Achieving both fat loss and muscle gain may seem like a paradox, but modern nutrition science shows that it is possible when approached strategically. For those looking to transform their bodies without sacrificing strength or energy, understanding how to properly fuel the body is crucial. The goal is not just to get leaner or more muscular in isolation but to pursue a balanced, sustainable transformation that supports long-term health and performance. This comprehensive guide explores how to eat for fat loss and muscle gain, offering evidence-based tips to optimize results with a focus on the best diet to build muscle and lose fat.
You may also like: Smart Meal Prep for Weight Loss: Expert-Approved Lunch Ideas and Recipes to Stay on Track
The Science Behind Fat Loss and Muscle Gain
Fat loss and muscle gain occur through distinct yet interrelated processes in the body. Fat loss requires a caloric deficit, while muscle gain typically demands a caloric surplus. However, with the right macronutrient balance and training stimulus, it is possible to strike a middle ground that allows for what’s known as body recomposition. Protein plays a critical role in this process, providing the building blocks for muscle repair while supporting satiety during caloric restriction. Strength training enhances this synergy by stimulating muscle protein synthesis, even when calories are moderately restricted.
Eating patterns that support body recomposition often prioritize high-protein, nutrient-dense whole foods. Incorporating foods that promote satiety while providing sufficient energy for performance is key. This approach supports what many refer to as the best diet for muscle growth and fat loss—an eating plan that emphasizes quality over mere calorie counting. The success of such diets is amplified when they’re aligned with your metabolic needs and activity levels.
Understanding Macronutrients for Body Recomposition
Each macronutrient serves a specific role in body recomposition. Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth. Most experts recommend consuming 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day for active individuals seeking muscle growth while minimizing fat gain. Carbohydrates fuel high-intensity workouts and support recovery, while fats are vital for hormone regulation, including those that influence metabolism and muscle-building processes.
The best weight loss muscle building diet often includes a variety of lean proteins such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, and seitan, particularly for those following a whole-food plant-based diet. Carbohydrates should come from complex sources like oats, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and fruits to maintain energy without spiking insulin unnecessarily. Healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are integral for reducing inflammation and optimizing hormonal balance, both of which are essential for those following a fat loss muscle gain diet.
Strategic Caloric Cycling for Optimal Results
To simultaneously lose fat and gain muscle, calorie intake must be carefully timed and adapted to training demands. One popular method is caloric cycling—eating more calories on training days to fuel performance and recovery, and slightly reducing calories on rest days to encourage fat loss. This strategy allows for better adherence and prevents the metabolic slowdown often associated with prolonged dieting.
A diet plan to burn fat and gain muscle often incorporates this technique to enhance metabolic flexibility. For example, one might increase carbohydrates post-workout to replenish glycogen stores and stimulate insulin—a hormone that, in the presence of amino acids, promotes muscle protein synthesis. On non-training days, reducing carbohydrates while maintaining high protein intake can support fat metabolism without compromising muscle maintenance. This method aligns with the core principles behind a proper diet to lose weight and gain muscle.
Protein Timing and Meal Frequency
Although total protein intake is the most important factor, the timing and distribution of protein throughout the day can enhance results. Consuming 20 to 40 grams of protein every 3 to 4 hours has been shown to optimize muscle protein synthesis. This pattern ensures that the body remains in an anabolic state, especially during periods of muscle repair following resistance training.
Pre- and post-workout nutrition are particularly critical for those on a lose weight build muscle diet. Pre-workout meals should contain both protein and carbohydrates to enhance performance and reduce muscle breakdown. Post-workout meals, ideally consumed within 60 minutes of training, should prioritize protein and easily digestible carbohydrates to stimulate recovery. This approach is often emphasized in diets designed to support gaining muscle and losing fat, especially when combined with strategic meal frequency.
Nutrient Density vs. Caloric Density
One of the biggest challenges when trying to reduce fat and build muscle is managing hunger and energy levels. The solution lies in choosing nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods that deliver high amounts of vitamins, minerals, and fiber without excess calories. Leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, legumes, and whole grains help create a feeling of fullness and provide sustained energy, making them staples in a good diet to lose weight and gain muscle.
Calorically dense but nutrient-poor foods—such as ultra-processed snacks, fried items, and sugar-laden beverages—undermine both fat loss and muscle gain. These foods often promote overeating and inflammation, which can interfere with recovery and metabolism. In contrast, whole foods with high water and fiber content support satiety, stabilize blood sugar, and enhance metabolic health. The best diet to lose weight and build muscle places a premium on quality, not just calorie quantity.
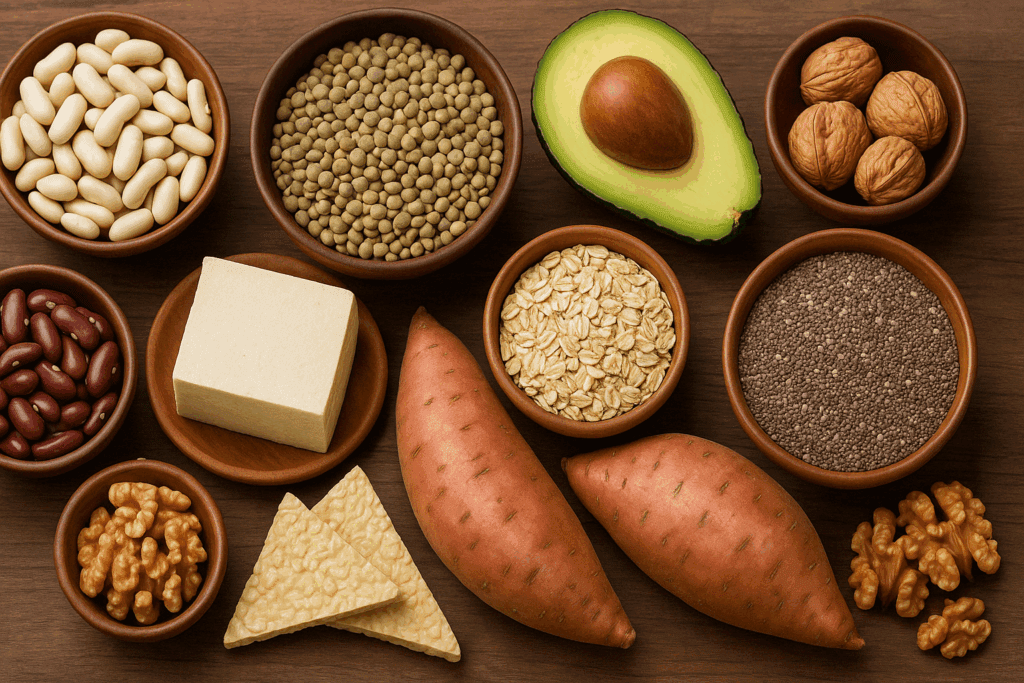

The Role of Resistance Training and Recovery
No diet alone can stimulate muscle growth. Resistance training is essential to create the stimulus for muscle protein synthesis. Compound movements like squats, deadlifts, presses, and rows recruit large muscle groups and elevate metabolism for hours post-exercise. When combined with a diet for muscle growth and fat loss, this creates the perfect physiological environment for body recomposition.
Equally important is recovery. Chronic stress and inadequate sleep hinder fat metabolism and muscle repair. Prioritizing at least 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep and practicing stress reduction techniques like mindfulness, stretching, and breathwork can significantly enhance results. This holistic approach supports the physiological balance needed for a lean and muscular diet to be effective.
Understanding Keto and Low-Carb Approaches
Many individuals turn to a low-carb or ketogenic approach in hopes of accelerating fat loss. However, it’s essential to distinguish between the two. A ketogenic diet typically restricts carbs to under 50 grams per day to induce ketosis, while a low-carb diet is less restrictive and allows for more carbohydrate intake depending on individual needs. Understanding the nuances of the ketogenic diet vs low carb strategies is critical for tailoring the right plan.
When evaluating the keto diet vs low carb diet, one must consider long-term sustainability, energy levels during training, and dietary preferences. A low carb diet keto diet hybrid may work for those who want flexibility in carb intake while still promoting fat burning. However, questions such as “is keto a low carb diet?” or “is keto no carbs?” highlight the need for individualized guidance. A ketogenic diet is indeed low in carbohydrates but is not entirely free of them. The best outcomes often arise when the chosen approach aligns with the individual’s training demands and lifestyle.

Is Keto a Good Diet for Muscle and Fat Goals?
While the ketogenic diet may be effective for rapid fat loss in some individuals, it poses limitations when it comes to building muscle. Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred fuel for anaerobic activities like resistance training. Reducing them too much may impair performance, recovery, and the anabolic response to training. Thus, the answer to “is keto a good diet for muscle gain?” depends largely on the individual’s goals, genetics, and ability to adapt.
For some, a modified ketogenic approach may allow for some carb cycling around workouts, supporting better performance while maintaining a fat-burning state. This is often used in extreme fat loss and muscle gain diet plans, where athletes alternate between low-carb and moderate-carb days to meet specific performance and physique goals. For others, a whole-food-based moderate-carb plan may be more sustainable, particularly if the aim is to optimize energy levels and preserve lean mass.
Choosing the Best Foods for Losing Weight and Gaining Muscle
Food selection plays a pivotal role in any healthy diet aimed at reducing fat and building muscle. The best foods for losing weight and gaining muscle are those rich in protein, fiber, and micronutrients. Plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, black beans, edamame, and quinoa offer not only essential amino acids but also complex carbohydrates and fiber to support digestion and metabolic health.
Vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, kale, and Brussels sprouts should be consumed daily for their antioxidant properties and ability to support detoxification. Healthy fats from flaxseeds, walnuts, and chia seeds contribute to hormone regulation and satiety. These ingredients form the foundation of a healthy diet to lose weight and gain muscle without relying on heavily processed products or extreme restrictions.
Sustainable Meal Planning for Long-Term Success
Consistency is key when it comes to body recomposition. Creating a sustainable meal plan that fits your lifestyle ensures adherence over the long term. A lean mass diet should include a variety of flavors, textures, and foods to reduce boredom and promote compliance. It should also provide enough calories to support activity while creating a slight deficit or surplus depending on the goal.
Batch cooking, meal prepping, and logging meals can improve awareness and reduce decision fatigue. This can be particularly helpful for those following a diet to gain muscle mass and lose fat, where nutrient timing and composition are more critical. Planning ahead helps prevent impulsive food choices and makes it easier to stay aligned with your fitness goals.
How to Eat for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain: Practical Guidelines
Learning how to eat for weight loss and muscle gain involves more than just selecting the right foods—it requires an understanding of hunger cues, mindful eating, and intuitive adjustments. Monitoring energy levels, digestion, and performance can help fine-tune your intake without the need for rigid rules or constant tracking.
Start by identifying your daily caloric needs based on your current body composition and activity level. Choose foods that support your training and recovery, and avoid extremes that compromise either fat loss or muscle maintenance. With a focus on consistency, nutrient quality, and personalized adjustment, even a reduce fat and build muscle diet can be enjoyable and deeply satisfying.
Is a Keto Diet Sustainable for Body Recomposition?
Sustainability is one of the most important factors in long-term success. The question “is a keto diet sustainable?” must be answered on a case-by-case basis. For some, the restrictive nature of keto is manageable and even enjoyable. For others, the lack of carbohydrate flexibility can be a significant barrier. When evaluating keto and low-carb strategies, it’s important to consider not only the short-term results but also the long-term impact on quality of life and relationship with food.
Blending elements of both approaches—such as integrating carb-rich plant foods around workouts while maintaining low-carb meals at other times—can create a more sustainable burn fat gain muscle diet. Ultimately, the goal is to find an eating style that supports your metabolic health, enhances your energy, and aligns with your values.

Frequently Asked Questions: How to Eat for Fat Loss and Muscle Gain
1. Can you build muscle while losing fat without tracking calories every day?
Yes, it is possible to follow a diet to build muscle and lose fat without daily calorie tracking, but it requires a strong awareness of portion sizes and hunger cues. Many individuals succeed by using intuitive eating strategies alongside consistent strength training and a whole-food-based diet. By prioritizing protein-rich meals and watching for signs of fullness, you can create the caloric balance needed for a fat loss muscle gain diet. However, some form of periodic assessment—like body measurements, strength performance, or weekly check-ins—helps ensure progress over time. Even when not tracking, staying consistent with meal structure and food choices supports a sustainable diet to lose weight and gain muscle.
2. How does age affect a diet to build muscle and burn fat?
Age impacts hormonal balance, recovery speed, and muscle protein synthesis—all of which influence how effectively you respond to a diet to build muscle and burn fat. As we age, our bodies become less efficient at building muscle and metabolizing fat, making resistance training and protein intake even more essential. For older adults, a best diet to build muscle and lose fat may include slightly more protein and omega-3-rich fats to counteract inflammation and age-related muscle loss. Sleep quality and recovery techniques like mobility work or massage also become more critical. With appropriate modifications, a diet to lose fat and gain muscle remains achievable well into your 50s, 60s, and beyond.
3. What are the social challenges of following a fat loss muscle gain diet, and how can they be managed?
Social events, dining out, and family habits can challenge even the best diet for muscle growth and fat loss. The key is flexibility—allowing for occasional indulgences without derailing progress. Planning ahead by checking menus, bringing a healthy dish, or setting boundaries with supportive communication can reduce pressure in social settings. A good diet to lose weight and gain muscle doesn’t have to be all-or-nothing; balance and consistency matter more than perfection. Focusing on your long-term goals can help you make empowered choices in social environments without sacrificing enjoyment.
4. Are there psychological strategies that support a diet to lose fat and gain muscle?
Absolutely. Mental resilience plays a powerful role in sustaining a proper diet to lose weight and gain muscle. Techniques such as visualization, journaling, and habit stacking can reinforce commitment and reduce decision fatigue. Cognitive reframing—viewing your food choices as acts of self-care rather than restriction—can also prevent burnout. Additionally, building a support system or working with a coach increases accountability and reduces the isolation that can come with body transformation efforts. Integrating mindfulness into your eating habits enhances the overall success of a lose weight build muscle diet.
5. Can plant-based diets be effective for an extreme fat loss and muscle gain diet?
Yes, when properly planned, plant-based eating can support even an extreme fat loss and muscle gain diet. Many athletes thrive on whole-food, plant-based protocols by focusing on legumes, tofu, seitan, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. These foods provide ample protein, complex carbs, and fiber while reducing inflammation and supporting recovery. The best diet to lose weight and build muscle doesn’t require animal products; it only requires nutrient density and sufficient calories from strategic sources. B12, iron, and creatine are nutrients to monitor on a plant-based plan, especially when following a diet for losing weight and gaining muscle.
6. How important is gut health in a gaining muscle and losing fat diet?
Gut health is increasingly recognized as a foundational pillar in any gaining muscle and losing fat diet. A balanced gut microbiome supports digestion, nutrient absorption, inflammation control, and even mood—all of which affect consistency and performance. Fermented foods like kimchi, tempeh, and unsweetened yogurt (or plant-based alternatives) can aid digestion and reduce bloating during a lean and muscular diet. Fiber-rich foods, like legumes and whole grains, not only feed beneficial bacteria but also stabilize blood sugar levels critical to a burn fat gain muscle diet. Addressing gut imbalances can enhance your ability to stick to healthy diets to lose weight and gain muscle.
7. What role does hydration play in a lean mass diet?
Hydration is essential to the success of a lean mass diet because water affects every metabolic process, from muscle contractions to fat oxidation. Dehydration can reduce strength output, hinder protein synthesis, and impair nutrient transport—all of which compromise your diet to put on muscle and lose fat. Additionally, drinking water before meals may help regulate appetite and prevent overconsumption, especially when adjusting to a diet to gain muscle mass and lose fat. Electrolytes like potassium and magnesium are also crucial, particularly for those training in heat or engaging in intense activity. Optimal hydration enhances both muscle growth and fat loss.
8. How can busy professionals follow a diet for cutting fat and gaining muscle?
Time constraints are one of the biggest barriers to maintaining a diet for cutting fat and gaining muscle, but meal prepping and batch cooking can make a world of difference. Prioritizing simple, high-protein meals that travel well—like lentil salads, quinoa bowls, or protein smoothies—helps keep consistency high without demanding hours in the kitchen. Scheduling workouts and setting calendar reminders for meals or hydration also creates structure amidst a hectic schedule. Choosing the best foods for losing weight and gaining muscle often means looking for options with minimal prep time but maximal nutrient impact. With some planning, even the busiest person can thrive on a best diet for weight loss and muscle gain.
9. Are cheat meals compatible with a burn fat gain muscle diet?
Cheat meals can be part of a sustainable burn fat gain muscle diet if approached with mindfulness and intention. Rather than being seen as a break from the plan, they can be viewed as strategic resets—both psychological and metabolic. Occasional indulgences may increase adherence and reduce feelings of deprivation, which are common challenges in any best weight loss muscle building diet. However, frequent binge episodes or emotional eating can undermine progress, so it’s important to differentiate between moderation and overindulgence. Reintegrating structure quickly afterward keeps your diet for muscle growth and fat loss on track.
10. What are the long-term health benefits of following a healthy diet to lose weight and gain muscle?
Beyond aesthetics, a healthy diet to lose weight and gain muscle promotes insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular health, and reduced risk for chronic disease. Muscle tissue is metabolically active and protects against age-related frailty, while reducing excess fat improves hormonal function and immune resilience. A good diet for losing weight and building muscle also fosters improved mental clarity, mood stability, and better sleep. Over time, the lifestyle changes associated with a diet plan to burn fat and gain muscle create a ripple effect—enhancing not just physical wellness but also confidence and emotional resilience. The pursuit of a diet for cutting fat and gaining muscle is ultimately a long-term investment in vitality and longevity.
Final Thoughts on Finding the Best Diet to Build Muscle and Burn Fat
Successfully navigating the path to body recomposition requires more than just discipline—it calls for insight, personalization, and a commitment to sustainable habits. Whether you lean toward a plant-based eating pattern, a ketogenic protocol, or a balanced whole-food strategy, the principles of the best diet for weight loss and muscle gain remain the same: prioritize nutrient-dense foods, fuel performance, and maintain consistency.
A truly effective diet to lose fat and gain muscle is not a short-term fix but a lifestyle that supports vitality, strength, and resilience. With science-backed strategies and a flexible mindset, you can create a plan that works with your body rather than against it—allowing you to achieve and maintain your ideal balance of leanness and strength.
By making informed choices and focusing on long-term wellness over quick fixes, you not only reshape your body—you transform your health from the inside out.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
How to Lose Fat and Gain Muscle for Body Recomposition
How To Lose Fat and Gain Muscle at the Same Time
How to Lose Fat and Gain Muscle: It Starts With Diet
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.

