Understanding the Importance of Early Detection and Preventive Wellness
In the complex landscape of modern healthcare, the question arises again and again: how can we prevent illness before it begins? As medical science advances and public health strategies evolve, the focus has increasingly shifted toward early detection and prevention as cornerstones of sustainable well-being. Rather than waiting for disease to manifest and then reacting, we now have the tools and knowledge to anticipate health risks and intercept them before they escalate. This proactive approach not only improves quality of life but also reduces the strain on healthcare systems worldwide. Recognizing symptoms in their earliest stages, employing targeted screening tools, and cultivating daily habits that bolster the body’s defenses are all part of this essential health paradigm.
From chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes to infectious illnesses and cancers, early detection can dramatically alter outcomes. Advances in genetics, wearable technology, and diagnostic imaging have made it possible to foresee and forestall disease in ways unimaginable just a few decades ago. But while technology plays a role, prevention also lies in everyday choices: nutrition, exercise, sleep, and stress management all influence our susceptibility to illness. By examining both clinical innovations and lifestyle strategies, we can begin to fully answer the question: how can we prevent illness before it takes root?
You may also like: The Vital Health Benefits of Preventive Medicine: Why Early Detection Matters More Than Ever
How Can We Prevent Illness Through Proactive Screening?
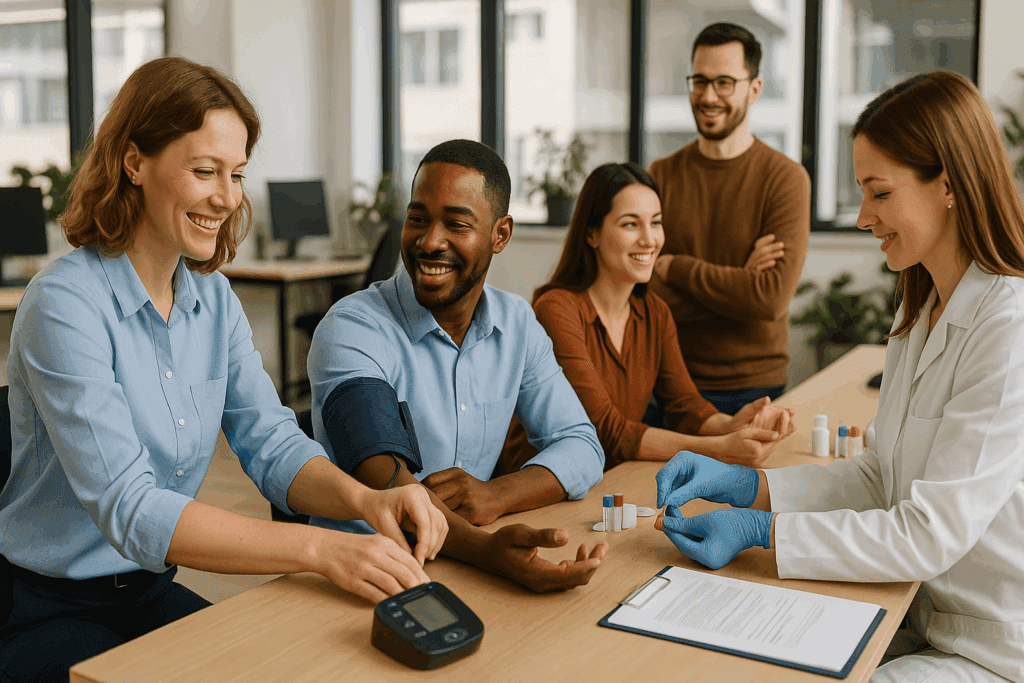
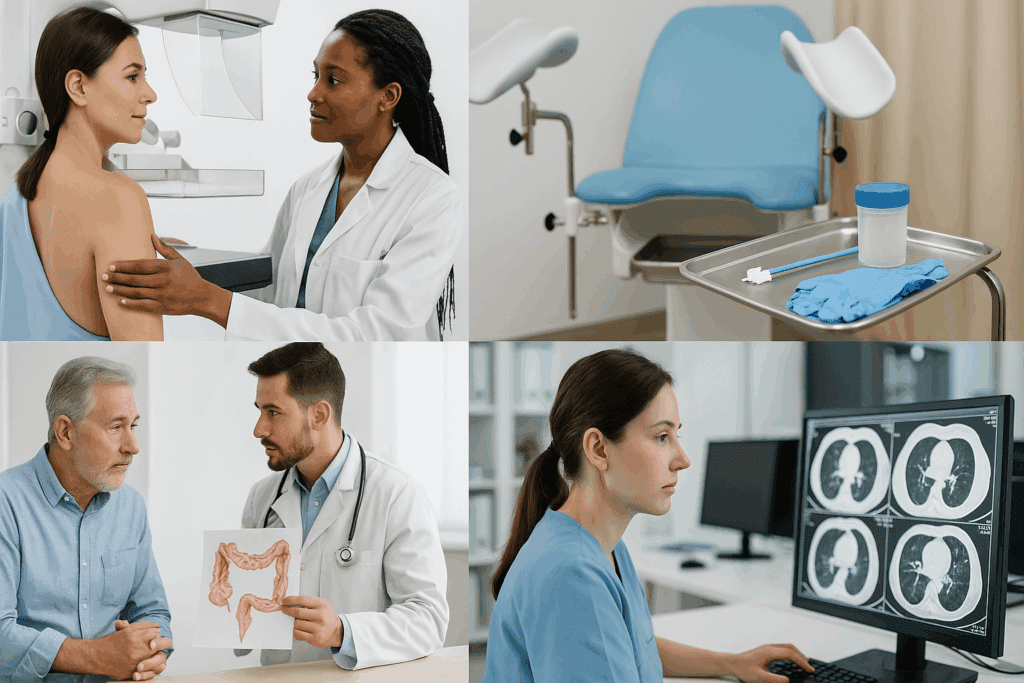
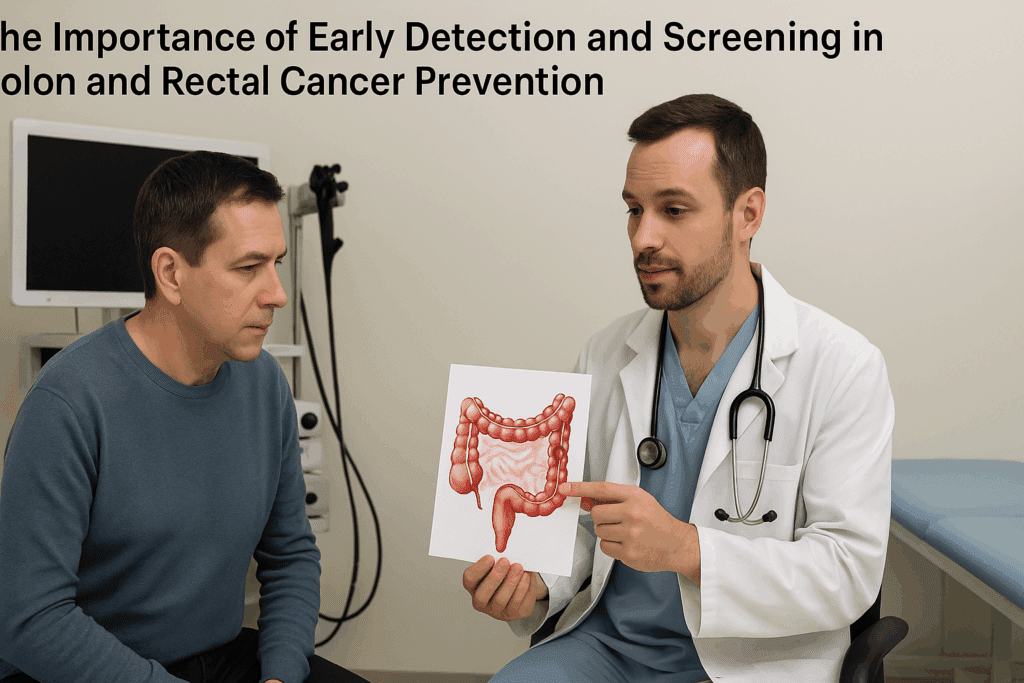
Screening is one of the most powerful tools in our prevention arsenal. Unlike diagnostic tests, which confirm the presence of disease after symptoms arise, screening tests aim to detect disease in asymptomatic individuals. Their value lies in identifying conditions at an early, often more treatable stage. For example, routine mammograms have been instrumental in reducing breast cancer mortality, and colonoscopies have significantly decreased colon cancer rates in populations adhering to recommended screening guidelines.
A key component of effective screening is risk stratification. Not every individual needs the same screening tests at the same intervals. Age, family history, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions all influence risk profiles. For instance, individuals with a family history of cardiovascular disease may benefit from earlier cholesterol monitoring, while those with BRCA gene mutations may require enhanced surveillance for breast and ovarian cancer. Personalized screening protocols enhance efficiency and reduce unnecessary procedures.
Moreover, public health initiatives have made screening more accessible and widespread. Mobile screening units, telemedicine consultations, and community health programs have removed many barriers to early detection. For underserved communities, this shift is crucial, as it bridges the gap between diagnosis and care. Digital tools and AI-powered algorithms are further refining the accuracy of screening by analyzing patterns invisible to the human eye. From retinal scans that detect diabetic complications to machine-learning models predicting stroke risk, screening is evolving into a predictive science.

The Role of Lifestyle in Answering How Can We Prevent Illness
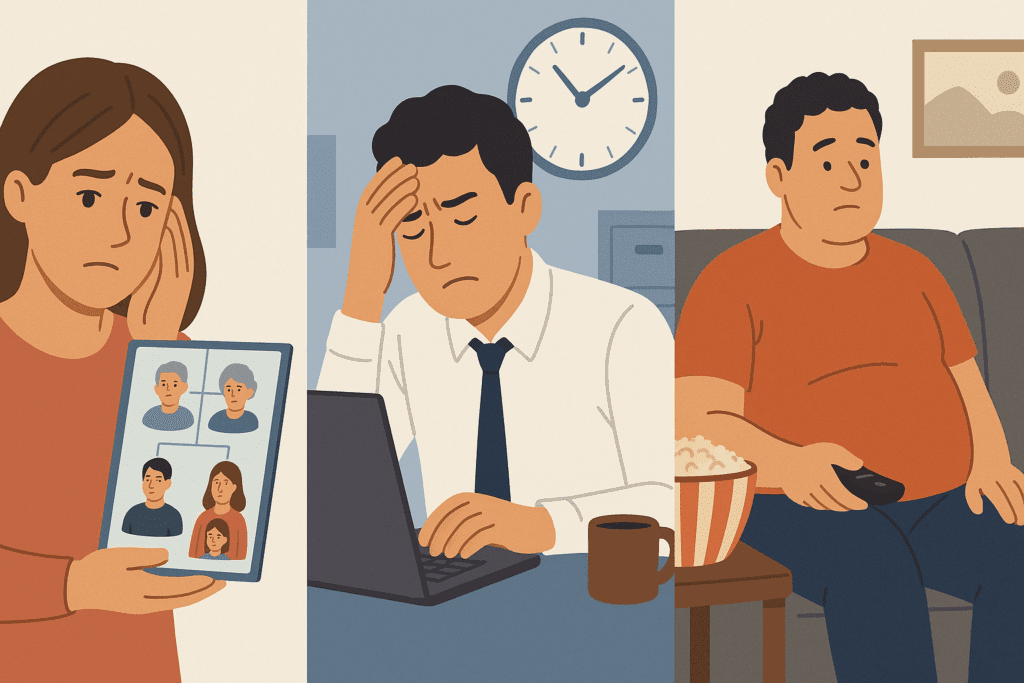
Beyond medical screenings, everyday lifestyle choices are fundamental in preventing illness. Chronic diseases, which account for the majority of healthcare costs and mortalities globally, are heavily influenced by behaviors that are modifiable. Tobacco use, sedentary behavior, poor nutrition, and excessive alcohol consumption are known risk factors that, when addressed, can significantly reduce disease incidence.
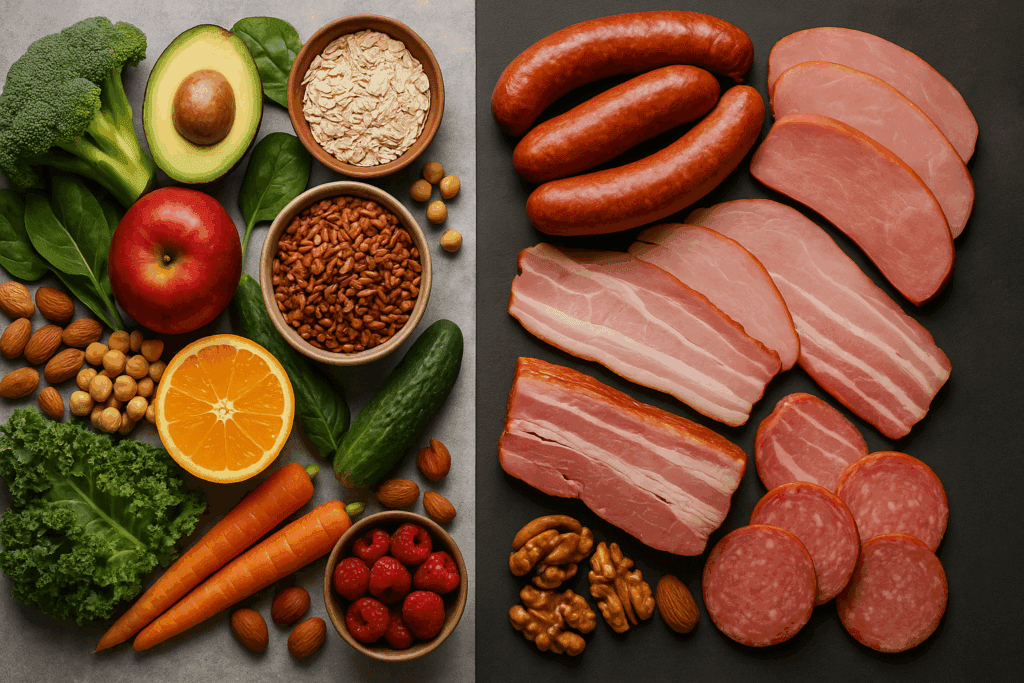
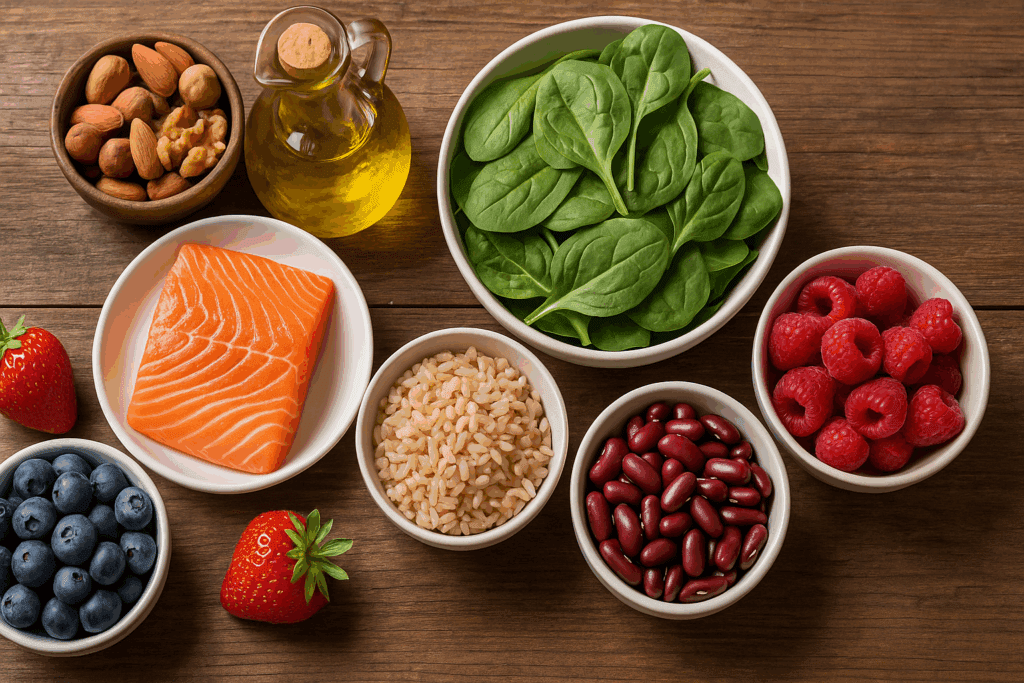
Nutrition is a particularly potent preventive force. Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains have been shown to reduce the risk of hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers. Conversely, high consumption of processed foods and added sugars correlates with metabolic disorders and inflammation. Gut health, now recognized as central to immunity and mental wellness, can be supported through prebiotic and probiotic foods, adequate fiber intake, and limited use of antibiotics.
Physical activity is another pillar of wellness. Regular movement not only strengthens the cardiovascular system but also improves insulin sensitivity, mental health, and sleep quality. Even moderate daily activity, such as walking or yoga, has measurable health benefits. Incorporating movement into daily routines—through active commuting, standing desks, or family exercise time—can make a lasting impact.
Stress management and sleep hygiene round out the lifestyle triad. Chronic stress contributes to inflammation, hormonal imbalance, and weakened immunity, all of which raise disease vulnerability. Sleep deprivation, similarly, disrupts cellular repair and cognitive function. Techniques like mindfulness meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and consistent sleep schedules offer preventive benefits as significant as those achieved through diet and exercise.
Genetic Testing and Personalized Prevention: How Can We Prevent Illness at the Molecular Level?
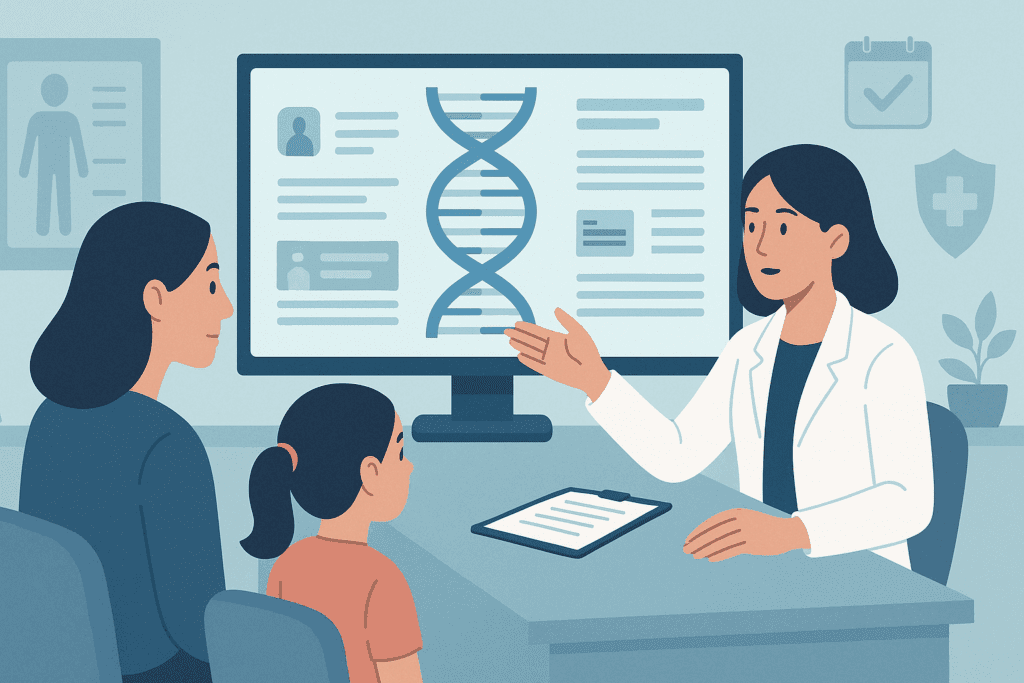
Genomic medicine has opened a new frontier in personalized prevention. By analyzing an individual’s DNA, clinicians can identify inherited risks for a wide array of conditions. These insights inform not only which screening tests are necessary but also when they should begin and how frequently they should be administered. For example, individuals with Lynch syndrome may begin colonoscopy screening decades earlier than the general population.
Pharmacogenomics, a subfield of genetic testing, predicts how a person will respond to certain medications, thereby optimizing treatment and minimizing adverse effects. This approach reduces trial-and-error prescribing and enhances treatment adherence. Meanwhile, nutrigenomics explores the interaction between genes and nutrients, offering tailored dietary recommendations that align with one’s genetic makeup.
Despite its promise, genetic testing requires careful interpretation and ethical oversight. Not all gene variants confer the same level of risk, and the presence of a mutation does not guarantee disease. Genetic counseling is essential to help individuals understand their results and make informed decisions. Confidentiality, insurance discrimination, and psychological stress are also considerations that must be addressed.
Nevertheless, integrating genetic data into primary care holds enormous potential. With proper infrastructure and education, we can move toward a model of precision prevention, where interventions are as individualized as the patients receiving them. This molecular-level insight adds a new layer of depth to the question: how can we prevent illness with the information encoded in our genes?
Community Engagement and Public Health: Scaling the Prevention Paradigm
While individual efforts are critical, the role of community-level interventions in disease prevention cannot be overstated. Public health programs have successfully reduced rates of infectious diseases, improved maternal outcomes, and increased life expectancy through targeted campaigns and systemic changes. Vaccination initiatives, clean water access, and health education are foundational examples.
Community health workers (CHWs) serve as vital links between medical systems and the populations they serve. By providing culturally competent education, conducting screenings, and facilitating access to care, CHWs enhance engagement and trust, especially in marginalized groups. Their role is particularly important in addressing social determinants of health, such as income, housing, education, and food security, which strongly influence disease risk.
School-based health programs also contribute significantly to early detection. Routine vision and hearing screenings, mental health assessments, and nutrition monitoring in children provide early warning signs that can be addressed before they lead to chronic issues. Moreover, these programs instill lifelong habits, teaching children the importance of hygiene, nutrition, and physical activity.
Public policy shapes the environment in which prevention operates. Urban planning that supports walkability, legislation that restricts tobacco use, subsidies for healthy foods, and mandates for workplace wellness programs are all policy-level interventions that affect population health. The interplay between government action and community involvement creates a fertile ground for sustainable wellness.

Digital Health Innovations: A New Frontier in Preventive Care
The digital revolution has transformed how we monitor and manage health. Wearable devices, mobile apps, and telehealth platforms empower individuals to track vital signs, receive personalized recommendations, and consult providers from anywhere in the world. These technologies democratize access to preventive care, especially for those in remote or underserved regions.
Fitness trackers monitor activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns, encouraging users to meet wellness goals and alerting them to anomalies that may warrant further evaluation. Smartwatches with ECG capabilities have already identified cases of atrial fibrillation in users without symptoms, prompting early medical intervention. Meanwhile, mobile applications can remind users to take medications, schedule screenings, or perform self-examinations.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being increasingly employed to analyze large datasets for early warning signs of disease. AI can identify patterns in medical images, flagging tumors or abnormalities at their earliest stages. Algorithms also aid in predicting outbreaks, allocating resources, and stratifying patient risk, all of which support preventive strategies on both individual and systemic levels.
Telemedicine facilitates timely consultations, reducing the delay between symptom onset and evaluation. In chronic disease management, virtual check-ins enhance adherence and allow for swift adjustments to treatment plans. These interactions can be life-changing for patients with mobility challenges, time constraints, or limited transportation.
While technology offers immense promise, it must be paired with digital literacy and data privacy safeguards. Equitable access to digital tools remains a challenge, and efforts must be made to ensure that innovations do not widen existing health disparities. Still, as digital health evolves, it will play a central role in answering how can we prevent illness with greater speed, accuracy, and inclusivity.
How Can We Prevent Illness by Addressing Environmental and Occupational Risks?
The environments in which we live and work exert profound influence on our health. Air and water quality, exposure to toxins, noise levels, and even the design of our physical spaces all play roles in disease development. Addressing these environmental determinants is essential to a comprehensive prevention strategy.
Air pollution has been linked to respiratory and cardiovascular conditions, particularly in urban centers with high vehicular and industrial emissions. Reducing exposure through policy interventions, such as clean air regulations and emission controls, has demonstrable health benefits. On an individual level, using air purifiers, avoiding outdoor activity during high pollution days, and supporting sustainable transportation can mitigate risk.
In the workplace, occupational hazards range from chemical exposure to ergonomic strain and psychological stress. Preventive strategies include regular safety audits, provision of protective equipment, and employee wellness programs. For example, shift workers are at increased risk for circadian rhythm disorders; targeted interventions like scheduled lighting and sleep hygiene education can help mitigate this risk.
The concept of “healthy buildings” is gaining traction, with architects and urban planners designing spaces that promote airflow, natural light, and physical activity. Green spaces, walking paths, and noise buffers are not merely aesthetic but functional tools in disease prevention. Schools and offices that prioritize these features report improved attendance, productivity, and health outcomes.
Waterborne diseases remain a concern in many regions, underscoring the need for clean drinking water, sanitation infrastructure, and public education. Preventing outbreaks of diseases such as cholera or hepatitis A hinges on these fundamental resources. Environmental health is not an ancillary consideration; it is integral to understanding how can we prevent illness by shaping the world around us.
How to Prevent Diseases Through Immune System Optimization
The immune system is our body’s frontline defense against pathogens and abnormal cells. Supporting immune resilience is a cornerstone of preventive health. Though immunity is influenced by genetics, a variety of modifiable factors can enhance or impair its function.
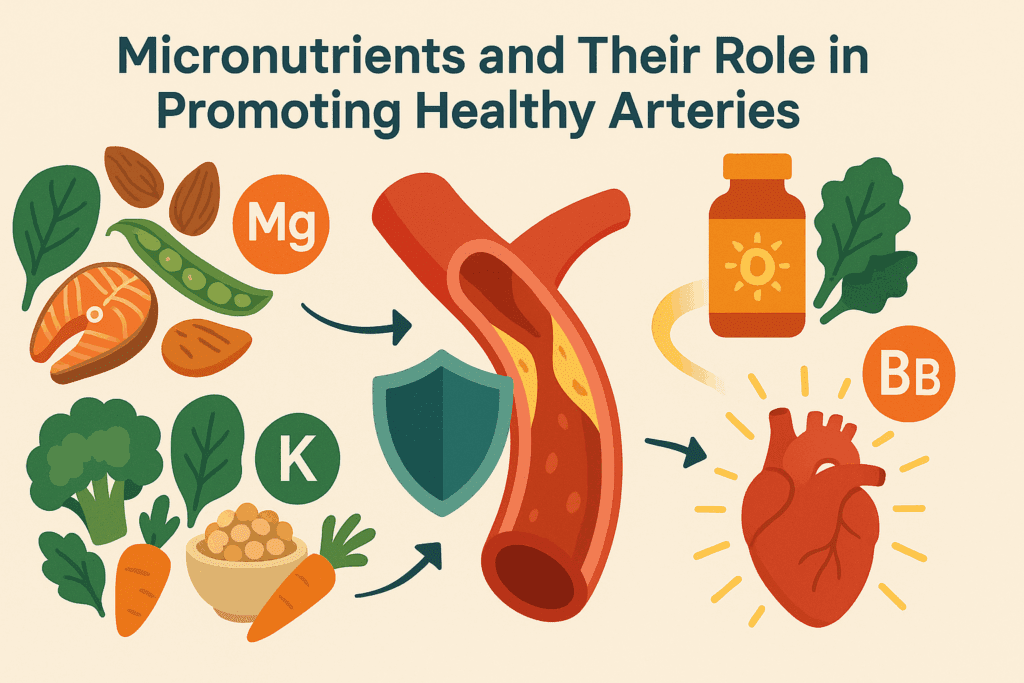
Nutrition plays a vital role in immune performance. Deficiencies in vitamins A, C, D, and E, as well as zinc and selenium, are associated with impaired immunity. Diets rich in colorful fruits, vegetables, nuts, and lean proteins supply the necessary micronutrients for robust immune responses. Fermented foods, including yogurt, kefir, and kimchi, also support the gut microbiota, which in turn modulates immune activity.
Regular physical activity improves circulation, supports lymphatic drainage, and reduces systemic inflammation. These effects enhance immune surveillance and the body’s ability to respond to threats. However, overtraining without adequate recovery can suppress immunity, illustrating the need for balance.
Sleep is another critical component. During sleep, the body produces cytokines that regulate immunity and reduce inflammation. Chronic sleep deprivation diminishes the production of these protective proteins, making individuals more susceptible to infection. Establishing consistent sleep routines and minimizing blue light exposure in the evening are simple yet powerful preventive measures.
Stress, particularly chronic psychological stress, has a well-documented suppressive effect on immune function. Cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, interferes with the production of infection-fighting white blood cells. Mind-body interventions, including meditation, biofeedback, and even laughter therapy, have demonstrated immune-boosting effects in clinical studies. By understanding how to prevent diseases through immune optimization, individuals can take proactive steps to fortify their internal defenses.

How Can We Prevent Illness in the Context of Aging and Longevity?
As populations around the globe age, prevention strategies must adapt to meet the needs of older adults. Aging is associated with increased risk for chronic diseases, cognitive decline, and frailty, but these outcomes are not inevitable. Early detection and targeted interventions can maintain function and independence well into advanced age.
Preventive care in older adults includes regular screenings for bone density, vision, hearing, and cognitive function. Early detection of osteoporosis, glaucoma, and mild cognitive impairment allows for interventions that delay or prevent progression. Vaccinations, including flu, shingles, and pneumonia, are particularly important in this demographic, reducing the burden of infectious diseases.
Nutrition in older adults requires special consideration, as appetite and nutrient absorption may decline with age. Ensuring adequate intake of protein, calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins supports muscle mass, bone health, and neurological function. Dietitians play a key role in designing meal plans that are both nutrient-dense and palatable for this population.
Physical activity remains vital. Resistance training can combat sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss), while balance exercises reduce fall risk. Even light activity, such as gardening or tai chi, contributes to overall wellness. Social engagement also serves a preventive function, reducing the risk of depression and cognitive decline.
By reframing aging as a phase of potential rather than decline, and by implementing strategic early interventions, we extend not only lifespan but healthspan—the period of life spent in good health. This shift in perspective is crucial in addressing how can we prevent illness across the lifespan.
The Path Forward: How Can We Prevent Illness Through a Holistic, Integrated Approach?
Preventing illness requires more than isolated actions; it demands a holistic, integrated strategy that bridges clinical medicine, public health, lifestyle, technology, and community engagement. The interplay between these domains creates a dynamic framework in which prevention can thrive.
Healthcare systems must prioritize preventive services, incentivizing screenings, wellness visits, and risk assessments. Insurance coverage for such services encourages participation and reduces downstream costs. Medical education should emphasize preventive care, equipping providers with the tools to counsel patients effectively.
Individuals must be empowered with knowledge and resources to take charge of their health. Health literacy campaigns, patient portals, and community programs can demystify prevention and make it accessible to all. At the same time, systemic barriers—such as inequities in access, education, and income—must be dismantled to ensure that prevention is not a privilege but a right.
Technology must be leveraged thoughtfully, with attention to data privacy, accessibility, and user-friendliness. Innovations should complement, not replace, the human touch that is essential in healthcare. Collaboration among stakeholders—governments, healthcare providers, educators, and citizens—is key to sustaining momentum.
Ultimately, the answer to how can we prevent illness lies not in a single intervention, but in the collective will to prioritize health before disease. It is a journey of awareness, action, and adaptability—one that promises a future in which well-being is the rule, not the exception.
Frequently Asked Questions: Expanding the Conversation on Early Detection and Prevention
How Can We Prevent Illness Through Mental and Emotional Health Strategies?
Mental and emotional well-being are often overlooked in discussions of disease prevention, yet their impact on physical health is profound. Chronic stress, anxiety, and unresolved emotional trauma can weaken the immune system, disrupt hormonal balance, and increase susceptibility to inflammatory diseases. Mind-body techniques like mindfulness meditation, guided imagery, and progressive muscle relaxation have been shown to lower cortisol levels and reduce systemic inflammation. Building emotional resilience through social support, journaling, and therapy not only improves mental outlook but fortifies the body’s natural defenses. Integrating mental health as a core component of wellness offers a more holistic approach to answering how can we prevent illness beyond traditional medical interventions.
How Can We Prevent Illness in the Workplace Without Sacrificing Productivity?
Workplaces can either support or sabotage our health, depending on their design, culture, and policies. Preventing illness at work requires reimagining productivity to include wellness as a foundational goal. Flexible scheduling, mental health days, ergonomic workspaces, and access to fresh air and natural light all reduce absenteeism and presenteeism. Providing on-site fitness classes, standing desks, and healthy meal options can significantly improve cardiovascular and metabolic markers over time. Encouraging open communication about burnout and offering mental health resources help create a psychologically safe environment. The key to how can we prevent illness in occupational settings lies in aligning organizational efficiency with human sustainability.
What Role Does Preventive Dentistry Play in Long-Term Health?
Oral health is intimately connected to systemic health, yet dental care is often treated as separate from medical care. Gum disease has been linked to increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes due to the inflammatory burden it places on the body. Regular dental cleanings, flossing, and fluoride treatments are essential for preventing oral infections that can spread beyond the mouth. Additionally, early detection of issues like bruxism or oral cancer during dental visits can lead to timely interventions that save lives. Incorporating preventive dentistry into broader health strategies is a critical but frequently neglected dimension of how to prevent diseases holistically.
How to Prevent Diseases in Children Beyond Vaccinations and Diet?
While vaccinations and balanced nutrition are foundational, disease prevention in children also involves cultivating lifelong habits and environmental awareness. Encouraging outdoor play supports immune development, motor coordination, and mental health. Teaching children proper handwashing, dental hygiene, and the importance of regular sleep routines instills autonomy over their well-being. Reducing exposure to environmental toxins like BPA, lead, and secondhand smoke protects developing systems from long-term harm. Early interventions in speech and developmental delays also prevent compounding issues later in life. To truly understand how to prevent diseases in the pediatric population, we must think beyond episodic care and adopt a long-term, developmental perspective.
How Can We Prevent Illness by Rethinking Social Determinants of Health?
Health outcomes are not shaped solely by biology but also by where we live, work, and grow. Social determinants like access to education, clean air, safe housing, and nutritious food dramatically influence the prevalence of disease. Communities with higher poverty rates often experience higher burdens of asthma, obesity, and depression. Addressing these upstream factors requires policy reforms, community engagement, and cross-sector collaboration. For instance, urban farming initiatives have reduced food deserts, and transportation subsidies have improved access to healthcare for underserved populations. If we’re serious about answering how can we prevent illness, we must invest in equity as a public health strategy.
Can Art and Music Therapy Help Prevent Illness in Vulnerable Populations?
Creative therapies are gaining recognition not just for treatment but also for their preventive potential, especially in vulnerable groups like the elderly or those with chronic stress. Music therapy has been shown to reduce anxiety, improve memory in dementia patients, and decrease cortisol levels. Art therapy helps individuals process trauma, manage emotions, and foster social connection. These therapies stimulate neuroplasticity, which strengthens the brain’s adaptability and resilience. When integrated into community health programs, creative therapies offer non-pharmacological ways to enhance well-being and reduce reliance on conventional medications. In this context, how can we prevent illness becomes a question of cultivating joy, expression, and meaning.
How to Prevent Diseases in an Era of Antibiotic Resistance?
Antibiotic resistance poses a growing threat to global health, making prevention more critical than ever. Avoiding unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions, particularly for viral infections, is essential to slowing resistance. Educating patients about completing full courses and not demanding antibiotics for colds also plays a role. Hospitals and clinics must prioritize infection control through stringent hygiene protocols and antimicrobial stewardship programs. On a personal level, boosting immune resilience through nutrition, vaccination, and hygiene can reduce reliance on antibiotics altogether. As resistance rises, learning how to prevent diseases before they require treatment becomes a moral and medical imperative.
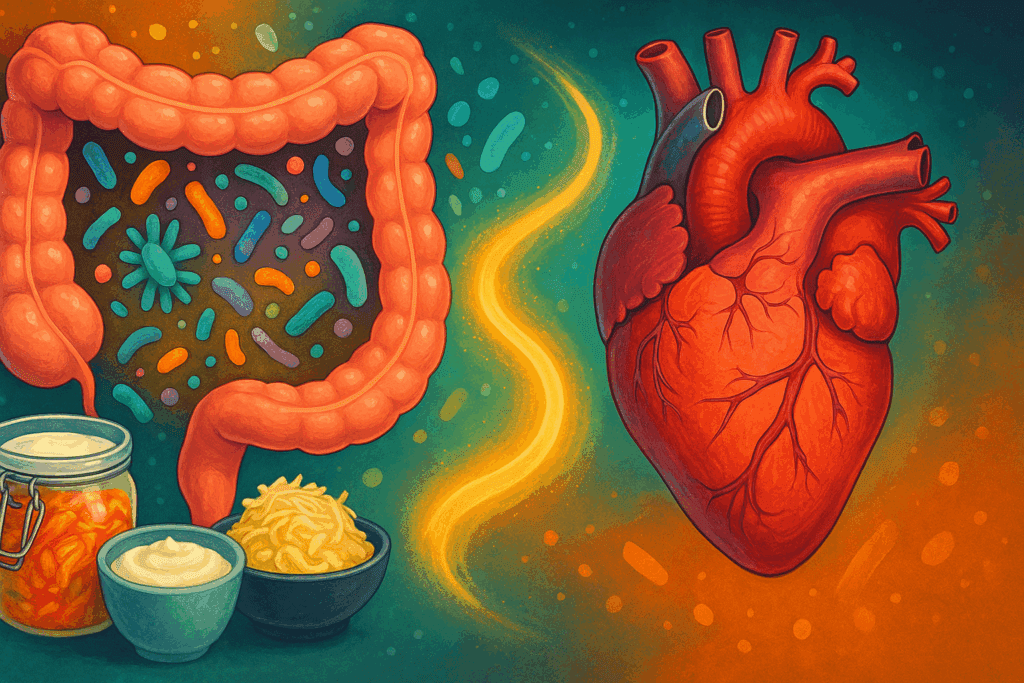
How Can We Prevent Illness by Supporting Microbiome Diversity?
Emerging research underscores the importance of a diverse gut microbiome in preventing a wide range of diseases, from autoimmune disorders to depression. Diets rich in fiber, polyphenols, and fermented foods support microbial diversity, which in turn influences immune regulation and nutrient absorption. Avoiding unnecessary antibiotics and artificial sweeteners can also preserve microbial balance. Fecal microbiota transplantation, though still experimental for most uses, offers a glimpse into future therapies rooted in microbial health. Understanding the symbiotic relationship between humans and their internal ecosystems reveals new insights into how can we prevent illness by nurturing our invisible allies.
What Are the Best Strategies for How to Prevent Diseases While Traveling?
Travel exposes individuals to unfamiliar pathogens, climate conditions, and dietary changes, all of which can compromise immunity. Strategies for prevention include pre-travel vaccinations, use of water purification tablets, and carrying a personalized travel health kit with medications and first aid essentials. Avoiding raw foods and undercooked meats in high-risk areas helps reduce gastrointestinal infections. Jet lag can impair immunity, so adjusting sleep cycles before departure and staying hydrated during flights is important. Understanding destination-specific risks and consulting a travel medicine specialist can dramatically increase the safety and enjoyment of international trips, demonstrating practical, scenario-based solutions for how to prevent diseases abroad.
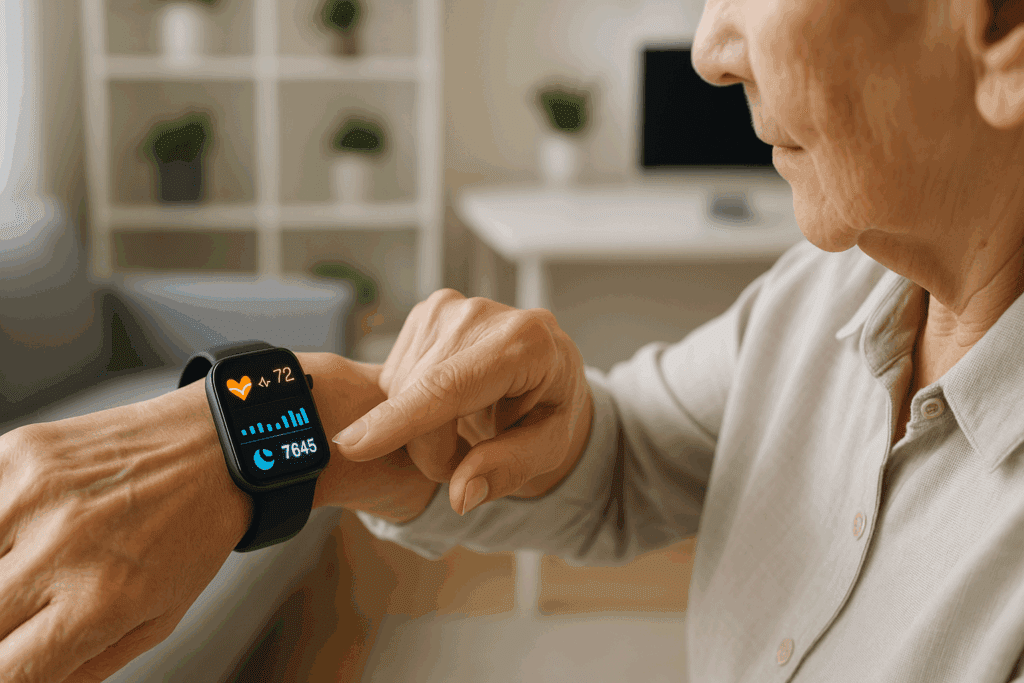
How Can We Prevent Illness With Innovative Wearable Tech and Health Forecasting?
Today’s wearable technology is evolving beyond fitness tracking into real-time health forecasting. Devices can now monitor blood oxygen levels, sleep cycles, arrhythmias, and even blood glucose trends noninvasively. Future innovations may include sweat-based hormone sensors and integrated AI capable of detecting subtle physiological changes before symptoms arise. These devices allow for micro-interventions—like increasing hydration or adjusting posture—that can prevent complications before they start. By capturing data continuously, wearables empower individuals to make informed, proactive decisions. The question of how can we prevent illness is increasingly being answered not just in clinics, but on our wrists, in real time, with precision.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Wellness Through Early Detection and Prevention
As we consider the complexities of health in the 21st century, one truth emerges with clarity: the greatest power we have lies in prevention. Whether through routine screenings, lifestyle optimization, genetic insights, or digital tools, we hold the ability to shape our health trajectories long before illness sets in. The journey to answer how can we prevent illness is both a scientific and deeply human endeavor, one that calls on us to be proactive, compassionate, and informed.
Early detection is not simply a clinical measure; it is a mindset—a commitment to vigilance, education, and action. Prevention, similarly, is a daily practice rooted in choices that honor our bodies and communities. Together, these strategies form a blueprint for resilient health, extending not only life but the quality with which it is lived.
As innovation continues and our understanding deepens, the tools to prevent illness will become more precise, more personalized, and more powerful. But at the heart of it all is a simple question that guides us forward: how can we prevent illness before it starts? With each step toward prevention, we move closer to a healthier, more hopeful future for all.