Understanding the Role of Breath in Physical Performance
For many fitness enthusiasts and even some seasoned athletes, breathing is often treated as a background process—an automatic, subconscious function. However, scientific research and real-world performance data alike have increasingly illuminated the central role that breathing plays in exercise physiology. Effective breathing techniques for working out do far more than simply deliver oxygen; they regulate carbon dioxide levels, influence the autonomic nervous system, and play a vital part in energy metabolism. By bringing awareness and control to this fundamental action, athletes can experience tangible improvements in both endurance and peak performance.
You may also like: How to Increase Stamina and Endurance Naturally: Smart Training Tips and Nutrition Habits That Support Cardiovascular Fitness
The human body is remarkably adaptive, but it thrives under conditions of optimized oxygen exchange. The act of inhaling brings in the oxygen necessary for aerobic metabolism, while exhaling helps expel carbon dioxide, a metabolic byproduct. In workouts that require sustained effort, such as running, swimming, or cycling, efficient respiration ensures that muscles receive the oxygen needed to delay fatigue. Moreover, breath control can reduce the build-up of lactic acid, thereby extending the time to exhaustion and enhancing athletic output. Thus, developing a refined workout breathing technique can elevate performance from average to elite.

How Breathing Affects the Nervous System and Energy Efficiency
Breathing is not merely a mechanical process; it is also deeply intertwined with the body’s stress response. The autonomic nervous system, which governs involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion, has two branches: the sympathetic (fight or flight) and the parasympathetic (rest and digest). Shallow, rapid breathing tends to stimulate the sympathetic branch, increasing heart rate and cortisol levels. While this response can be beneficial in short bursts, it becomes counterproductive during prolonged physical exertion, leading to quicker fatigue and inefficient energy use.
By contrast, slow and controlled breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system. This shift promotes a state of physiological calm and improved oxygenation, allowing athletes to conserve energy during endurance activities. For instance, diaphragmatic breathing—which emphasizes deep breaths that expand the belly rather than the chest—has been shown to increase lung capacity and improve blood oxygen levels. Athletes who employ this type of workout breathing technique often report lower perceived exertion and improved recovery times.
Incorporating these breathing strategies into regular training helps build neuromuscular efficiency. Over time, the body learns to allocate oxygen more effectively to working muscles while minimizing waste. This improved respiratory economy can have a compounding effect: better oxygen delivery leads to enhanced energy production, which in turn allows for more intense and sustained workouts.
The Science Behind Breathing Techniques and Athletic Endurance
Numerous studies support the relationship between controlled breathing and enhanced athletic performance. Research published in journals such as the Journal of Sports Sciences and Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology has demonstrated that breathing exercises can increase VO2 max, a key indicator of aerobic fitness. VO2 max refers to the maximum amount of oxygen the body can utilize during intense exercise. Athletes with higher VO2 max scores generally perform better in endurance-based sports, and breathing techniques are one of the few modifiable factors that can improve this metric.
Breathing efficiency also plays a role in anaerobic performance. During high-intensity intervals, the body often shifts from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism, which can lead to rapid accumulation of carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions. This acidification contributes to muscle fatigue and discomfort. By mastering breathing techniques for working out, athletes can better manage their acid-base balance, maintaining performance for longer durations. Rhythmic breathing, for example, encourages synchronization between respiratory and locomotor systems, reducing overall workload and stabilizing the body under strain.
It is also worth noting that proper breathing supports mental focus and psychological endurance. Athletes often encounter moments of doubt or distraction, particularly during long competitions. Intentional breathwork can serve as an anchor, drawing attention away from discomfort and toward the rhythm of movement. This meditative quality helps athletes stay present, pace effectively, and push through mental barriers.
Diaphragmatic Breathing: A Foundation for Efficiency
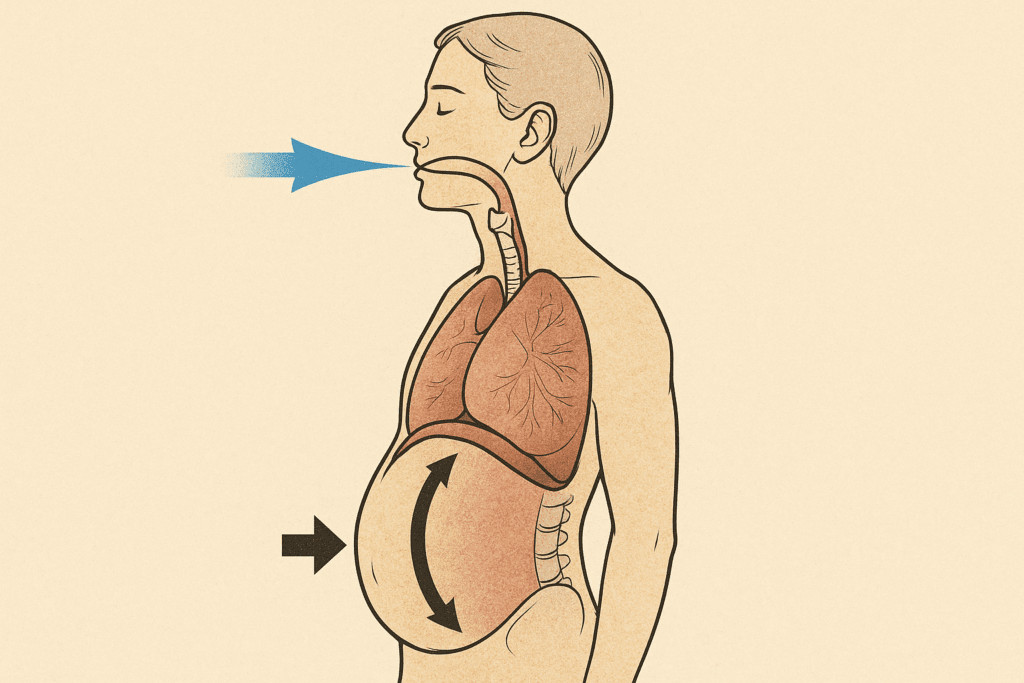
One of the most foundational and impactful breathing techniques for working out is diaphragmatic breathing. Unlike shallow chest breathing, which limits lung expansion and oxygen intake, diaphragmatic breathing promotes full inhalation and exhalation through the engagement of the diaphragm. This technique enhances respiratory efficiency, reduces unnecessary tension in the shoulders and neck, and optimizes gas exchange in the lungs.
Practicing diaphragmatic breathing involves consciously directing the breath into the lower abdomen. To do this effectively, individuals should place one hand on the chest and another on the stomach. As they inhale, the hand on the stomach should rise while the chest remains relatively still. This indicates that the diaphragm is fully engaging, allowing the lungs to expand downward and draw in a more substantial volume of air. During exhalation, the stomach should fall smoothly as the air is released.
Diaphragmatic breathing is especially beneficial for endurance athletes, such as distance runners, swimmers, and cyclists. These sports demand prolonged aerobic output, and efficient oxygen delivery can significantly extend performance capacity. Over time, training the diaphragm not only strengthens this crucial muscle but also cultivates a more relaxed and energy-efficient respiratory pattern. The result is a lower resting heart rate, improved circulation, and enhanced endurance.
Rhythmic Breathing and Synchronization with Movement
Rhythmic breathing is another workout breathing technique that can yield substantial benefits for athletes across a variety of disciplines. This approach involves synchronizing breath patterns with physical movements—for example, inhaling over a specific number of steps while running and exhaling over another set number. This coordinated approach helps distribute impact forces more evenly across both sides of the body, reducing the risk of repetitive stress injuries.
In running, a common rhythmic breathing pattern is 3:2, meaning three steps during inhalation and two steps during exhalation. This pattern helps ensure that exhalation alternates sides of the body, which can prevent side stitches and promote balanced muscle engagement. For strength training, rhythmic breathing often entails exhaling during the exertion phase (such as lifting a weight) and inhaling during the return or relaxation phase. This cycle stabilizes the core and provides additional support to the spine.
Integrating rhythmic breathing into a training routine requires practice and mindfulness. At first, it may feel unnatural to pay such close attention to the breath. However, with consistent effort, it becomes second nature and allows for a more harmonious connection between body and breath. This synchronization can elevate an athlete’s awareness of their own movement patterns, making adjustments more intuitive and enhancing overall performance.
Breath Holding and Hypoxic Training for Advanced Performance
While most breathing techniques emphasize increased oxygen intake, breath-holding exercises and hypoxic training take a different approach. These advanced strategies involve deliberately reducing oxygen availability to stimulate physiological adaptation. When used appropriately, they can enhance endurance, improve oxygen efficiency, and condition the body to perform under oxygen-deprived conditions.
Breath-holding drills, often incorporated into swimming and high-altitude training programs, trigger a series of adaptive responses. These include increased red blood cell production, improved CO2 tolerance, and enhanced mitochondrial efficiency. By intermittently depriving the body of oxygen, athletes can train their systems to become more resilient under stress and more capable of extracting oxygen from limited supplies.
Hypoxic training should be approached with caution and under professional supervision, as it places considerable strain on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. However, when integrated into a balanced training plan, it can provide a competitive edge. Athletes training for events held at elevation, or those seeking to boost their anaerobic threshold, often incorporate these techniques during specific mesocycles of their program.
Breathing Techniques in Strength and Resistance Training
Breathing techniques for working out are not limited to endurance sports. Strength and resistance training also benefit greatly from intentional breath control. In these contexts, proper breathing helps stabilize the core, protect the spine, and maximize force output during lifts. Holding the breath during the exertion phase—a method known as the Valsalva maneuver—can generate intra-abdominal pressure that enhances mechanical leverage and lifting capacity.
However, prolonged breath-holding can elevate blood pressure and may not be suitable for all individuals. Safer alternatives involve exhaling during the exertion phase and inhaling during the eccentric (lowering) phase. This controlled approach not only supports structural integrity but also improves muscular endurance. Moreover, it prevents unnecessary fatigue caused by poor oxygen delivery or hyperventilation.
Incorporating breath cues into strength training sessions promotes consistency and awareness. For instance, cues like “brace and exhale on the push” help athletes time their breath with movement, creating a rhythm that optimizes performance. Over time, this practice enhances mind-muscle connection and refines technique, making each lift more effective and efficient.

Integrating Breath Training into a Holistic Fitness Routine
To fully realize the benefits of breath control, it is essential to integrate breathing practices into every stage of a workout. This includes warm-up, active training, and cool-down phases. During the warm-up, breathing exercises such as box breathing or alternate nostril breathing can help focus the mind and prepare the respiratory system for increased demand. These practices calm the nervous system and create a state of readiness for physical exertion.
During the workout itself, breath awareness should be tailored to the activity. Endurance efforts call for rhythmic and diaphragmatic breathing, while strength sessions benefit from timed exhales and intra-abdominal bracing. Finally, the cool-down phase offers an opportunity to return the body to a parasympathetic state. Slow, deep breathing during stretching or foam rolling helps reduce cortisol levels, accelerate recovery, and signal to the body that the workout is complete.
Consistency is key in building breathing habits. Just as muscles require repeated stimulus to grow stronger, the respiratory system benefits from regular training. Incorporating breathwork into yoga, meditation, and even everyday moments of stress can reinforce these patterns and support overall well-being.
Enhancing Mind-Body Awareness Through Breath Control
One of the most profound benefits of adopting a mindful workout breathing technique is the heightened sense of mind-body awareness it cultivates. Breath serves as a bridge between conscious intent and unconscious function. By learning to observe and influence the breath, athletes gain a deeper understanding of their internal states and physical limitations.
This awareness is especially important during competition, where external pressures and internal anxiety can disrupt rhythm and performance. A controlled breathing practice allows athletes to reset mentally, reduce performance anxiety, and maintain composure under pressure. This mental edge can be the deciding factor in high-stakes environments, from marathons to weightlifting meets.
Beyond competition, breathwork supports recovery and emotional regulation. Athletes often face burnout, mental fatigue, and motivation dips. Intentional breathing activates the vagus nerve, a critical component of the parasympathetic system, promoting relaxation and mood balance. This holistic approach to training addresses both the physical and psychological dimensions of athletic performance, reinforcing the idea that the breath is not just a tool for movement, but for life.
Frequently Asked Questions: Breathing Techniques for Working Out
1. Can breathing techniques enhance cognitive focus during a workout? Yes, controlled breathing techniques for working out can significantly sharpen cognitive focus, especially during high-stakes or mentally demanding training sessions. When the breath is synchronized with movement, it minimizes distractions and fosters a state of flow, often referred to as being “in the zone.” This happens because intentional breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, calming mental chatter and improving concentration. Additionally, proper oxygenation through a deliberate workout breathing technique ensures that the brain is well-supplied with oxygen, which enhances alertness and decision-making capacity. Athletes practicing this approach often report improved coordination, timing, and overall mental resilience under pressure.
2. How can breathing techniques be tailored for high-intensity interval training (HIIT)? High-intensity interval training places unique demands on the respiratory system due to rapid shifts between anaerobic and aerobic states. To maintain performance and minimize recovery time, it’s important to adopt a workout breathing technique that emphasizes recovery during low-intensity phases. For example, nasal breathing during rest intervals can promote better oxygen absorption and help regulate carbon dioxide levels more efficiently. During high-effort bursts, exhaling forcefully can aid in stabilizing the core and enhancing explosive power. Many athletes integrate short breath-hold intervals to simulate oxygen deprivation, which conditions the body to tolerate lactic acid buildup more effectively over time.
3. Are there differences in breathing technique requirements across various sports? Absolutely. Different sports call for tailored breathing approaches based on their unique energy demands, durations, and movement patterns. For instance, swimmers must master breath control within a limited window, often timing their inhalations between strokes. Cyclists may benefit from deep, rhythmic nasal breathing to stabilize their core and maintain endurance. In contrast, martial artists often use quick, sharp exhales to brace for impact or deliver force. Each sport requires adaptation, but the foundational principles behind breathing techniques for working out—oxygen efficiency, rhythm, and nervous system regulation—remain consistent across disciplines.
4. Can breath training reduce the risk of injury during workouts? Yes, adopting a conscious workout breathing technique can help mitigate injury risks by improving core stability and posture. When the breath is synchronized with exertion, it activates the deep core muscles, such as the transverse abdominis and diaphragm, providing a natural brace for the spine. This is particularly critical during weightlifting or plyometric exercises, where improper breathing can lead to strain or imbalance. Furthermore, mindful breathing promotes better body awareness, allowing individuals to recognize early signs of fatigue or misalignment before they escalate into injury. It also contributes to balanced muscular engagement by reducing tension in overactive muscle groups.
5. What role does breath play in post-workout recovery? Breathwork is a powerful tool for accelerating post-exercise recovery. Engaging in slow, deep breathing after a workout helps shift the body from sympathetic (fight or flight) to parasympathetic (rest and digest) mode, facilitating muscle repair and reducing inflammation. Techniques such as 4-7-8 breathing or coherent breathing can lower cortisol levels and enhance heart rate variability, both of which are markers of improved recovery capacity. Breath-based recovery practices also promote mental decompression, helping athletes recalibrate emotionally after intense training. Incorporating breathing techniques for working out into the cooldown phase ensures that the gains made during training are consolidated through optimized physiological recovery.
6. How can breathing techniques support people with asthma or respiratory issues during workouts? While individuals with asthma or respiratory sensitivity must always consult their healthcare providers, many find that certain workout breathing techniques provide symptomatic relief and improve exercise tolerance. Diaphragmatic and pursed-lip breathing can help reduce the sensation of breathlessness by enhancing expiratory efficiency and keeping airways open. Breath pacing, where the intensity of effort is matched to breathing capacity, prevents hyperventilation and sudden bronchospasms. Over time, consistent breath training can increase lung capacity and improve the functional breathing reserve. These benefits make it possible for individuals with respiratory challenges to engage more confidently and consistently in physical activity.
7. Are there psychological benefits to learning advanced breath control for workouts? Definitely. Beyond physical performance, mastering breathing techniques for working out cultivates psychological resilience and emotional regulation. Intentional breathwork increases vagal tone, which is linked to better stress response, emotional stability, and even interpersonal connection. Many elite athletes use breath control as a gateway to mindfulness, reducing pre-competition anxiety and promoting calm under pressure. This emotional intelligence translates into better decision-making and leadership in team environments. Furthermore, breath-focused training often leads to greater self-awareness, empowering individuals to tune into their physical and emotional states with increased sensitivity.
8. Can breath training be used to simulate altitude training for endurance athletes? Yes, a growing number of endurance athletes use breath restriction techniques to mimic the effects of high-altitude environments. Methods such as hypoxic training or intermittent breath holding lower oxygen availability, encouraging the body to produce more red blood cells and improve mitochondrial function. These physiological changes enhance oxygen delivery during real-world competitions, particularly in sports like long-distance running, cycling, and rowing. While not a substitute for actual altitude exposure, this approach can be a cost-effective and accessible alternative. It’s crucial, however, to implement these techniques gradually and under guidance to avoid overexertion or hypoxia-related complications.
9. How do breathing techniques influence hormonal balance during and after exercise? Breath control directly affects hormonal regulation by influencing stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Rapid, shallow breathing during strenuous exercise spikes cortisol production, which, if unmanaged, can impair muscle recovery and immune function. Conversely, slowing the breath post-exercise helps suppress excessive cortisol and promote the release of restorative hormones like dopamine and serotonin. Practicing a consistent workout breathing technique also supports circadian rhythm alignment, indirectly impacting hormone secretion patterns such as melatonin production for sleep. In essence, the breath acts as a dial for hormonal balance, ensuring the body recovers fully and remains in homeostasis.
10. What innovations are emerging in the field of breath training and exercise performance? Technological advancements are bringing a new level of precision to breathing techniques for working out. Devices like respiratory muscle trainers and smart wearables now allow athletes to monitor lung capacity, breath rate, and even carbon dioxide tolerance in real-time. Virtual reality systems are being developed to teach controlled breathing through immersive scenarios that mimic competition environments. Biofeedback apps are gaining traction for guiding users through structured breath protocols tailored to their sport or physiological profile. As research continues to highlight the link between respiratory fitness and performance, we can expect further integration of breath training into mainstream athletic programming and rehabilitation settings.
Final Reflections: The Transformative Power of Breathing Techniques for Working Out
In the pursuit of athletic excellence, many factors come under scrutiny: training intensity, nutrition, recovery strategies, and supplementation. Yet, one of the most powerful tools for performance enhancement often goes overlooked—the breath. Embracing effective breathing techniques for working out can transform not only the quality of an athlete’s performance but also their entire approach to training, recovery, and self-awareness.
From diaphragmatic efficiency to rhythmic synchronization and hypoxic conditioning, each breathing method offers unique advantages tailored to specific training goals. These strategies are grounded in physiological science, supported by real-world outcomes, and applicable across a wide range of sports and fitness levels. Perhaps most importantly, they are accessible to anyone willing to invest the time and attention needed to cultivate this skill.
As awareness of breathwork continues to grow in the athletic community, it is likely that more coaches, trainers, and sports medicine professionals will begin to prioritize respiratory education alongside traditional conditioning. For athletes seeking to boost endurance, sharpen focus, and maximize performance, mastering the breath may be one of the most impactful decisions they ever make. In a world where marginal gains often determine success, breathing may just be the competitive edge that sets the elite apart.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
Why Proper Breathing During Exercise Is Important & How to Avoid Common Mistakes