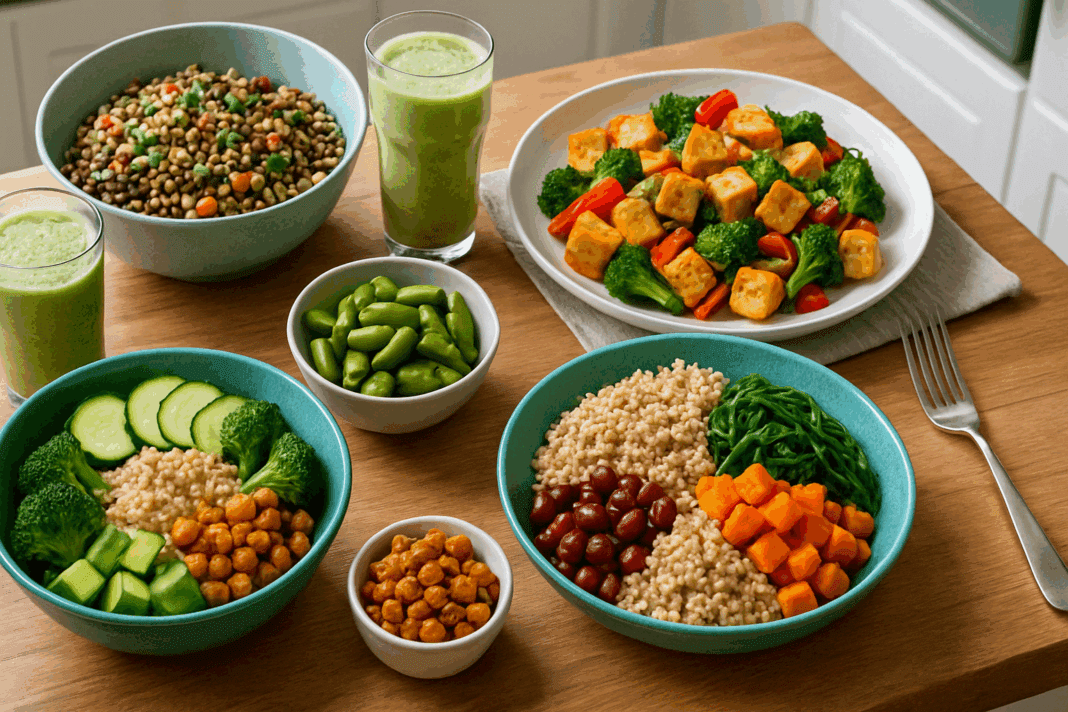A high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss is more than just a trendy concept—it’s a scientifically grounded strategy that combines the benefits of plant-based nutrition with the metabolic power of protein. As interest in whole-food, plant-based eating grows, so does the need for detailed, evidence-based guidance on how to create a satisfying, high protein vegetarian diet plan that promotes both fat loss and long-term health. This article explores how to build a high protein vegetarian diet meal plan that supports weight loss, improves fullness, and aligns with the best practices in nutritional science.
You may also like: Plant Based Diet vs Standard American Diet: What the Latest Studies Reveal About Long-Term Health Outcomes
Understanding the Role of Protein in Vegetarian Weight Loss
Protein plays a central role in the regulation of appetite, body composition, and metabolic rate. For those pursuing vegetarian high protein weight loss goals, getting enough protein without animal products can be a concern—but it is entirely achievable with strategic food choices. Numerous studies have shown that higher-protein diets can help preserve lean muscle mass during caloric restriction, leading to more sustainable weight loss. In addition, protein has a thermogenic effect, meaning it requires more energy to digest than fats or carbohydrates, boosting calorie expenditure.
In vegetarian diets, high-quality protein sources such as legumes, lentils, soy products, seitan, quinoa, chia seeds, and plant-based protein powders can effectively meet daily protein needs. Moreover, these foods are naturally rich in fiber, which supports gut health and enhances satiety. Unlike typical meat-centric diets, a high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss can also provide a broader range of micronutrients and phytochemicals, contributing to overall well-being.
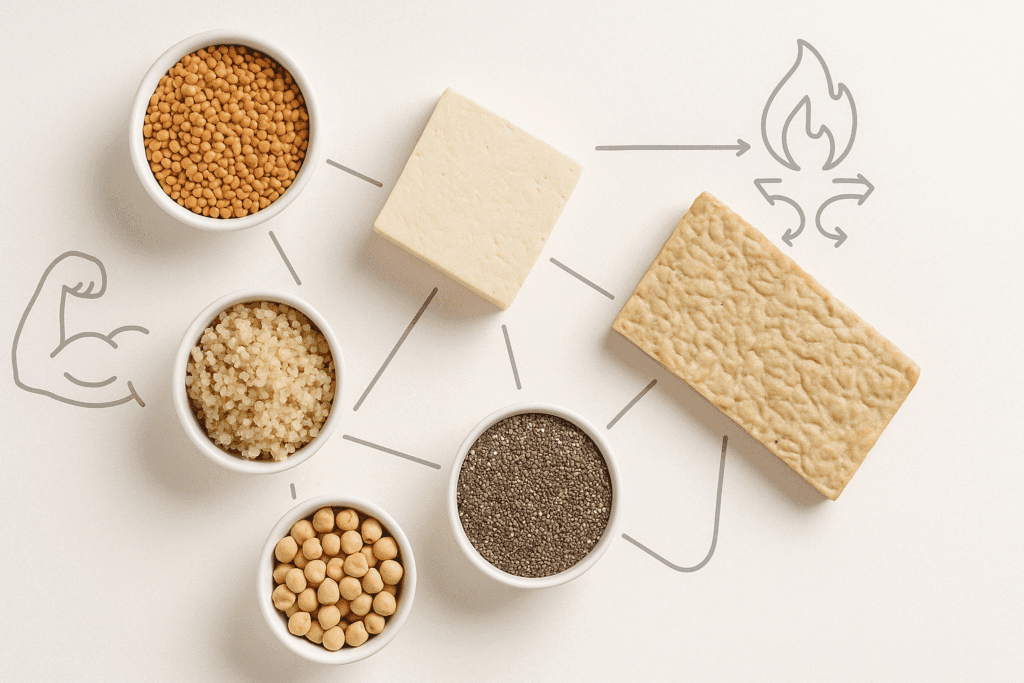
Crafting a High Protein Vegetarian Diet Plan: Evidence-Based Foundations
To create a sustainable high protein vegetarian diet plan, the key is balance. It’s not just about loading up on protein-rich foods—it’s about combining them intelligently with high-fiber, low-glycemic carbohydrates and healthy fats to stabilize blood sugar and reduce cravings. Whole grains such as brown rice, farro, and barley, when paired with legumes, form complete protein profiles. Soy-based foods, such as tempeh and edamame, are especially effective in vegetarian diets due to their high bioavailability.
The inclusion of high protein low fat vegetarian foods is particularly important for those aiming to lose weight. Foods such as nonfat Greek yogurt (for lacto-vegetarians), low-fat cottage cheese, tofu, and seitan deliver substantial protein with minimal fat. For those wondering, “Can vegetarians eat eggs and milk?” the answer depends on the type of vegetarian. Lacto-ovo vegetarians do consume dairy and eggs, which can be excellent sources of complete protein. Meanwhile, vegans rely on plant-exclusive sources like legumes, hemp seeds, and fortified protein powders.
Low calorie high protein foods vegetarian eaters can benefit from include mushrooms, lentils, zucchini, and leafy greens, which provide both volume and nutrients without excessive caloric intake. These foods are ideal for crafting a high protein diet plan for vegetarians focused on fat loss while maintaining fullness and energy levels.
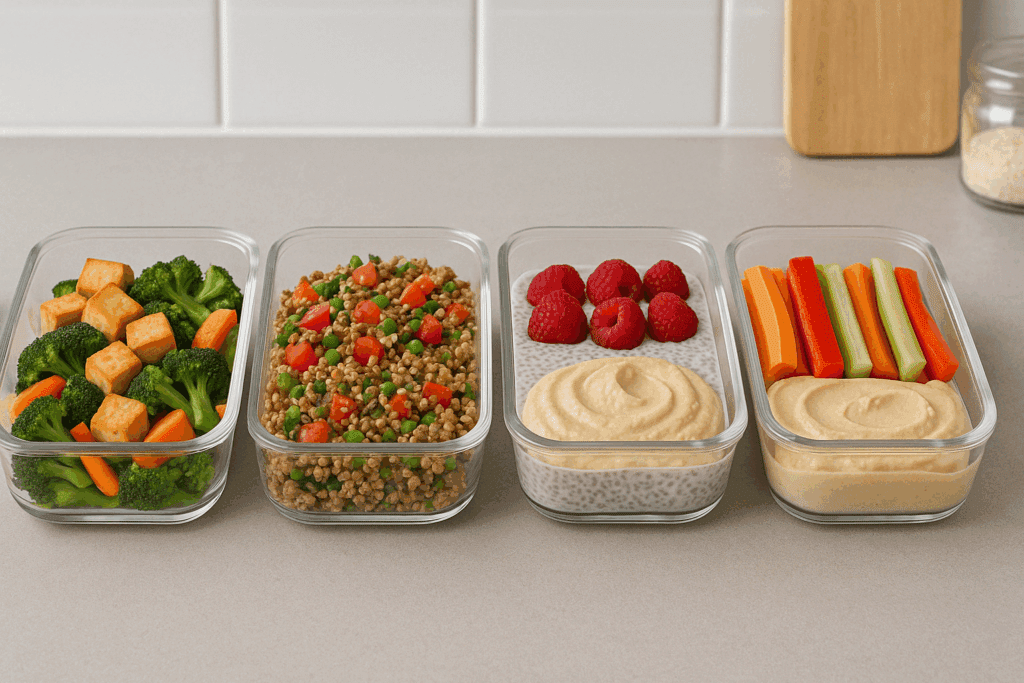
Meal Planning for Fat Loss and Fullness: What Science Suggests
Creating a high protein vegetarian diet meal plan that enhances satiety and supports fat loss requires attention to timing, portion control, and nutrient density. Starting the day with a protein-rich breakfast, such as a tofu scramble with vegetables or a chia seed pudding blended with plant-based protein powder, can prevent mid-morning hunger and reduce overall caloric intake.
Lunch and dinner should include a combination of protein, fiber, and healthy fats. For example, a lentil and quinoa salad with tahini dressing offers a satisfying and nutrient-dense option. Snack choices matter, too. Instead of processed chips or sugary granola bars, high protein meal plan vegetarian snack ideas might include roasted chickpeas, edamame, or a smoothie with unsweetened almond milk, spinach, flaxseed, and vegan protein powder.
It’s also worth noting that slow digestion of high-fiber, high-protein meals can prevent blood sugar crashes and reduce the likelihood of overeating later in the day. Incorporating high protein vegan diet for weight loss strategies that include whole plant foods also aligns with anti-inflammatory and disease-preventing dietary patterns.
Comparing Plant-Based Protein Strategies to Other Popular Diets
A common question for those considering a high protein vegetarian approach is how it stacks up against popular low carbohydrate eating plans, particularly ketogenic and low carb diets. While it may seem that a vegetarian diet is the opposite of a high fat, low carb approach, there are important overlaps worth understanding.
So, is keto a low carb diet? Yes, the ketogenic diet is a form of very low carbohydrate, high fat dieting that induces a state of ketosis in the body, promoting fat burning. But when comparing ketogenic diet vs low carb alternatives, the distinction lies in the extent of carb restriction. A standard low carb diet may include up to 150 grams of carbohydrates per day, whereas keto usually restricts this to under 50 grams.
In discussions of low carb diet keto diet comparisons, it’s important to recognize that while keto can lead to rapid short-term weight loss, it may not be sustainable for all individuals, especially those on plant-based diets. Is a keto diet sustainable in the long term? Research suggests that strict carb restriction can lead to nutrient deficiencies and reduced adherence over time. In contrast, a high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss emphasizes whole foods and sustainable habits, often leading to better long-term success.
Additionally, when comparing a keto diet vs low carb diet for vegetarians, the question arises: is keto no carbs? The answer is no. While extremely low in carbohydrates, keto still allows trace amounts, often from vegetables and nuts. However, the limited intake of grains and legumes makes keto less compatible with vegetarian preferences, especially those emphasizing plant diversity.
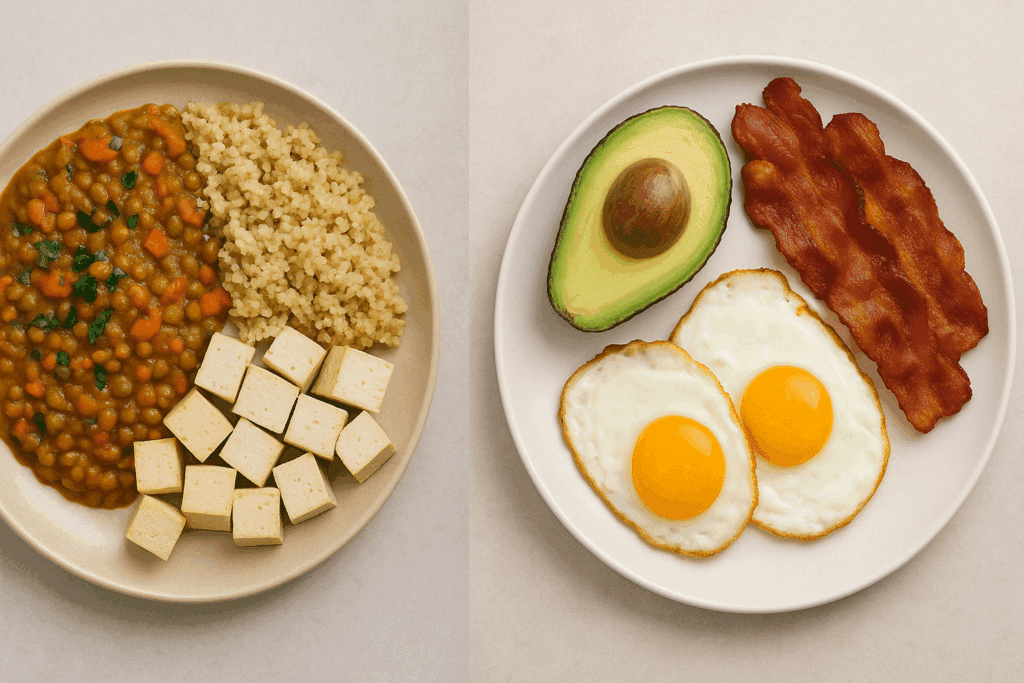
Addressing Common Questions About Vegetarian Eating Patterns
Newcomers to vegetarian diets often have questions that affect meal planning and protein intake. For example, do vegetarians eat rice? Absolutely. Whole grains like brown rice are staples in many vegetarian meal plans and pair well with beans to create a complete protein. Another frequent question is: does vegetarian eat butter? This depends on the type of vegetarian. Lacto-vegetarians may consume butter, while vegans avoid all animal-derived products.
For those following a high protein diet for vegetarians to lose weight, understanding these distinctions is crucial. Eggs and dairy can be significant protein contributors for lacto-ovo vegetarians, while vegans rely more heavily on soy, legumes, and grains. The flexibility of vegetarianism allows individuals to tailor their high protein meal plan vegetarian style to fit ethical, nutritional, and lifestyle needs.
The Science Behind Protein Needs for Weight Management
Scientific research supports the idea that increasing dietary protein can help with appetite regulation and body composition. A high protein diet plan for vegetarians should aim for 1.2 to 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day for weight loss support, depending on activity levels. For example, a 150-pound person (about 68 kg) would need between 82 and 109 grams of protein daily.
For vegetarians, meeting these targets requires careful food pairing and frequent meals. Fortunately, plant-based proteins often come with additional fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants that support whole-body health. This makes the vegetarian high protein weight loss approach not only effective but also beneficial for long-term wellness, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Is Keto a Good Diet Compared to Vegetarian High Protein Plans?
Is keto a good diet? The answer depends on the individual. For some, a ketogenic diet offers short-term benefits, especially in managing epilepsy or insulin resistance. However, its high intake of saturated fats and exclusion of fiber-rich foods can present long-term health challenges. When comparing the ketogenic diet vs low carb vegetarian alternatives, plant-based approaches offer greater flexibility, diversity, and nutrient density.
A high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss emphasizes whole foods, including legumes, grains, nuts, and vegetables. This provides a more sustainable and evidence-based path to health. It also sidesteps common keto pitfalls such as constipation, vitamin deficiencies, and excessive reliance on animal fats. So, while keto may be effective in certain clinical scenarios, a vegetarian approach grounded in high protein and whole food principles is often more appropriate for long-term weight management and disease prevention.
Building Your Personalized High Protein Vegetarian Diet Meal Plan
Personalization is essential when developing a high protein vegetarian diet plan. This means aligning food choices with calorie needs, preferences, and any specific health considerations. Start by calculating your daily calorie target, then allocate about 25-30% of those calories to protein. With a 1,600-calorie weight loss plan, this would translate to around 100 to 120 grams of protein per day.
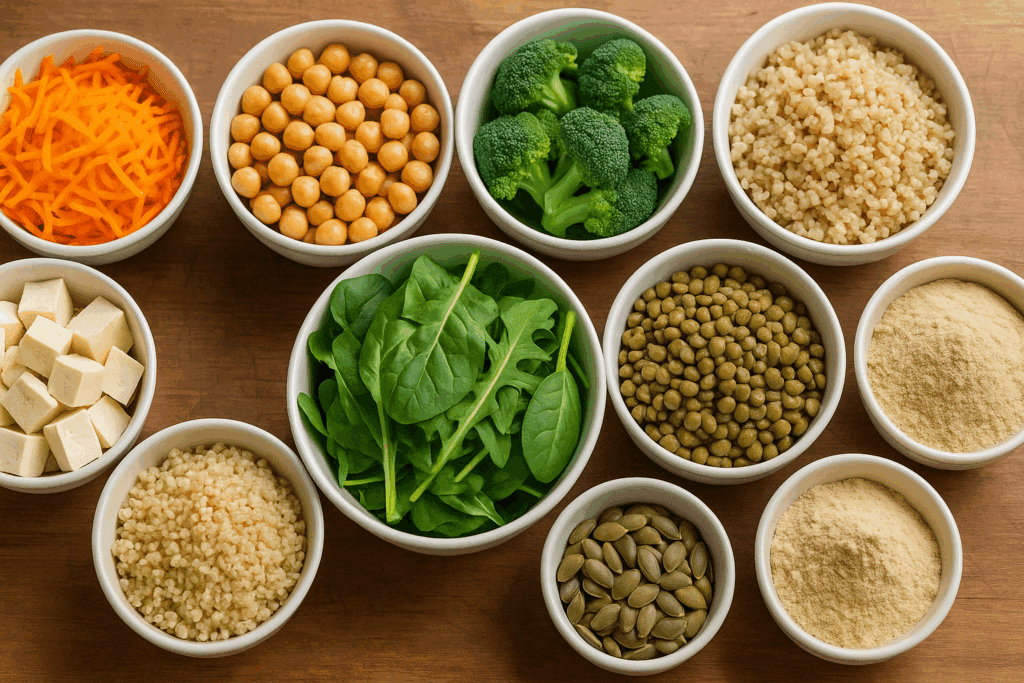
Focus on including low calorie high protein foods vegetarian eaters thrive on, such as lentils, black beans, nonfat dairy, tofu, tempeh, and textured vegetable protein. Plan meals around these staples, and supplement as needed with a high-quality plant-based protein powder. Don’t forget to include a wide variety of vegetables, which add volume, nutrients, and satiety without contributing excessive calories.
For those pursuing a high protein vegan diet for weight loss, it is important to ensure adequate intake of essential amino acids. Combining foods such as rice and beans, hummus and whole grain pita, or oats with hemp seeds can provide balanced protein. Fortified foods and B12 supplementation may also be needed for optimal health.
Sustaining Success with Whole-Food Nutrition and Lifestyle Habits
No diet plan works in isolation. To truly benefit from a high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss, one must pair nutrition with supportive lifestyle habits. This includes regular physical activity, adequate sleep, mindful eating, and stress management. Exercise enhances muscle preservation and metabolic rate, especially when paired with higher protein intake.
Mindful eating practices can further enhance the effectiveness of your high protein meal plan vegetarian style. By slowing down during meals, savoring flavors, and listening to hunger cues, individuals are less likely to overeat or turn to low-quality snacks. Over time, this builds a positive relationship with food and improves long-term outcomes.
When comparing sustainable eating strategies, the question often arises again: is a keto diet sustainable? While some may adhere to it for months, long-term adherence is generally low due to its restrictive nature. In contrast, a high protein vegetarian diet meal plan is more flexible, satisfying, and inclusive—making it easier to maintain over the long haul.

Standalone Resource Complementing the Main Article
1. How can a high protein vegetarian diet plan support sustainable weight loss without relying on processed meat substitutes?
A high protein vegetarian diet plan can be highly effective for long-term weight management when built around whole foods like legumes, quinoa, tofu, Greek yogurt, and nuts. Unlike ultra-processed meat alternatives, these foods provide not only protein but also fiber, essential micronutrients, and healthy fats that support satiety and metabolic health. For instance, lentils and black beans deliver both protein and resistant starch, which aid in appetite regulation and blood sugar control. With proper meal planning, a vegetarian high protein weight loss approach can avoid the sodium and additives often found in faux meats while still offering variety and satisfaction. Incorporating minimally processed, high protein low fat vegetarian foods like tempeh or edamame can further enhance results without compromising on health.
2. What psychological benefits are associated with following a high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss?
While most people focus on the physical outcomes, the psychological impact of a high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss is significant and under-discussed. Studies suggest that improved body composition and blood sugar stability from high protein intake may help reduce mood swings, anxiety, and depressive symptoms, especially when paired with regular physical activity. Additionally, aligning eating habits with ethical or environmental values can enhance a person’s sense of purpose and self-efficacy. This alignment fosters intrinsic motivation, making dietary adherence more sustainable over time. By choosing a high protein vegan diet for weight loss that aligns with personal values and supports mental clarity, individuals often report a greater sense of control and well-being.
3. How can meal timing enhance the effectiveness of a high protein vegetarian diet meal plan?
Meal timing plays a critical role in the success of any dietary approach, especially when weight loss is the goal. When following a high protein vegetarian diet meal plan, consuming protein-rich meals earlier in the day—such as a tofu scramble or lentil oatmeal breakfast—can help regulate appetite hormones and reduce evening cravings. Front-loading protein also improves energy balance and metabolic rate during peak activity hours. Emerging research even supports time-restricted eating within a plant-based framework, where eating within an 8–10 hour window amplifies fat-burning benefits. Thus, aligning a high protein diet for vegetarians to lose weight with strategic meal timing can elevate both compliance and metabolic outcomes.
4. Are there cultural variations of high protein meal plan vegetarian styles that can be used to avoid dietary boredom?
Absolutely. Many global cuisines offer rich traditions of plant-based eating that naturally align with a high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss. For example, Indian cuisine features dal (lentils), chana masala (chickpeas), and paneer (if not vegan), which can be easily adapted for low-calorie, high-protein vegetarian meals. Middle Eastern dishes like hummus, falafel (baked), and mujadara provide diverse flavor profiles with lentils and beans as staples. Southeast Asian cuisines often use tofu, tempeh, and edamame as protein bases with minimal oil. Incorporating these cultural styles into your high protein vegetarian diet meal plan not only prevents flavor fatigue but also increases nutrient diversity and long-term satisfaction.
5. What lesser-known low calorie high protein foods vegetarian eaters can rely on?
Beyond the usual suspects like tofu and legumes, there are several underrated options in a high protein vegetarian diet plan. Hemp seeds, for instance, contain all nine essential amino acids and provide about 10 grams of protein per 3 tablespoons with minimal calories. Seitan, while more processed, is extremely high in protein and can be used sparingly for variety. Nutritional yeast adds cheesy flavor and a protein boost to soups and salads. Additionally, lupini beans are gaining traction as a low calorie high protein food for vegetarians, offering over 25 grams of protein per cup with very little fat. Strategically rotating in these unique options can enrich a high protein meal plan vegetarian strategy without redundancy.
6. How do high protein low fat vegetarian foods impact hormonal health, particularly for women?
For women, especially those navigating perimenopause or postmenopause, a diet rich in high protein low fat vegetarian foods can offer hormonal balance by supporting muscle mass and reducing insulin resistance. Plant-based proteins like lentils, tempeh, and soy milk contain phytoestrogens, which can mildly mimic estrogen and help alleviate hormonal fluctuations. Additionally, stabilizing blood sugar with balanced high protein vegetarian diet plans may reduce the risk of PCOS symptoms and improve menstrual regularity. Importantly, choosing whole foods over processed vegetarian protein bars or faux meats limits exposure to endocrine-disrupting additives. As such, a well-structured high protein vegan diet for weight loss can serve both metabolic and hormonal goals.
7. What’s the role of high protein vegetarian diets in preserving lean muscle during weight loss?
One of the primary challenges during weight loss is minimizing muscle loss. A high protein diet plan for vegetarians is critical in maintaining lean body mass while promoting fat reduction. Research shows that diets providing 1.2–1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight preserve muscle better during caloric restriction. Vegetarian sources like tempeh, Greek yogurt, and quinoa deliver complete amino acid profiles when combined thoughtfully. Resistance training enhances this effect, especially when paired with a consistent high protein vegetarian diet meal plan. This dual approach not only protects strength but also boosts basal metabolic rate, making weight maintenance easier post-diet.
8. What are some effective strategies for meal prepping a high protein vegan diet for weight loss?
Meal prep is a game-changer for sticking to a high protein vegan diet for weight loss. Begin by selecting a few versatile staples like black beans, lentils, chickpeas, and quinoa, which can be used across multiple meals. Prepare large batches of roasted tofu, tempeh, or lentil loaves, and pair them with steamed veggies and healthy starches. Snack prep is just as important—think edamame, roasted chickpeas, or protein-packed hummus with carrots. Using airtight containers and freezing in portions can prevent spoilage and support adherence. With just a few hours of prep weekly, a high protein meal plan vegetarian approach becomes significantly more practical and consistent.
9. Can high protein vegetarian diet plans support athletic performance or muscle gain?
Yes, high protein vegetarian diet plans are increasingly popular among athletes and bodybuilders, proving that plant-based doesn’t mean protein-deficient. With proper planning, athletes can meet their needs using soy products, legumes, whole grains, and plant-based protein powders. For muscle synthesis, pairing complementary proteins—like rice and beans—ensures all essential amino acids are consumed. Pre- and post-workout meals in a high protein diet for vegetarians to lose weight or build muscle may include smoothies with pea protein or tempeh stir-fries with brown rice. Many plant-based athletes report enhanced recovery and reduced inflammation, making a high protein vegan diet for weight loss and performance a powerful combination.
10. How will advancements in food tech affect high protein vegetarian diets in the future?
Food technology is revolutionizing the way we approach high protein vegetarian diets. Innovations like precision fermentation are making it possible to produce animal-identical proteins without animals, offering new options for high protein low fat vegetarian foods. Meanwhile, developments in cellular agriculture and algae-based proteins may soon enhance the sustainability and nutrient density of vegetarian high protein weight loss products. Personalized nutrition apps will also allow users to tailor their high protein vegetarian diet plan to genetics and microbiome data. As plant-based food systems evolve, the potential for a high protein meal plan vegetarian lifestyle to meet both personal and planetary health goals is unprecedented.

A Science-Backed Path to Fat Loss and Fullness with Vegetarian Protein
Choosing a high protein vegetarian diet for weight loss is not only possible—it’s supported by a growing body of nutritional science. By focusing on low calorie high protein foods vegetarian eaters enjoy, incorporating diverse plant-based proteins, and structuring meals for satiety and metabolic efficiency, individuals can achieve significant health improvements.
This approach is particularly advantageous when considering the limitations of more restrictive options. Questions like “Is keto a good diet?” or “Is keto no carbs?” reflect growing concerns about the sustainability and nutritional balance of ketogenic eating. In comparison, the high protein vegetarian model offers a nutrient-dense, fiber-rich, and ethically aligned path to long-term wellness.
Ultimately, with proper planning and consistent habits, a high protein diet for vegetarians to lose weight can deliver not just fat loss, but enhanced energy, digestive health, and overall vitality. Whether you’re new to plant-based eating or looking to refine your current approach, a high protein vegetarian diet meal plan offers a compelling, science-backed solution for achieving your weight loss goals while nourishing your body from the inside out.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
7-Day No-Sugar High-Protein Vegetarian Meal Plan, Created by a Dietitian
How to Lose Weight on a Vegetarian Diet
High Protein Vegetarian Diet: Weight Loss Plan
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.