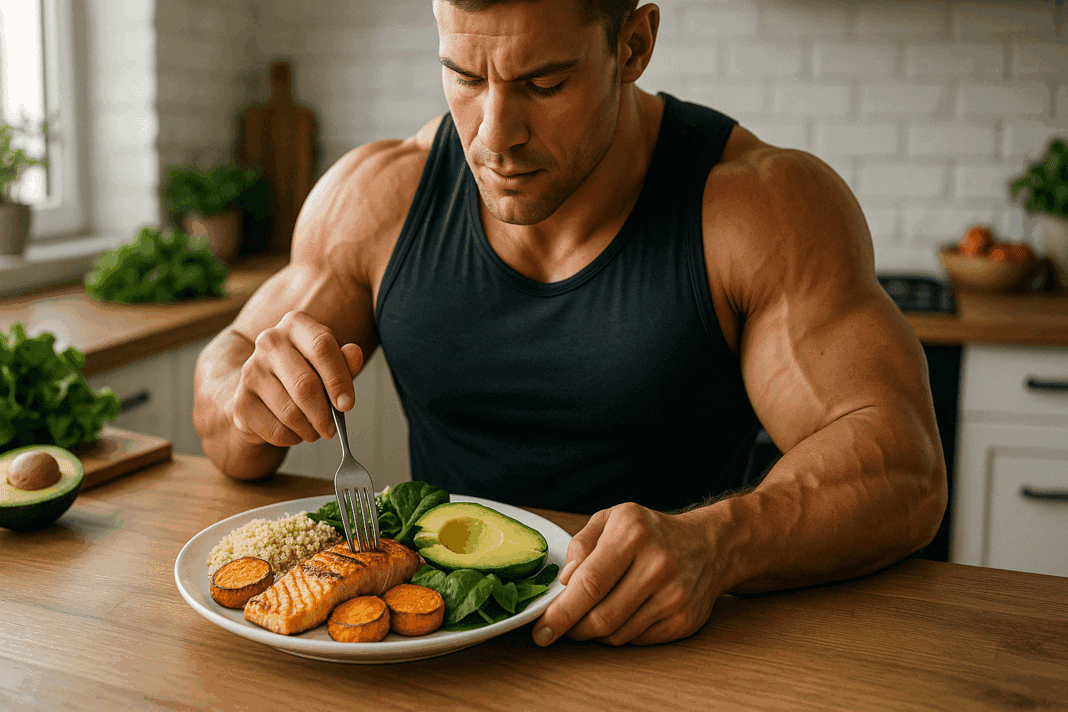
Gaining lean muscle mass is a strategic process that goes far beyond simply eating more food. When executed with intention, a clean bulking approach can help individuals build strength and size without compromising long-term health. This article explores what a healthy bulking diet entails, how to create an evidence-based bulking meal plan, and the best bulking foods to fuel your progress. We’ll also dive into what to eat on a bulk without sacrificing nutritional quality, how to select the best bulking meals for your goals, and how a clean meal plan for bulking compares to other popular dietary frameworks such as low carb and ketogenic approaches. Rooted in science and aligned with mindful eating, this guide provides everything you need to know about building a proper bulking diet.
You may also like: Smart Meal Prep for Weight Loss: Expert-Approved Lunch Ideas and Recipes to Stay on Track
Understanding the Principles of a Healthy Bulking Diet
A healthy bulking diet focuses on gradually increasing calorie intake while prioritizing nutrient-dense foods. Unlike dirty bulking, which often encourages unrestricted consumption of high-calorie junk foods, clean bulking emphasizes balance, metabolic health, and controlled weight gain. This method helps optimize muscle protein synthesis while limiting fat accumulation—a key distinction that separates a good bulking diet from one that could undermine long-term health.
At the core of any effective bulking diet program is a calculated calorie surplus. This typically ranges from 250 to 500 extra calories per day, depending on your metabolic rate, training intensity, and current physique goals. The bulk eating program should prioritize high-quality protein, complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, and micronutrients. Building muscle efficiently also depends on timing meals strategically around workouts and ensuring consistent energy availability throughout the day.
Equally important is consistency. A proper bulking diet doesn’t rely on sporadic overeating but on daily, structured meals tailored to your individual needs. It’s also critical to recognize that the best bulking meals are those that support training performance, recovery, and lean muscle growth without overwhelming your digestive system or spiking inflammation.
Best Foods to Eat When Bulking: What the Science Recommends
If you’re wondering what to eat on a bulk, the answer lies in a mix of whole food staples and targeted nutritional strategies. The best bulking foods are high in both calories and nutrients, supporting muscle repair and growth. Among protein-rich options, lean meats such as chicken breast, grass-fed beef, and wild-caught salmon are consistently highlighted in research as the best meat for bulking due to their amino acid profiles. For plant-based athletes, tofu, tempeh, lentils, chickpeas, and quinoa provide complete protein options that are ideal for a healthy bulking diet.
Complex carbohydrates are equally important. They replenish glycogen stores, support high training volumes, and help maintain a caloric surplus. Whole grains like brown rice, oats, sweet potatoes, and whole wheat pasta form the backbone of clean bulk meal plans. Fruit and vegetables should not be overlooked—they provide the antioxidants and phytonutrients necessary to combat the oxidative stress that often accompanies intense training.
Healthy fats are another essential component. Foods like avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and nut butters offer dense sources of calories and support hormonal health. Together, these form the foundation of the best bulking meals, delivering sustained energy and supporting muscle growth with minimal fat gain.
Designing a Clean Bulking Meal Plan: Balance, Timing, and Portioning
Creating a clean meal plan for bulking begins with an understanding of your daily calorie and macronutrient needs. Depending on your goals, a typical bulking meal plan may allocate around 40–50% of total calories from carbohydrates, 25–30% from protein, and 20–30% from fats. This macro distribution ensures muscle-building support while maintaining metabolic flexibility.
Spacing meals evenly throughout the day—ideally every 3 to 4 hours—helps sustain energy, promote digestion, and minimize blood sugar fluctuations. Pre- and post-workout meals are especially important. A combination of fast-digesting carbs and lean protein after training helps maximize muscle protein synthesis and recovery. Options like a smoothie with banana, oats, protein powder, and almond butter make excellent post-workout bulking meals.
Snacks are also an underrated tool in any bulking diet meal plan. Greek yogurt with granola, hummus with whole grain pita, and trail mix with dried fruit and seeds are portable, nutrient-rich choices that contribute to your daily surplus. These additions help fill nutritional gaps and prevent under-eating..
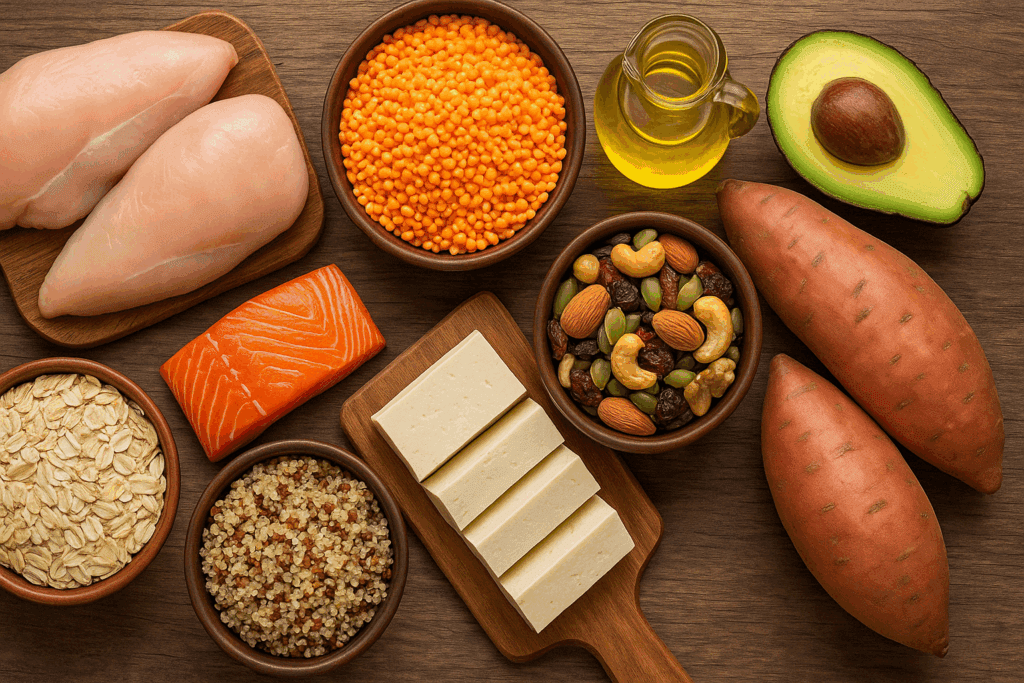

Sample Meals for Bulking Muscle the Clean Way
Healthy bulking meals should be diverse, flavorful, and satisfying. Here’s a snapshot of what a day might look like on a clean bulking diet plan:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal made with almond milk, chia seeds, banana slices, and a scoop of plant-based protein powder.
- Mid-morning snack: Whole grain toast with avocado and hemp seeds.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken with quinoa, roasted vegetables, and olive oil dressing.
- Pre-workout: Brown rice and lentils with sautéed kale and tahini.
- Post-workout: Smoothie with berries, peanut butter, spinach, and protein powder.
- Dinner: Baked salmon, sweet potatoes, and steamed broccoli.
- Evening snack: Cottage cheese with walnuts and honey.
Each meal is designed to deliver quality calories, build lean mass, and support overall health. This approach offers far more than just caloric overload; it fosters mindful eating habits and supports metabolic resilience.
How the Bulking Diet Compares to Low Carb and Keto Diets
The rise of carbohydrate-restrictive diets has prompted many athletes to compare the ketogenic diet vs low carb approaches when planning their nutrition. However, the low carb diet keto diet comparison often leads to confusion, particularly around their applicability to muscle gain. So, is keto a low carb diet? Yes, but not all low carb diets are ketogenic.
A ketogenic diet is an ultra-low-carb, high-fat approach designed to shift the body into ketosis, where fat becomes the primary energy source. While it can be effective for fat loss and metabolic disorders, its application in a bulking context is limited. This is primarily because glycogen—the storage form of carbohydrate—is crucial for high-intensity strength training and muscle hypertrophy.
In contrast, traditional bulking diets require ample carbohydrates to fuel performance, enhance recovery, and stimulate insulin release—a hormone critical for muscle building. When comparing the keto diet vs low carb diet, it’s important to note that even moderate carbohydrate restrictions can impair training intensity and limit caloric intake, making clean bulking difficult to sustain.
Furthermore, the question “is a keto diet sustainable” remains contentious. While some find long-term success, others struggle with energy dips, nutrient deficiencies, and digestive issues. This is especially true when prioritizing clean muscle gain. A healthy bulking diet thrives on a broader spectrum of whole foods—including legumes, whole grains, and starchy vegetables—which are largely restricted on keto.
Diets People Do When Bulking: Exploring Variations and Pitfalls
Within the world of strength training, there are numerous diets people do when bulking, ranging from the classic “see food” diet to more structured macro-tracked regimens. Dirty bulking—where anything and everything is consumed in the name of size—often leads to excessive fat gain, poor insulin sensitivity, and inflammation. In contrast, a clean bulking approach offers a far more sustainable and health-conscious path.
A well-constructed bulking diet program considers not just calorie quantity, but also quality. This includes paying attention to food sources, nutrient timing, fiber intake, and gut health. Relying heavily on processed foods may seem convenient, but it disrupts hormonal balance, promotes bloating, and undercuts muscle definition. By contrast, healthy bulking meals support overall vitality, boost immune function, and help preserve a leaner physique.
It’s also important to tailor the bulk food plan to individual preferences. For vegetarians or those leaning into plant-based nutrition, incorporating protein-dense legumes, soy products, seeds, and whole grains can help meet muscle-building needs. For omnivores, rotating between the best meat for bulking (such as turkey, lean beef, and bison) prevents monotony and supports micronutrient diversity.
Crafting a Bulk Eating Program That Works for Your Lifestyle
There’s no one-size-fits-all bulk eating program. Your bulking meal ideas should reflect your schedule, taste preferences, ethical beliefs, and training style. This is where mindful eating becomes essential. Rather than forcing yourself to choke down calorie-dense foods with no enjoyment, focus on building meals you look forward to. When eating is pleasurable, adherence improves—and so do your results.
Mindful bulking also means checking in with your body. Are you recovering well between workouts? Do you feel energized and mentally sharp? Are you gaining weight at a reasonable rate (typically 0.25 to 0.5 pounds per week)? These markers help ensure that your bulking diet meal plan is serving you, not sabotaging you.
Meal prep is another cornerstone of success. Batch-cooking staples like brown rice, lentils, grilled tofu, or roasted veggies ensures that you always have good bulking meals on hand. This reduces reliance on takeout or impulse eating and promotes better portion control. Even simple freezer-safe containers can help keep your bulk food plan on track.
Is Keto a Good Diet for Muscle Gain?
When evaluating whether is keto a good diet for building muscle, it’s crucial to consider the metabolic demands of hypertrophy. Resistance training relies heavily on glucose for fuel, particularly during compound lifts and high-rep sets. Because the keto diet limits carbohydrate availability, it often hinders performance in these scenarios. For this reason, clean bulking is better served by diets that provide a robust supply of complex carbohydrates.
Some athletes attempt a cyclical ketogenic diet—cycling periods of carb intake around workouts—to combine the benefits of keto with the muscle-building potential of carbs. However, this strategy can be difficult to execute and often leads to energy crashes and digestive irregularities. Moreover, for those seeking a healthy bulking diet rooted in whole foods, this approach may prove unnecessarily complicated.
It’s also worth noting that very low-carb diets often require supplementation with fiber, electrolytes, and key vitamins to prevent deficiencies. In contrast, the best bulking diet built around diverse plant and animal foods naturally supports nutrient adequacy, stable energy, and digestive health. So while keto may work for specific clinical goals, it remains less compatible with clean muscle-building ambitions.
The Role of Proper Macronutrient Balance in a Bulking Diet Plan
Striking the right balance of protein, carbohydrates, and fat is the cornerstone of any proper bulking diet. Each macronutrient plays a distinct role: protein repairs and builds muscle tissue, carbohydrates replenish glycogen and fuel intense workouts, and fats support hormone production and cellular function. Neglecting any one of these elements can derail your progress.
As a general guideline, aim for 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, paired with 4 to 6 grams of carbohydrates and around 1 gram of fat per kilogram. However, these numbers should be adjusted based on body composition, training load, and metabolic response. The most effective bulking diet plan is both structured and flexible, allowing for personal tweaks based on feedback from your body.
This is also where understanding the ketogenic diet vs low carb approach becomes useful. While both minimize carbs, only keto induces nutritional ketosis. For muscle building, the distinction matters because low carb diets may still offer enough carbohydrates to support performance, whereas keto rarely does. So when choosing between low carb diet keto diet options, it’s crucial to weigh their impact on your energy levels and training volume.
Frequently Asked Questions: Clean Bulking and Healthy Muscle Gain
1. What’s the most common mistake people make when starting a bulking diet plan?
One of the most overlooked mistakes in a bulking diet plan is drastically increasing calories without gradually tracking progress. Many individuals assume that eating more automatically equals muscle gain, but the quality of your food and how your body responds to it matters immensely. Even a good bulking diet can backfire if you exceed your caloric needs too aggressively, leading to excessive fat gain instead of lean mass. Rather than blindly following popular diets people do when bulking, it’s critical to personalize your plan based on your body composition, training intensity, and metabolism. Monitoring metrics like waist circumference, strength progression, and digestion can guide effective adjustments to your bulk eating program.
2. Can you follow a vegetarian or vegan approach to bulking effectively?
Absolutely. A healthy bulking diet can be fully plant-based with the right planning. In fact, many athletes have successfully developed a clean meal plan for bulking using legumes, tofu, seitan, nuts, seeds, and fortified plant-based protein powders. The key is to include a variety of complementary proteins and energy-dense foods to meet both caloric and macronutrient needs. Some of the best bulking foods in plant-based diets include lentils, quinoa, peanut butter, avocado, and tempeh—each offering unique benefits for muscle synthesis and metabolic health. Plant-based bulking meal ideas should also prioritize nutrient timing to support energy and recovery around workouts.
3. What role does sleep play in a successful bulking meal plan?
Sleep is often underestimated in a bulking meal plan, yet it directly impacts muscle recovery, hormone regulation, and appetite. Without sufficient sleep, cortisol levels may rise, which can increase fat storage and reduce testosterone—two outcomes that undermine the goals of any bulking diet. Moreover, poor sleep impairs glucose metabolism, which can make even healthy bulking meals feel less effective in practice. Strategic use of certain bulking meals—such as those with complex carbohydrates and magnesium-rich foods—can promote better sleep quality. Incorporating sleep-friendly options like bananas, oats, and pumpkin seeds into your evening bulk food plan may help support deeper, more restorative rest.
4. Are there specific bulking meal ideas that help minimize bloating?
Yes, and this is especially important for those who struggle to increase calories without discomfort. Choosing good bulking meals that are lower in fermentable fibers and free from common allergens can help. For example, rice-based dishes with lean protein and cooked vegetables are gentler on the digestive system compared to raw salads or high-lactose options. Fermented foods like kefir or sauerkraut can also support gut health when included in a bulking diet meal plan. Hydration, mindful chewing, and spacing meals evenly throughout the day are additional tactics that enhance digestion and reduce bloating while following a proper bulking diet.
5. How can busy professionals stick to a bulking diet program without compromising quality?
Time constraints often derail the consistency needed for success in a bulking diet program. One solution is to simplify the structure of your bulking meal plan by relying on batch-cooked staples and assembling meals from pre-prepped ingredients. Overnight oats, quinoa bowls, and mason jar salads with legumes and olive oil make excellent healthy bulking meals for on-the-go professionals. Investing in quality storage containers and setting aside time each weekend to prepare a bulk food plan can make weekday eating effortless. Prioritizing portable snacks like trail mix or protein muffins helps fill in gaps while maintaining a good bulking diet even on the busiest days.
6. How can I rotate my meals without losing nutritional consistency in a clean bulking diet?
Variety in a clean bulking diet not only prevents palate fatigue but also broadens your intake of essential nutrients. Instead of changing every item in your bulking meals, rotate key ingredients—such as swapping brown rice for farro, chicken for turkey, or lentils for black beans—while keeping the macronutrient structure intact. This approach ensures your bulking meal plan remains balanced and aligned with muscle-building needs. Adding herbs, spices, and sauces made from whole-food ingredients can also breathe new life into familiar dishes without compromising on your goals. Ultimately, the best bulking meals are ones you’ll stick to, so building in flexibility is vital.
7. What advanced strategies can enhance the effectiveness of a bodybuilding bulking diet?
Advanced athletes may benefit from periodizing their bulking diet to include strategic refeed days or cycling carbohydrate intake based on training load. These strategies can improve insulin sensitivity and promote more efficient nutrient partitioning. Additionally, nutrient timing becomes increasingly important at higher training volumes. Consuming carbohydrate and protein-rich meals within 30–60 minutes post-workout can maximize recovery and lean mass retention. For serious lifters, tracking micronutrients, electrolyte balance, and even inflammation markers may refine their approach to the best bulking diet, especially when fine-tuning a competitive bodybuilding bulking diet.
8. Are there psychological challenges that come with following a bulking diet?
Yes, and they’re often underestimated. Gaining weight—even muscle—can be mentally difficult for individuals with a history of restrictive eating or a focus on leanness. Clean bulking requires a shift in mindset toward nourishment and long-term performance rather than aesthetics alone. Structured check-ins with a coach or registered dietitian can help reinforce the benefits of a healthy bulking diet while managing body image concerns. Social dynamics also play a role; explaining your bulk eating program at gatherings can feel awkward, so having supportive people around you who understand your goals is essential.
9. What are the best foods to eat when bulking if you struggle with appetite?
For hard gainers or those with small appetites, choosing calorie-dense, low-volume options is crucial. Smoothies are a staple here—they can pack in hundreds of calories using ingredients like oats, banana, peanut butter, and protein powder without being overly filling. Full-fat dairy, nut butters, trail mix, and granola also fit seamlessly into a good bulking diet for those struggling to meet their targets. Incorporating these into meals for bulking muscle can help maintain a calorie surplus without constant eating. Many of the best bulking foods are those that deliver a high energy payload with minimal digestive load.
10. What are some long-term health considerations when following a bulking diet plan repeatedly?
While bulking is effective for muscle growth, repeated bulking phases without attention to metabolic health can lead to insulin resistance, elevated blood lipids, or chronic inflammation. A healthy bulking diet should always include regular health screenings, including blood work to monitor lipid profiles, liver enzymes, and glucose levels. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, leafy greens, and fatty fish into your bulking meals can offer protective benefits. Cycling between lean bulking and maintenance phases gives your body time to recalibrate and prevents burnout. The best bulking diet is sustainable, flexible, and adaptive to your changing health and fitness needs over time.

Conclusion: Building Muscle with Purpose and Precision
At its core, clean bulking is about aligning your muscle-building goals with your overall health and lifestyle. A healthy bulking diet doesn’t rely on gimmicks or extremes but on the consistent intake of nutrient-dense, whole foods that support your body’s needs. By understanding what to eat on a bulk, choosing the best bulking meals, and tailoring your bulking meal plan to your unique physiology, you create a foundation for sustainable progress.
Whether you’re exploring bulking meal ideas, testing a new bulk food plan, or reconsidering if is keto a low carb diet that fits your training, it’s vital to return to the fundamentals. The best foods to eat when bulking are those that fuel performance, aid recovery, and promote long-term well-being—not just the ones that stack calories quickly.
Ultimately, the most effective bulking diet meal plan is one that’s rooted in experience, guided by science, and customized to support both your fitness and your health. By applying EEAT principles—experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness—you ensure your bulking journey is informed, intentional, and built to last.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
Clean Bulking: Overview, Guide, and Best Foods

