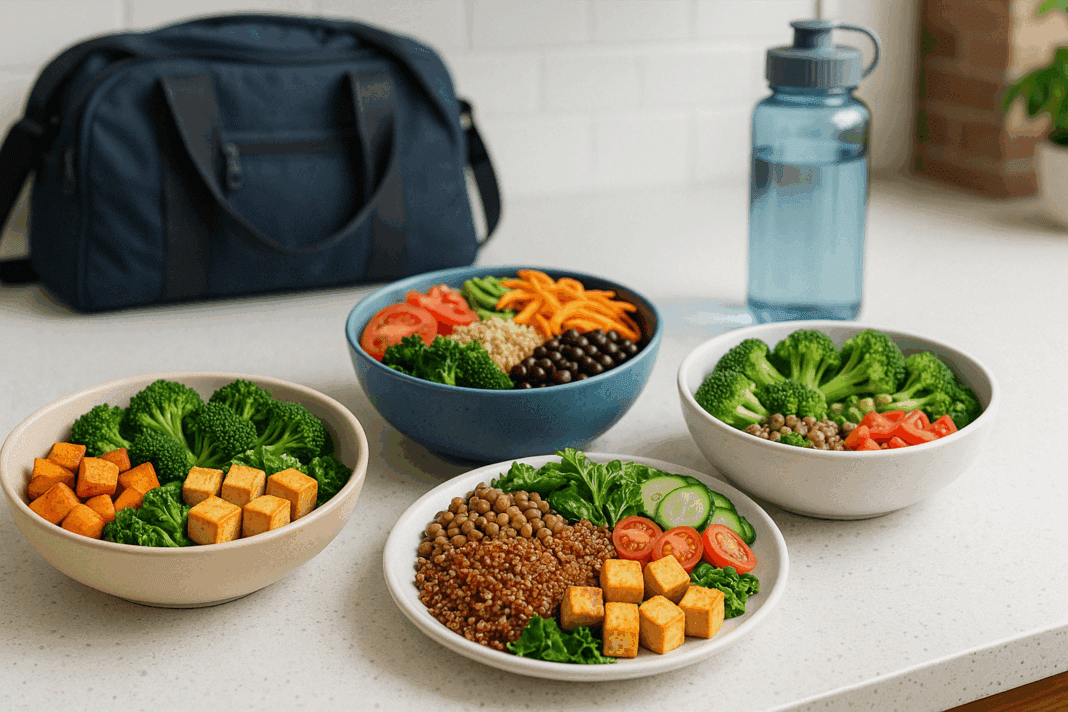Building lean muscle isn’t just about what you lift in the gym—it’s also about what you put on your plate. While resistance training is essential, nutrition is what fuels, repairs, and grows your muscles. If you’re seeking easy high protein meals for muscle gain, you’re already halfway there. But how do you create meals that are not only protein-packed but also science-backed, sustainable, and simple to prepare? That’s where the real magic lies. In this article, we’ll explore how high protein meals can drive hypertrophy, how they compare to other popular diet trends like the ketogenic and low carb diets, and most importantly, how to build muscle with real, whole food recipes that actually taste good.
You may also like: Smart Meal Prep for Weight Loss: Expert-Approved Lunch Ideas and Recipes to Stay on Track
Understanding Muscle Growth and the Role of Protein
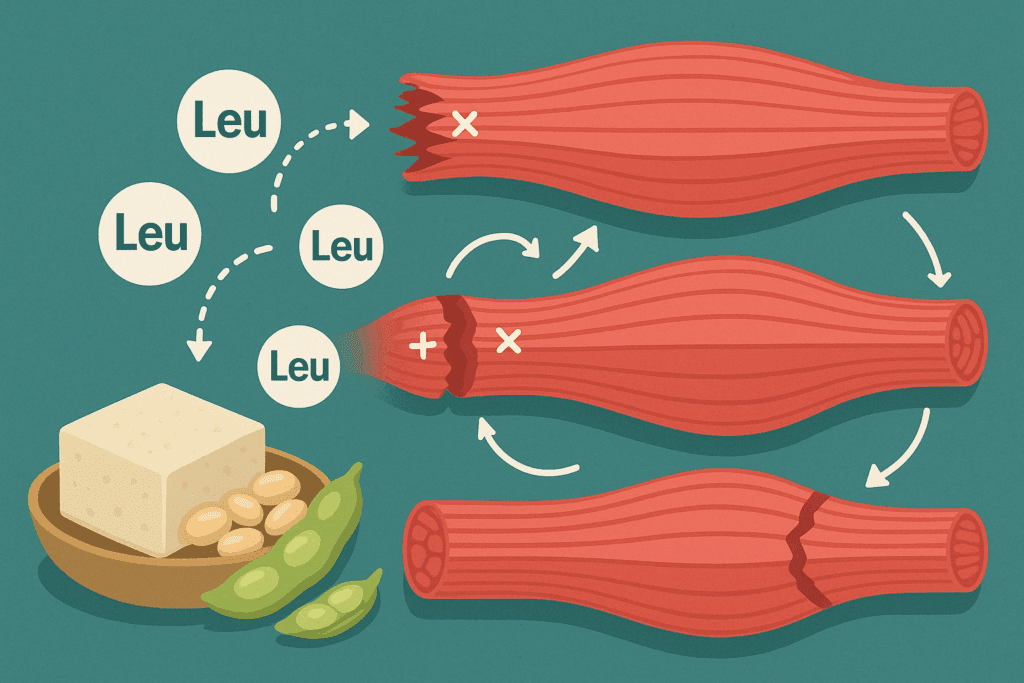
Muscle gain, or hypertrophy, occurs when the rate of muscle protein synthesis exceeds muscle protein breakdown. The cornerstone of this process is dietary protein, which provides the amino acids necessary to repair and build new muscle tissue. But not all proteins are created equal. The body requires essential amino acids, particularly leucine, to activate muscle growth. This is why high protein meals for muscle gain often emphasize sources rich in complete proteins—foods that contain all nine essential amino acids.
Scientific evidence supports the consumption of protein in spaced-out intervals throughout the day to optimize muscle protein synthesis. Consuming 20 to 40 grams of high-quality protein per meal is generally recommended for active individuals. For plant-based eaters, this means combining foods strategically to create complete profiles. Think rice and beans, tofu with quinoa, or lentils with whole grains.
Debunking the Protein Myth: More Isn’t Always Better
It’s a common misconception that eating massive amounts of protein guarantees muscle growth. While adequate protein intake is essential, there is a threshold beyond which excess protein is either oxidized for energy or stored as fat. Current guidelines suggest that athletes aiming for muscle gain should consume about 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. What matters most is consistency, timing, and the quality of your meals.
Interestingly, when comparing protein strategies to other dietary approaches like the ketogenic diet or low carb diets, research highlights unique differences. A low carb diet or keto plan may prioritize fat as the primary fuel source, but the lack of sufficient carbohydrates can sometimes impair muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment, especially for athletes. While some claim the keto diet is high in protein, it’s often moderate at best. This has sparked ongoing debate over the ketogenic diet vs low carb diets, especially regarding their suitability for muscle gain.
Navigating the Keto Confusion: Is Keto a Good Diet for Muscle Gain?
Many people ask: is keto a good diet for building muscle, or is keto a low carb strategy that falls short? The answer depends on individual metabolism, goals, and dietary preferences. While some individuals thrive on a ketogenic plan, maintaining muscle mass with keto requires meticulous planning, as the diet emphasizes fat over protein. If you’re not careful, you may fall short of your protein needs.
The keto diet vs low carb diet debate continues, with studies indicating that keto may not be ideal for all athletes. Low carb diets typically allow more protein and moderate carbs, while the standard ketogenic diet severely restricts carbohydrates to encourage ketosis. However, muscle growth depends on the availability of amino acids and insulin—a hormone stimulated by carbohydrate intake. As a result, those following a keto diet for muscle gain must work harder to get adequate protein without sacrificing metabolic balance. So, is a keto diet sustainable for long-term hypertrophy? That remains an open question.
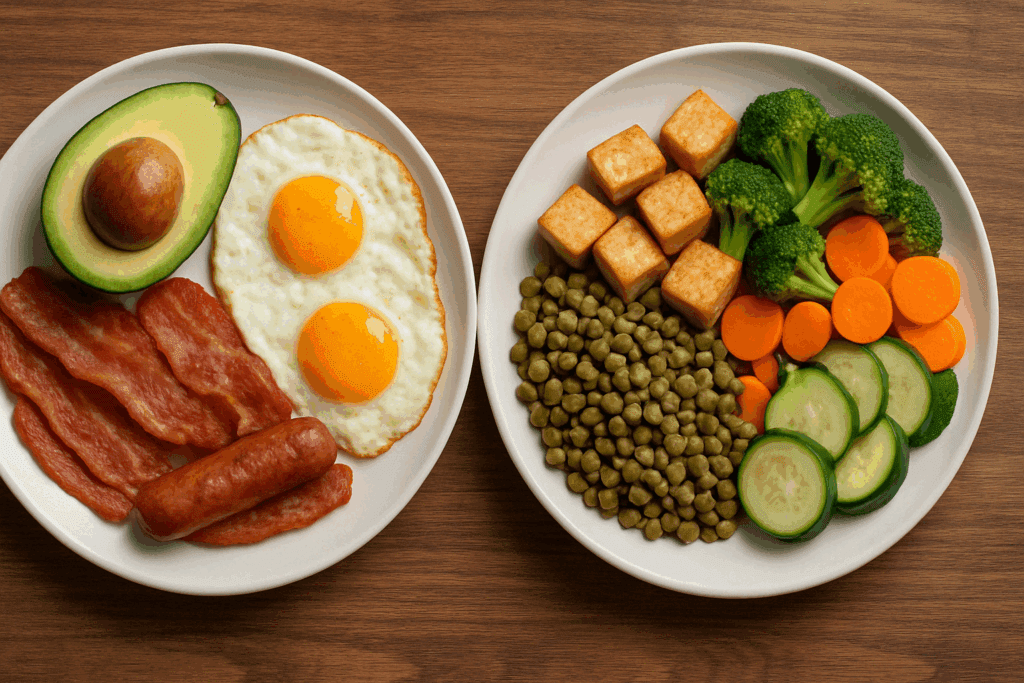
Benefits of Whole Food High Protein Recipes for Muscle Gain
When building your diet, the most sustainable and effective approach involves whole foods. Easy high protein meals for muscle gain made from minimally processed ingredients not only provide the amino acids needed for hypertrophy but also deliver fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients that support recovery and overall health. These whole food-based recipes avoid the pitfalls of ultra-processed protein bars or powders, which often come with added sugars, artificial additives, or digestive discomfort.
Examples of whole food high protein recipes for muscle gain include:
- Quinoa and black bean burrito bowls with roasted vegetables
- Baked tofu stir-fry with buckwheat noodles and sesame sauce
- Red lentil and sweet potato stew with kale and tahini drizzle
- Chickpea pasta with walnut “meat” sauce and nutritional yeast
Each of these meals can be tailored to meet the protein needs of individuals seeking muscle gain, while also keeping preparation simple and ingredients accessible.
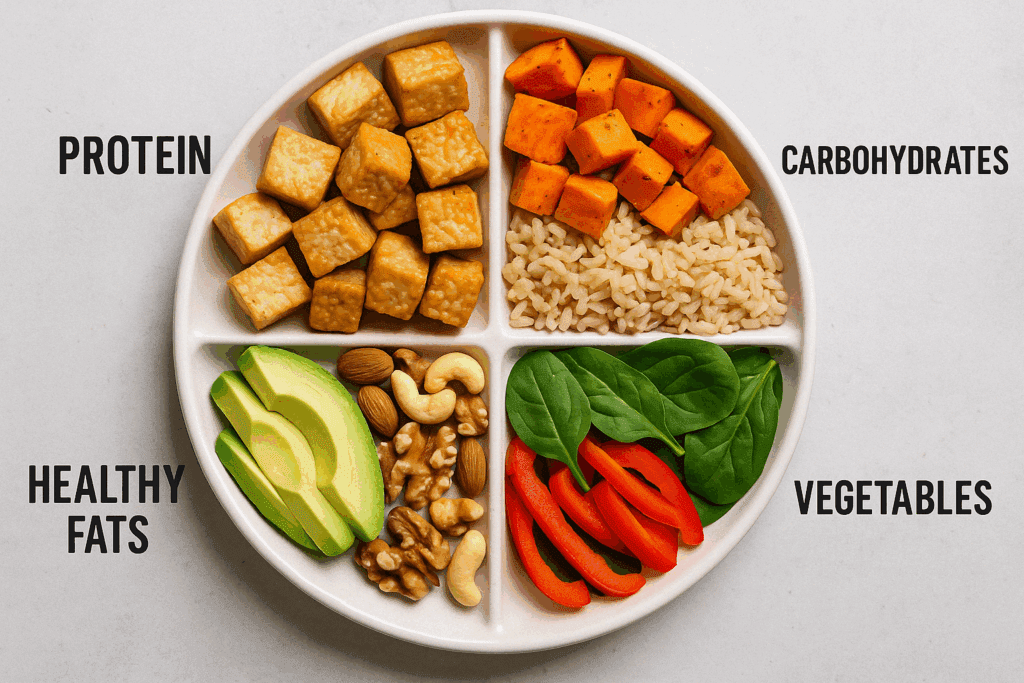
How to Build Balanced High Protein Meals for Muscle Gain
Building a balanced, high protein meal is part art, part science. Start with a solid protein base, then layer in fiber-rich complex carbs and healthy fats to support sustained energy and satiety. Key components of a balanced high protein meal include:
- Protein Source: Tempeh, tofu, seitan, legumes, quinoa, lentils
- Carbohydrates: Brown rice, oats, sweet potatoes, whole wheat pasta
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil
- Micronutrients: Dark leafy greens, colorful vegetables, herbs
By integrating these components into your daily meals, you’ll meet both macronutrient and micronutrient needs. And, contrary to the perception that keto is no carbs, even those pursuing a lower-carb approach can benefit from incorporating strategic carbohydrates to support performance and recovery.
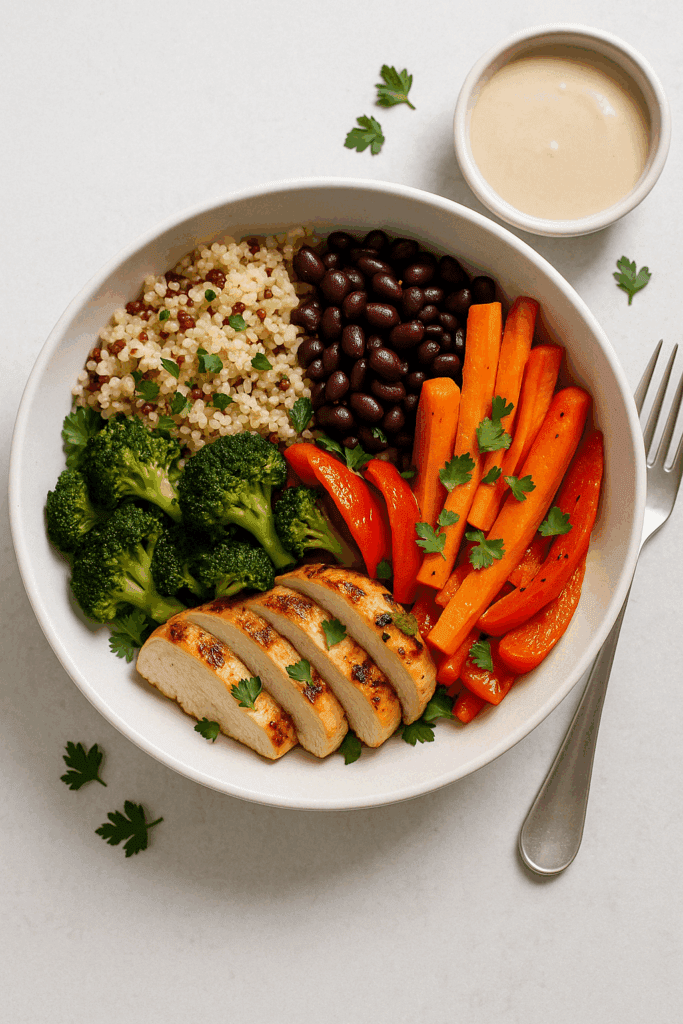
Plant-Based vs Animal Protein: What the Research Says
Another ongoing debate in the realm of muscle nutrition is whether plant or animal protein is superior. Multiple studies now confirm that, with proper planning, plant-based diets can support muscle gain as effectively as omnivorous diets. The key lies in food diversity and total protein intake. While some argue that animal proteins are more bioavailable, plant proteins can be just as effective when consumed in adequate amounts and variety.
For example, pea protein and soy protein have been shown to support muscle hypertrophy comparably to whey. Additionally, plant-based diets offer benefits for cardiovascular health, inflammation reduction, and longevity—which supports not just short-term muscle gains, but long-term performance and vitality. And for those comparing the ketogenic diet vs low carb or plant-based approaches, the sustainability and nutritional density of plant-focused meals often tip the balance.
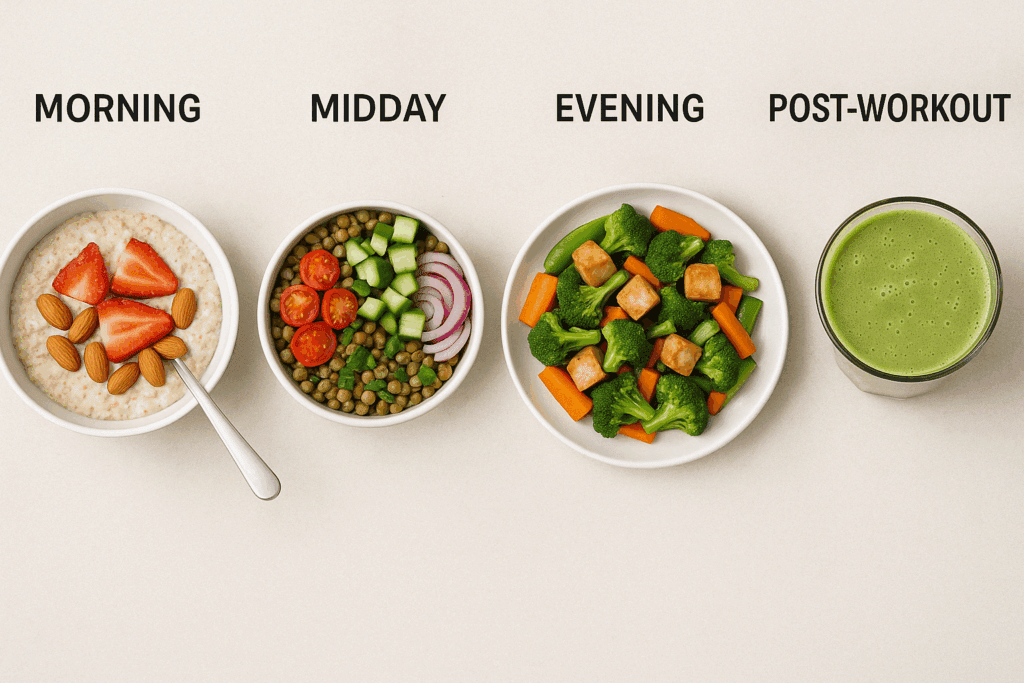
Timing and Distribution: Optimizing Protein Intake Throughout the Day
Meal timing matters more than many realize. Research supports the idea of evenly distributing protein across three to four meals per day to maximize muscle protein synthesis. Skipping meals or consuming most of your protein at dinner may reduce the body’s ability to build muscle efficiently. Start your day with a protein-rich breakfast, continue with a balanced lunch, and finish strong with a hearty dinner and optional post-workout snack.
Easy examples include a protein oatmeal bowl with soy milk and chia seeds in the morning, a lentil and quinoa salad for lunch, and a tempeh stir-fry at dinner. Post-workout, a smoothie with hemp seeds, plant-based protein powder, and berries can help replenish amino acids and glycogen.
Is Keto a Low Carb Diet or Something More?
The terms low carb diet and keto diet are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. A low carb diet typically allows anywhere from 50 to 150 grams of carbs per day, while a standard keto plan restricts carbs to under 50 grams to maintain ketosis. So when considering low carb diet keto diet overlaps, it’s important to understand the nuances. The keto diet is low carb, but not all low carb diets are ketogenic.
This difference matters when evaluating the impact on muscle gain. While some people find success with muscle preservation on keto, it can be more difficult to build new muscle due to limited glycogen stores and insulin response. Carbohydrates play a vital role in insulin release, which is anabolic and helps shuttle amino acids into muscle cells. Therefore, those prioritizing muscle growth may find a balanced approach that includes strategic carbohydrates to be more effective in the long run.
Is a Keto Diet Sustainable for Lifelong Muscle Health?
Sustainability is one of the most important yet overlooked factors in any dietary approach. So is a keto diet sustainable when your goal is long-term muscle gain and overall health? While keto may offer initial fat loss benefits, maintaining it over months or years can be challenging, especially in the context of building or preserving muscle. Social eating, performance needs, and nutrient variety all influence sustainability.
In contrast, a whole food, plant-forward high protein plan offers flexibility, accessibility, and long-term adherence. When you rely on high protein recipes for muscle gain that are rooted in whole grains, legumes, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, you create a pattern that is nutritionally robust and easier to maintain. And when muscle gain is the goal, consistency is far more valuable than any short-term trend.
Sample High Protein Meals for Muscle Gain
Here are a few simple, delicious meals that make building muscle feel effortless:
- Breakfast: Steel-cut oats with soy milk, almond butter, hemp seeds, and sliced banana. This combo delivers fiber, protein, and healthy fats in one bowl.
- Lunch: Lentil and brown rice bowl with roasted vegetables, tahini sauce, and a sprinkle of pumpkin seeds. This meal offers complex carbs, plant-based iron, and complete proteins.
- Dinner: Tofu and vegetable stir-fry over buckwheat noodles with a peanut-ginger glaze. Easy to prep, this dish is high in protein and antioxidants.
- Snack or Post-Workout: Smoothie with frozen berries, a scoop of vegan protein powder, oat milk, chia seeds, and a handful of spinach. Quick, refreshing, and nutrient-dense.
Each of these options represents how easy high protein meals for muscle gain can be when built from real, whole ingredients. And best of all, they taste as good as they perform.
Making Muscle-Friendly Nutrition a Lifestyle, Not a Phase
Muscle gain doesn’t come from a single meal or workout—it’s the cumulative effect of months of consistent effort. When your everyday meals are built on the foundation of whole foods and optimal protein intake, muscle building becomes a sustainable, enjoyable process. Prioritize meals that are easy to prepare, nutritionally complete, and supportive of your physical goals.
Whether you’re drawn to plant-based eating, exploring high protein recipes for muscle gain, or still deciding between the ketogenic diet vs low carb diet, always come back to one question: is this approach sustainable for my life, my body, and my performance? The answer will guide you toward a path that aligns with both your values and your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions: Easy High Protein Meals for Muscle Gain
1. What are some unexpected plant-based ingredients that boost the protein content of easy high protein meals for muscle gain?
While legumes, tofu, and quinoa are commonly known, there are a few underrated ingredients that can significantly elevate the protein profile of your meals. For example, nutritional yeast offers a cheesy flavor while providing about 8 grams of protein per two tablespoons. Blackstrap molasses, often used in marinades or dressings, contains not only trace proteins but also vital minerals that aid muscle metabolism. Water lentils (also known as duckweed), a newer superfood, are emerging as a highly bioavailable plant protein. When crafting easy high protein meals for muscle gain, integrating these less conventional ingredients helps diversify your nutrient intake while keeping meals creative and satisfying.
2. How can meal prep enhance the effectiveness of high protein meals for muscle gain?
Meal prepping ensures consistency in both macronutrient intake and overall dietary discipline, which is crucial when building muscle. Pre-portioned, protein-rich dishes reduce the risk of under-eating protein or over-consuming calories from less beneficial sources. A well-organized meal prep strategy can include rotating high protein recipes for muscle gain throughout the week, preventing monotony and encouraging long-term adherence. Additionally, preparing meals in bulk allows better control over ingredient quality, especially when avoiding overly processed options. Ultimately, structured meal prep reinforces your commitment to muscle growth goals while minimizing daily decision fatigue.
3. Are fermented foods useful when incorporating recipes for muscle gain into your diet?
Yes, fermented foods can complement your muscle-building plan in multiple ways. Although they may not always be high in protein themselves, items like tempeh, miso, and fermented soy curd contribute to gut health, which enhances nutrient absorption—including amino acids critical for muscle synthesis. Furthermore, the natural probiotics found in fermented foods can reduce gastrointestinal inflammation, often improving overall digestion of dense high protein meals for muscle gain. Including a small portion of kimchi, sauerkraut, or kombucha alongside your main meals can help optimize gut microbiota, indirectly supporting your muscle development. This approach aligns with emerging evidence linking gut health to athletic performance and recovery.
4. How do high protein recipes for muscle gain support hormonal balance during resistance training?
Adequate protein intake is closely tied to the regulation of key hormones involved in muscle repair and recovery, including insulin, growth hormone, and testosterone. High protein meals for muscle gain promote the secretion of insulin, which helps shuttle amino acids into muscle cells while also minimizing muscle breakdown. In plant-based contexts, zinc-rich legumes and seeds, paired with vitamin C from vegetables, support testosterone synthesis naturally. Omega-3 fatty acids from flax or chia seeds further modulate cortisol levels, preventing stress-related muscle degradation. Therefore, when your recipes for muscle gain are thoughtfully composed, they do more than just feed your muscles—they fine-tune your entire hormonal landscape.
5. What is the psychological advantage of eating easy high protein meals for muscle gain on a regular schedule?
Routine consumption of well-timed, easy high protein meals for muscle gain fosters a powerful sense of autonomy and purpose. Psychologically, when you consistently nourish your body with high protein meals that support physical goals, it enhances self-efficacy—the belief that your actions produce meaningful results. This structured eating pattern also reduces anxiety associated with uncertain meal timing or suboptimal food choices. Additionally, protein-rich meals support neurotransmitter function, particularly dopamine and serotonin, which are involved in mood regulation and motivation. Over time, this reinforces a positive feedback loop between your physical progress and mental resilience.
6. Can easy high protein meals for muscle gain be tailored for night-time consumption without compromising sleep?
Yes, the timing and composition of your final meal can support both recovery and restful sleep. Opt for recipes for muscle gain that include tryptophan-rich ingredients like pumpkin seeds, oats, or tofu, which promote melatonin production. Avoid overly fatty or spicy elements that may disrupt digestion, and limit stimulants like cacao late in the day. Incorporating slow-digesting proteins such as casein (if not strictly plant-based) or a chickpea-based stew with quinoa can supply a steady amino acid release during the night. Crafting high protein meals for muscle gain that also consider circadian rhythms helps optimize overnight muscle repair and improves sleep quality—a key component of recovery.
7. What emerging food technologies are transforming how we approach high protein recipes for muscle gain?
Innovations in plant-based food science are expanding the accessibility and appeal of high protein recipes for muscle gain. Mycoprotein derived from fungi, lab-grown meat alternatives, and precision-fermented proteins (such as animal-free whey) are becoming increasingly available and nutritionally comparable to traditional sources. These developments allow for greater flexibility and ethical alignment in meal planning without compromising protein density or amino acid profile. Additionally, high-tech meal tracking apps can now calculate amino acid ratios, making it easier to fine-tune easy high protein meals for muscle gain in real-time. These advancements are making personalized nutrition for muscle growth more effective and sustainable than ever.
8. How can someone with a small kitchen or limited time still succeed with recipes for muscle gain?
Contrary to popular belief, you don’t need an industrial kitchen to prepare effective recipes for muscle gain. With just a blender, stovetop, and a few multipurpose tools, you can batch-cook staples like lentils, quinoa, and tofu-based dishes in under 30 minutes. One-pot meals, sheet pan dinners, and overnight oats are all examples of low-effort, high-impact meals that require minimal space and cleanup. Leveraging frozen vegetables and pre-chopped legumes can also accelerate meal assembly without sacrificing nutritional value. With thoughtful planning, even the most space-limited cooks can routinely enjoy easy high protein meals for muscle gain without logistical barriers.
9. Are there any social or cultural strategies that make sticking to high protein meals for muscle gain easier?
Absolutely. Social accountability can dramatically increase adherence to a muscle-building nutrition plan. Cooking in groups, participating in online meal challenges, or even simply sharing your favorite high protein recipes for muscle gain on social media can foster a sense of community and motivation. Additionally, drawing on cultural cuisines that emphasize legumes, grains, and vegetables—such as Indian dals or Ethiopian stews—can make easy high protein meals for muscle gain both flavorful and culturally enriching. Aligning your food choices with traditions or peer support systems transforms dietary discipline into an enjoyable, shared experience.
10. How do you prevent dietary fatigue when consuming high protein meals for muscle gain over the long term?
Preventing monotony is essential for sustaining motivation and nutritional adequacy. Rotate your ingredients every one to two weeks—for example, switching from lentils to chickpeas or from brown rice to farro—to keep your palette and nutrient profile diverse. Explore international recipes for muscle gain that use different spices, textures, and cooking techniques to bring novelty to your meals. Seasonal produce can also guide recipe variation while providing optimal freshness and micronutrient content. Finally, allow for some flexibility with occasional high-protein treats or restaurant-quality meals at home to maintain enthusiasm for your muscle-building journey.
Final Thoughts: Why Easy High Protein Meals for Muscle Gain Are the Smartest Path Forward
In the sea of diet trends, from keto to low carb to plant-based, it can be easy to feel overwhelmed. Yet, when you focus on easy high protein meals for muscle gain that are grounded in science and built from whole foods, you create a lifestyle that fuels strength and longevity. While debates about whether the keto diet is low carb, whether is keto a good diet for muscle gain, or whether is a keto diet sustainable continue, one truth remains clear: your best results will come from an approach you can maintain.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
26 Foods to Eat to Gain Muscle
What are some easy to make high protein meals?
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.