetables interact with hormones that regulate hunger and metabolism?
Fruits and vegetables play a vital role in modulating hormones like leptin, ghrelin, and insulin. Soluble fiber found in many fruits that can burn fats—such as oranges and berries—slows gastric emptying, which helps signal fullness to the brain. Simultaneously, fiber reduces the secretion of ghrelin, the hormone responsible for hunger, while stabilizing insulin levels. This hormonal harmony is essential for those looking to consume the best fruits and veggies for weight loss without experiencing intense cravings. Additionally, certain phytochemicals in cruciferous vegetables may influence estrogen metabolism, further supporting hormonal balance in weight management.
Are there any new or underrated produce items showing promise in weight loss research?
Yes, recent studies have highlighted emerging options such as sea vegetables, jicama, and jackfruit. Sea vegetables like kelp contain fucoxanthin, a compound shown to promote fat metabolism in preliminary studies. Jicama is high in inulin, a type of prebiotic fiber that supports gut health and reduces appetite. These lesser-known options may not yet be household staples but are proving to be among the best fruits and vegetables for weight loss based on their functional properties. As research continues, these innovative additions offer exciting new avenues for people seeking fruits that help in weight loss and vegetables that optimize digestion and fat burning.
How does the timing of fruit and vegetable intake affect weight loss outcomes?
Timing can subtly enhance or hinder the effectiveness of food and fruits for weight loss. Eating fruits earlier in the day may provide energy while giving your body more time to metabolize natural sugars. Conversely, consuming high-fiber vegetables with dinner can promote satiety and reduce nighttime snacking. For optimal results, distribute your intake of the healthiest fruits for weight loss and the best vegetables for weight loss evenly across meals. This practice helps regulate appetite hormones and sustains metabolic rhythm throughout the day, supporting a more balanced and consistent approach to fat reduction.
How can fruits and vegetables be used to overcome emotional eating patterns?
Emotional eating is often driven by a need for comfort or distraction rather than genuine hunger. Integrating fruit for weight loss into mindful eating practices can create positive emotional associations with nourishment. Preparing aesthetically pleasing fruit bowls or vibrant vegetable-based dishes can elevate the sensory experience and shift emotional responses toward healthier choices. Fruits good for fat loss, like kiwi or watermelon, also offer a natural sweetness that can satisfy cravings without derailing progress. By consistently choosing fruits to lose weight during emotional triggers, individuals can gradually rewire their behavior and develop a more intuitive relationship with food.
What are some practical shopping strategies to support consistent fruit and vegetable consumption for weight loss?
Successful integration of the top fruits and vegetables for weight loss starts at the grocery store. Begin by shopping the perimeter, where fresh produce is typically located, and plan meals around seasonal availability to maximize freshness and nutritional value. Keeping a diverse supply of frozen options can also ensure that fruits that can burn fats and weight reducing vegetables are always accessible, even during busy weeks. Make a habit of preparing grab-and-go containers of pre-cut produce to reduce the friction of healthy snacking. With a little forethought, maintaining a supply of the best fruits to eat for weight loss and what are the best veggies to eat to lose weight becomes second nature, reinforcing consistency and long-term success.
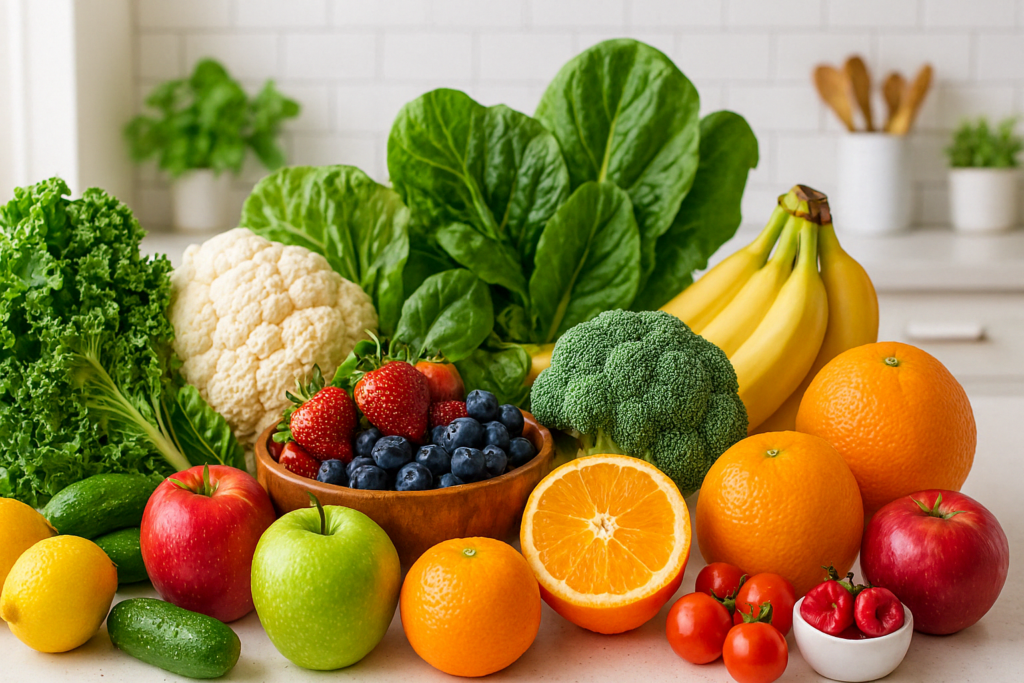

Reflecting on Results: Why Choosing the Right Fruits and Vegetables Matters
In the pursuit of healthy, lasting weight loss, it’s not just about reducing calories—it’s about nourishing the body in ways that support metabolism, satisfaction, and long-term wellness. Fruits to lose weight are abundant, but their true value lies in how they’re incorporated into daily habits. Likewise, selecting the best greens to eat to lose weight means prioritizing nutrient density and culinary versatility.
Research supports the idea that food and fruits for weight loss, when consumed in their whole, unprocessed forms, provide more than just energy—they offer a therapeutic synergy of fiber, water, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds. These elements work together to reduce inflammation, balance blood sugar, and encourage fat loss. Choosing the best fruit for losing weight is not about demonizing other foods but about emphasizing those that contribute positively to both satiety and metabolic health.
The most successful and sustainable approaches to weight loss are those grounded in evidence, mindfulness, and personalization. While the science points us toward specific fruits good for fat loss and weight reducing vegetables, it is our daily habits that transform this knowledge into meaningful results. For anyone asking, “Does eating fruit help you lose weight?” or “What fruit is good to lose weight?” the answer is not only yes—but also that how, when, and why you eat matters just as much.
Embracing fruits that can burn fats and vegetables that reduce cravings isn’t just about numbers on a scale. It’s about building a relationship with food that prioritizes nourishment, vitality, and sustainability. In this way, the top fruits and vegetables for weight loss become more than diet tools—they become allies in a lifelong journey toward better health.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
8 Best Foods to Eat for Weight Loss
Which fruits and vegetables are best for weight loss?
15 Healthy Foods to Lose Weight Efficiently; Backed By Science
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.

