For individuals managing diabetes, nutrition is not merely about curbing sugar intake—it is about crafting a long-term, health-sustaining relationship with food that supports both blood sugar control and overall well-being. At the same time, the growing popularity of plant-based diets, including veganism, has prompted many to consider how such a dietary lifestyle can align with the unique needs of diabetes management. This has led to a rising interest in developing a vegan diabetic diet meal plan that is not only nutritious and satisfying but also evidence-based and tailored for glycemic control. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the intricacies of such a plan, offering expert insights and scientific backing to empower readers with actionable strategies. Whether you’re newly diagnosed, transitioning to a plant-based lifestyle, or seeking to refine your existing habits, this article is your companion on the journey toward sustainable, plant-powered diabetic wellness.
You may also like: Smart Strategies for Plant-Based Eating on a Budget: How to Nourish Your Body Without Overspending
Understanding the Intersection of Veganism and Diabetes
Veganism, by definition, excludes all animal products, focusing instead on whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. When considering diabetes management, the primary concern revolves around carbohydrate intake and its effect on blood glucose levels. Some mistakenly believe that a vegan diet is inherently high in carbohydrates and therefore unsuitable for diabetes. However, research suggests the opposite when the diet is properly structured. Whole plant foods contain fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients that can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, two key factors in diabetes control. Furthermore, by eliminating saturated fats from animal products, a vegan diet may support cardiovascular health, which is particularly important for those with diabetes, who are at higher risk of heart disease.
Creating a balanced vegan diabetic diet meal plan requires an understanding of how different plant-based foods affect blood sugar. While fruit, legumes, and whole grains do contain carbohydrates, their high fiber content often results in slower glucose absorption, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. Additionally, focusing on the glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) of foods helps in selecting those that will minimize spikes in blood sugar. Incorporating low-GI foods like lentils, quinoa, leafy greens, and berries can provide a robust nutritional foundation while supporting glycemic control. With thoughtful planning and a focus on whole foods, veganism can be an effective and sustainable dietary pattern for managing diabetes.

Macronutrient Balance in a Vegan Diabetic Meal Plan
One of the core principles in constructing a vegan diabetic diet meal plan is achieving the right macronutrient balance. This involves carefully managing carbohydrate intake while ensuring adequate protein and healthy fats. A well-rounded meal plan will typically include complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and starchy vegetables, which offer sustained energy without causing sharp blood sugar increases. Unlike refined carbohydrates, these foods are digested more slowly, resulting in a more gradual glucose release into the bloodstream.
Protein plays a vital role in maintaining muscle mass and promoting satiety, both of which are important for individuals with diabetes. In a vegan context, protein sources include lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, edamame, hemp seeds, and seitan. These not only supply essential amino acids but also contribute to the fiber intake that supports gut health and glucose metabolism. Equally important are healthy fats, which aid in nutrient absorption and provide a sense of fullness. Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are excellent plant-based sources of unsaturated fats that align well with a diabetic-friendly eating pattern.
Fiber is another crucial component often overlooked in standard diets but is abundant in plant-based eating. Soluble fiber, in particular, helps regulate blood sugar by slowing the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Beans, oats, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are standout choices for boosting soluble fiber intake. When these macronutrients are balanced thoughtfully in each meal, they create a foundation for stable blood sugar levels, sustained energy, and overall metabolic health.
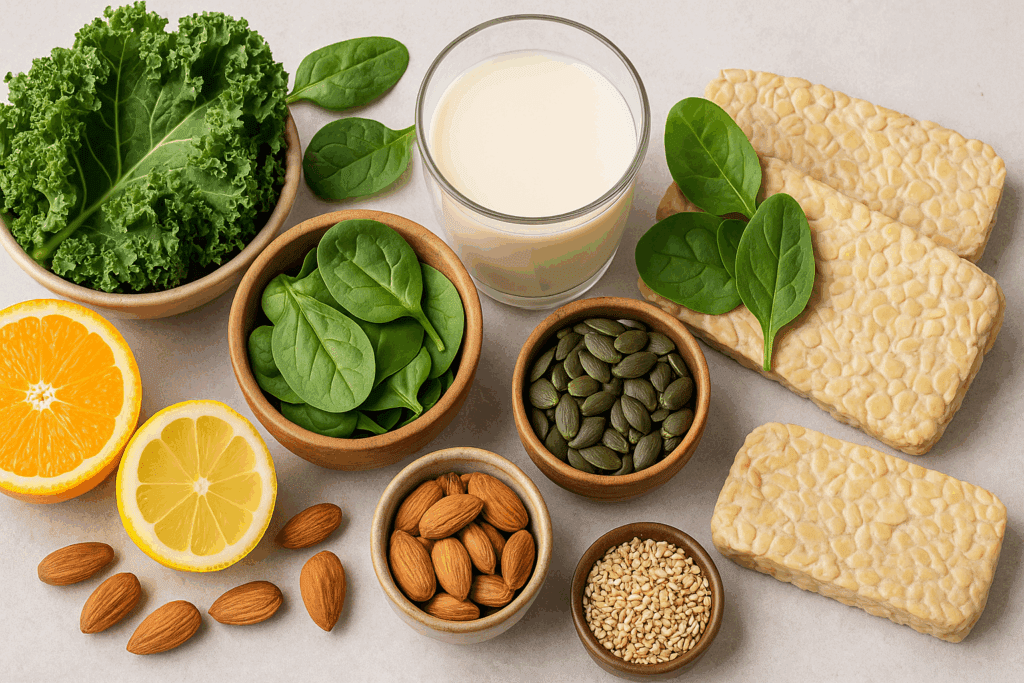

Essential Micronutrients to Consider
While a vegan diet can provide most nutrients through a variety of whole foods, certain micronutrients require special attention, especially when managing a chronic condition like diabetes. Vitamin B12 is perhaps the most well-known nutrient of concern, as it is naturally found in animal products. Supplementation or fortified foods are necessary for adequate intake. B12 plays a critical role in nerve function and energy metabolism, both of which are important for individuals with diabetes who may be prone to neuropathy.
Another key nutrient is vitamin D, which supports immune function and bone health. Although sunlight exposure can facilitate vitamin D synthesis in the skin, many individuals, especially those living in northern climates or with darker skin, may need fortified foods or supplements. Calcium, often associated with dairy, is readily available in plant-based sources like fortified plant milks, leafy greens, tahini, and almonds.
Iron and zinc are also essential minerals to monitor. While plant sources provide non-heme iron, its absorption is enhanced when consumed with vitamin C-rich foods like bell peppers, citrus fruits, or strawberries. Zinc, vital for immune health and wound healing, can be found in legumes, seeds, and whole grains. Omega-3 fatty acids, typically associated with fish, can be obtained through flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and algae-based supplements. By addressing these micronutrients in a vegan diabetic diet meal plan, individuals can safeguard against deficiencies while optimizing their health outcomes.
Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load: Tools for Smarter Food Choices
For individuals with diabetes, understanding the glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) of foods can transform the way they approach meals. GI measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood glucose levels, while GL takes into account the portion size and the food’s overall carbohydrate content. These tools are especially valuable when crafting a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF that emphasizes low-GI choices for optimal blood sugar regulation.
Low-GI foods include legumes, sweet potatoes, quinoa, non-starchy vegetables, and most fruits—particularly berries and apples. These foods provide a steady release of glucose, reducing the likelihood of post-meal spikes. On the other hand, high-GI foods like white bread, sugary cereals, and processed snacks can lead to rapid glucose increases, which are detrimental for long-term blood sugar control.
It is worth noting that the preparation method also influences the GI of foods. For example, al dente pasta has a lower GI than its overcooked counterpart, and intact whole grains like steel-cut oats have a more favorable effect than instant versions. By becoming familiar with these dynamics, individuals can make informed choices that align with both their health goals and taste preferences. When this knowledge is integrated into a well-structured vegan diabetic meal plan, it creates a roadmap for daily eating that promotes stability and satisfaction.
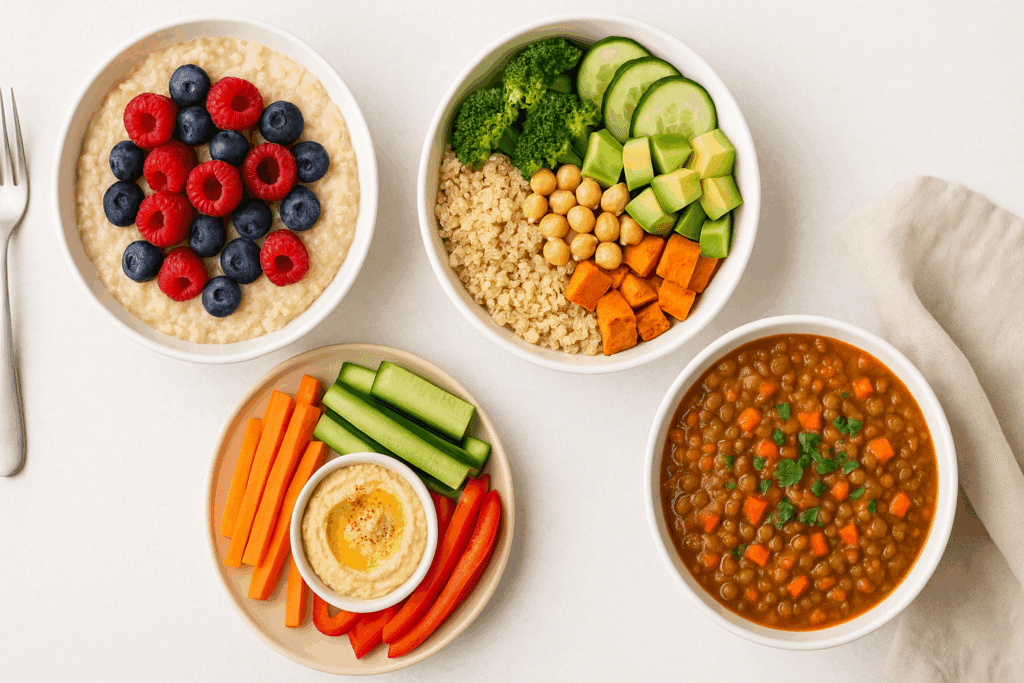

Building a Practical Daily Vegan Diabetic Meal Plan
Designing a daily meal plan requires both creativity and attention to nutritional details. A well-structured vegan diabetic diet meal plan should provide consistent carbohydrate intake throughout the day, spaced across meals and snacks to maintain steady glucose levels. Breakfast might feature steel-cut oats topped with chia seeds, blueberries, and a dollop of almond butter, offering complex carbs, fiber, protein, and healthy fats in one bowl.
For lunch, a quinoa salad with black beans, chopped kale, cherry tomatoes, avocado, and a lemon-tahini dressing delivers a nutrient-dense combination of low-GI carbohydrates and plant-based proteins. An afternoon snack could consist of hummus with cucumber slices or a small handful of walnuts with an apple. Dinner might involve a hearty lentil stew with brown rice and a side of steamed broccoli, balancing macronutrients while keeping the glycemic load in check.
It’s also beneficial to include a late-night snack, especially for individuals on insulin or medications that increase the risk of hypoglycemia. A small bowl of unsweetened soy yogurt with ground flaxseeds or a few roasted chickpeas can provide gentle, sustained nourishment through the night. Consistency, variety, and balance are the pillars of a successful meal plan, and when followed diligently, they can transform not just blood sugar levels but overall energy and well-being.
Meal Prep Strategies for Long-Term Success
Sticking to a vegan diabetic diet meal plan becomes significantly easier when supported by practical meal prep strategies. Preparing meals in advance reduces daily stress and makes it more likely that individuals will adhere to their dietary goals. Batch cooking staples such as brown rice, lentils, quinoa, and roasted vegetables creates a versatile base for multiple meals throughout the week.
Planning meals around seasonal produce not only enhances flavor and nutritional diversity but also supports sustainability and affordability. For instance, incorporating winter squash, Brussels sprouts, or dark leafy greens during colder months brings a rotation of nutrients while keeping the menu fresh. Storing meals in portioned containers helps with portion control and makes it easy to grab healthy options when time is limited.
Keeping healthy snacks readily available is another essential tactic. Pre-cut veggies, portioned nuts, or homemade energy balls made with oats, flaxseeds, and dates offer convenient choices that support blood sugar stability. Leveraging a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF can serve as a visual reminder and checklist, reinforcing habits and inspiring new ideas. With planning and organization, meal prep becomes an empowering ritual that fosters consistency and confidence.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Vegan Diets for Diabetes Management
The growing body of scientific literature supports the role of plant-based diets in managing and even preventing type 2 diabetes. Numerous studies have shown that vegan diets can lead to improved glycemic control, weight loss, and reduced dependency on medications. For example, a landmark study published in Diabetes Care found that participants who adopted a low-fat vegan diet experienced greater reductions in HbA1c levels compared to those following a conventional diabetes diet.
Mechanistically, this improvement is believed to stem from increased insulin sensitivity resulting from lower fat intake and higher fiber consumption. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of plant foods further contribute to metabolic improvements, offering protective benefits for organs affected by diabetes. Additionally, plant-based diets are associated with lower risks of cardiovascular disease, a leading cause of mortality among people with diabetes.
It is also important to acknowledge the psychological benefits of a vegan lifestyle. Many individuals report increased energy, improved digestion, and a greater sense of purpose in their food choices. When reinforced with a structured vegan diabetic meal plan, these dietary changes can lead to long-term adherence and a higher quality of life. As the evidence continues to accumulate, healthcare providers are increasingly recommending plant-based approaches as part of comprehensive diabetes care.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Despite its many benefits, a poorly executed vegan diet can fall short of supporting diabetes management. One common mistake is relying too heavily on processed vegan foods, which often contain added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats. These products may be labeled as vegan but can be counterproductive when it comes to maintaining healthy blood glucose levels.
Another frequent issue is inadequate protein intake, particularly if meals are not planned with a variety of legumes, soy products, and seeds. Skipping meals or consuming unbalanced ones can also lead to erratic blood sugar fluctuations. To prevent these pitfalls, it is essential to prioritize whole foods, plan meals in advance, and maintain a consistent eating schedule.
Nutrient deficiencies, particularly in B12, iron, or omega-3 fatty acids, can also pose challenges if not properly addressed. Regular blood work and consultation with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider can help monitor nutritional status and ensure all dietary needs are met. Education, planning, and support are key to avoiding these common errors and thriving on a vegan diabetic diet meal plan.
Accessing and Using a Free Vegan Diabetic Meal Plan PDF
One of the most useful tools for those starting or refining their dietary approach is a comprehensive vegan diabetic meal plan PDF. These downloadable resources provide sample menus, grocery lists, and nutrient breakdowns, simplifying the process of meal planning and making it more accessible. By following a well-designed guide, individuals can ensure that their meals are both nutritionally adequate and supportive of blood sugar control.
Such guides often include weekly meal plans with breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks mapped out for each day. They may also provide tips for dining out, managing social situations, and adjusting portion sizes based on personal energy needs. Many include educational material about reading nutrition labels, understanding the glycemic index, and pairing foods effectively.
Using a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF also fosters accountability and consistency. Keeping the plan visible on a refrigerator or accessible via mobile device helps reinforce habits and streamlines decision-making. For those new to veganism or diabetes management, these resources provide reassurance and clarity, turning an overwhelming task into a manageable, even enjoyable, process. As interest in plant-based health continues to grow, the availability of high-quality meal plans will only expand, offering more opportunities for individuals to take charge of their health with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions: Vegan Diabetic Diet Meal Plan
1. What are some advanced tools or apps that can support a vegan diabetic diet meal plan?
Several advanced tools can enhance how individuals approach their vegan diabetic diet meal plan. Apps like Cronometer and MyNetDiary allow for precise tracking of macronutrients and micronutrients, which is essential when balancing plant-based nutrition with blood sugar management. They also offer features tailored for people with diabetes, such as glucose monitoring and medication reminders. Integrating a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF into these platforms provides a structured baseline that can be customized daily. Over time, these tools empower users to adjust their diet based on patterns, making meal planning more data-driven and effective.
2. Can intermittent fasting be combined with a vegan diabetic diet meal plan?
Yes, intermittent fasting can be safely combined with a vegan diabetic diet meal plan, but it requires careful planning and medical oversight. People with diabetes, particularly those on insulin or glucose-lowering medications, should monitor their blood sugar closely when fasting. The key is to ensure that when food is consumed, it aligns with balanced principles of the vegan diabetic meal plan PDF, emphasizing fiber-rich whole foods and avoiding processed options. During eating windows, meals should be strategically spaced to support stable glucose levels and prevent post-fast spikes. With professional guidance, this approach can help improve insulin sensitivity and metabolic flexibility over time.
3. How can social dining or eating out be managed on a vegan diabetic diet?
Social dining can pose unique challenges, but it’s entirely manageable with the right strategies. Reviewing menus in advance allows for informed decisions and helps align restaurant choices with a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF. It’s also helpful to communicate dietary needs clearly with restaurant staff—most establishments are increasingly accommodating of both plant-based and diabetic-friendly requests. Opting for dishes centered on legumes, whole grains, and vegetables ensures better glycemic control even when dining out. Bringing a small emergency snack that aligns with your vegan diabetic diet meal plan can be a safeguard when healthy options are limited.
4. Are there specific culinary techniques that enhance blood sugar control in vegan meals?
Yes, certain cooking methods can significantly influence glycemic response. For example, steaming and roasting tend to preserve fiber and nutrients better than frying, which often adds unnecessary fats that can impact insulin sensitivity. Allowing cooked grains and legumes to cool before eating them—a method known to increase resistant starch—can lower their glycemic load. Using herbs and spices like cinnamon, turmeric, and fenugreek may also offer mild blood sugar benefits. When these techniques are incorporated into a vegan diabetic diet meal plan, they enhance both the culinary experience and its metabolic impact. This is especially useful for those customizing their vegan diabetic meal plan PDF based on individual glucose responses.
5. How can someone with diabetes assess whether their vegan diet is truly working for them?
While tracking blood sugar is a primary method, it’s equally important to monitor energy levels, mood stability, digestion, and satiety. An effective vegan diabetic diet meal plan should support consistent energy throughout the day without crashes or cravings. Regular lab tests such as HbA1c, fasting glucose, and lipid panels provide objective data on how the diet affects long-term markers. Comparing this data against progress outlined in a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF can help identify which foods and patterns are most beneficial. Journaling meals, glucose readings, and symptoms is another powerful self-assessment tool that reveals how well the plan is working in real life.
6. What are emerging food trends that could benefit a vegan diabetic diet meal plan?
One emerging trend is the use of ancient grains like teff, fonio, and amaranth, which are nutrient-dense and have low to moderate glycemic indexes. Fermented plant-based foods like tempeh, miso, and plant-based kefirs are gaining popularity for their gut-health benefits, which can indirectly influence insulin sensitivity. Innovations in high-fiber pasta alternatives and legume-based snacks also align well with the structure of a vegan diabetic diet meal plan. Additionally, meal delivery services offering tailored, whole-food vegan options are becoming more sophisticated, often integrating a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF into their service model. These innovations allow for greater convenience without sacrificing nutritional precision.
7. How can emotional and psychological factors affect adherence to a vegan diabetic meal plan?
Managing diabetes can be emotionally taxing, and when combined with the discipline required for a vegan lifestyle, it can sometimes feel overwhelming. Stress, emotional eating, and social pressures can derail even the most well-intentioned vegan diabetic diet meal plan. To counter this, it’s vital to incorporate emotional resilience strategies such as mindfulness, support groups, or therapy. Having a visually appealing vegan diabetic meal plan PDF on hand can reduce decision fatigue and reinforce positive eating patterns. Over time, building rituals around meal prep and focusing on food as a form of self-care can strengthen long-term adherence.
8. Can a vegan diabetic meal plan support athletic performance and muscle gain?
Absolutely. Many plant-based athletes thrive on diets that align closely with the principles of a vegan diabetic diet meal plan. With the right balance of complex carbohydrates, plant proteins, and healthy fats, it’s possible to support intense training while keeping blood sugar stable. High-protein plant sources like tempeh, tofu, lentils, and protein powders derived from pea or brown rice are staples in this context. Meal timing becomes particularly important for athletes managing diabetes, and integrating guidance from a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF can optimize both recovery and glucose control. Ensuring adequate caloric intake is also key to maintaining muscle mass and preventing catabolism.
9. What is the long-term impact of following a vegan diabetic diet meal plan on medication use?
Several studies suggest that adhering to a well-structured vegan diabetic diet meal plan can reduce the need for diabetes medications over time, particularly in type 2 diabetes. Improved insulin sensitivity, weight management, and reduced systemic inflammation are key mechanisms behind this shift. Of course, changes to medication should always be made under medical supervision, but many patients experience significant enough improvements to warrant dosage reductions. Comparing outcomes with benchmarks found in a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF helps document progress and guide clinical conversations. Long-term success often depends on consistency, regular monitoring, and personalized adjustments to the meal plan.
10. Are there unique benefits of using a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF versus tracking meals manually?
A vegan diabetic meal plan PDF offers structured guidance, helping eliminate guesswork and reducing daily decision fatigue. Unlike manual tracking, which can be inconsistent or incomplete, a well-designed PDF ensures nutritional adequacy and glycemic balance with each meal. It also offers a visual layout that can be more user-friendly, especially for beginners or those overwhelmed by managing multiple health goals. Many PDFs now include grocery lists, prep timelines, and substitution tips, which enrich the planning experience. Incorporating a vegan diabetic diet meal plan into this format helps users maintain focus and confidence, particularly in the initial stages of dietary transition.
Empowering Your Health Journey with a Vegan Diabetic Diet Meal Plan
Incorporating a vegan diabetic diet meal plan into your lifestyle is more than just a dietary shift—it’s a strategic, empowering decision to prioritize both immediate health and long-term wellness. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense plant foods and integrating practical tools like a vegan diabetic meal plan PDF, individuals can take control of their blood sugar levels, enhance metabolic function, and reduce their risk of complications. This evidence-backed approach not only supports glycemic control but also promotes overall vitality, offering a sustainable and compassionate path to better health. As with any significant lifestyle change, success is grounded in education, preparation, and support. When those elements are in place, the result is a nourishing, energizing way of eating that aligns with both personal values and optimal diabetes management. Whether you are just beginning or deepening your plant-based journey, know that each meal is an opportunity to support your body, honor your health, and build a future rooted in well-being.
Further Reading:
A Complete Vegan Meal Plan and Sample Menu
Vegetarian Meal Plan for Diabetes, Created by a Dietitian

