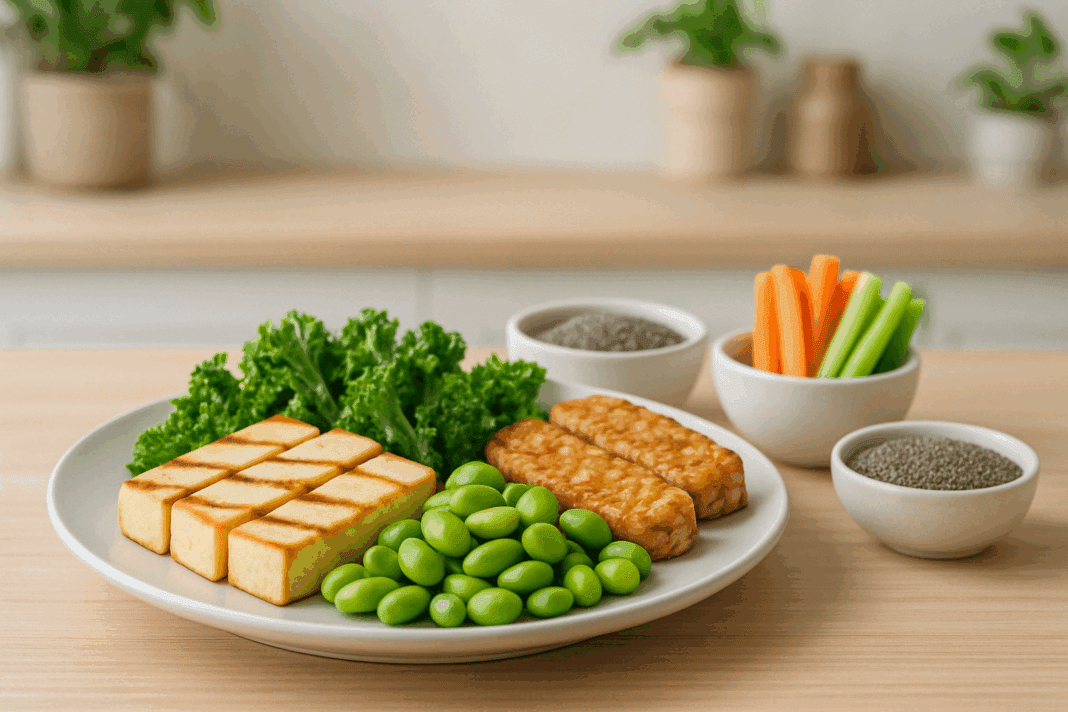
In the ever-expanding landscape of nutrition advice, diet trends, and miracle meal plans, the quest for effective weight loss strategies often leads us to one compelling solution: foods that are both low in calories and high in protein. This winning combination not only supports fat loss but also preserves lean muscle mass, enhances satiety, and stabilizes energy levels throughout the day. For individuals striving to lose weight while staying nourished and satisfied, understanding the science and application behind high protein low calorie foods is essential.
You may also like: Plant Based Diet vs Standard American Diet: What the Latest Studies Reveal About Long-Term Health Outcomes
The emphasis on low calorie protein sources marks a shift from outdated calorie-cutting models toward a more strategic, evidence-based nutritional approach. Rather than depriving the body, the modern low calorie diet supports metabolic health, hormonal balance, and psychological well-being—all critical for sustainable results. Whether you’re navigating plant-based eating, exploring flexitarian plans, or simply aiming to make more mindful food choices, discovering what to eat to feel full on a low calorie plan can be the key to long-term success.
Understanding Protein Density and Satiety in a Low Calorie Diet
Protein’s role in a low calorie diet extends far beyond muscle repair or bodybuilding. In fact, protein is the macronutrient most responsible for promoting satiety and curbing overeating. Studies have consistently shown that meals rich in low calorie high protein ingredients activate appetite-regulating hormones like GLP-1 and peptide YY while suppressing ghrelin, the hunger hormone. This biochemical response leads to a significant reduction in overall caloric intake, often without conscious restriction.
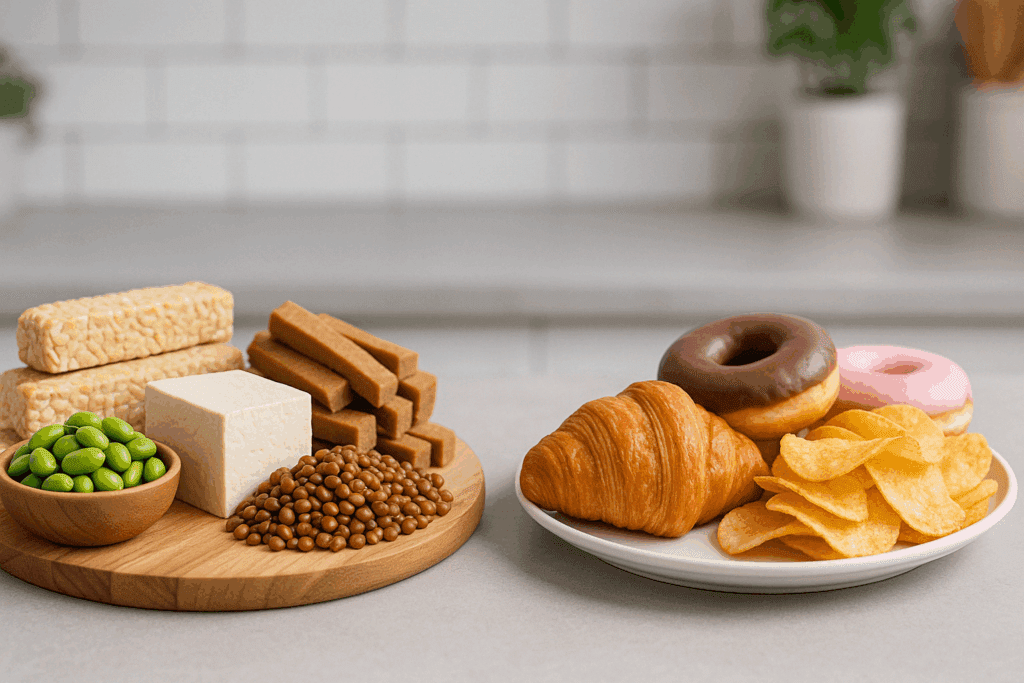
But it’s not just about eating more protein—it’s about choosing the highest protein foods with lowest calories. Foods like tempeh, lentils, edamame, seitan, and tofu top the list in plant-based diets. These offer a remarkably high protein content per calorie while also delivering fiber, vitamins, and minerals that support a healthy metabolism. A food with most protein and least calories becomes the linchpin of a filling low calorie diet when strategically combined with nutrient-dense sides like leafy greens or low starch vegetables.
The key to optimizing results lies in protein density: how many grams of protein you get per calorie. The lowest calorie high protein foods can deliver up to 10 grams of protein per 100 calories, making them ideal for portion control without nutrient deprivation. When incorporated into a structured plan, these choices form the foundation of what many call the best low calorie high protein foods for achieving sustained weight loss.

Low Calorie Vegetables That Enhance Volume and Fullness
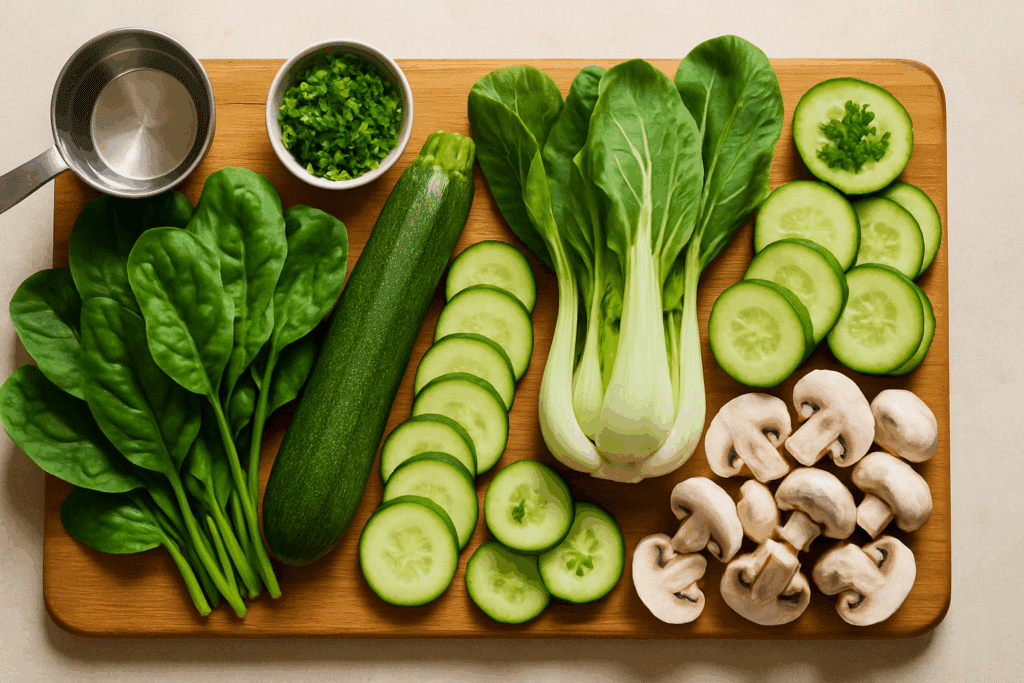
While protein takes center stage in many weight loss discussions, the role of vegetables with least amount of calories is just as vital. These foods serve a dual function: they add bulk to meals without adding excess energy and contribute essential micronutrients and antioxidants. For example, vegetables like zucchini, spinach, bok choy, arugula, cucumbers, and mushrooms can all be consumed in generous portions, helping you feel full while staying within your daily calorie goals.
Low calorie vegetables also contribute water and fiber, two elements that are often overlooked in satiety science. Water-rich vegetables like celery and lettuce physically expand in the stomach, activating stretch receptors that signal fullness. Similarly, high-fiber vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts slow gastric emptying and promote prolonged satiety, making them excellent foods that are low calorie but filling.
Integrating these vegetables into meals alongside low calorie protein sources improves the palatability and sustainability of a low calorie whole foods plan. The pairing of low cal veggies with foods like lentil pasta or grilled tofu not only satisfies the palate but also balances blood sugar, supporting energy levels and mood stability. These factors play a crucial role in adherence to any low calorie diet, especially over the long term.

The Science Behind Low Calorie Protein Rich Foods and Metabolic Function
Beyond hunger control, the strategic use of low calorie protein rich foods enhances several aspects of metabolism. High-protein diets have been shown to increase thermogenesis—the energy cost of digestion—resulting in a slight metabolic boost after each meal. This phenomenon, known as the thermic effect of food, is significantly higher for protein than for fat or carbohydrates.
In addition, protein supports lean muscle preservation during weight loss, which is critical for maintaining basal metabolic rate (BMR). When caloric intake is reduced, the body may catabolize muscle tissue for energy unless adequate protein is consumed. Including high protein low cal foods in each meal counters this loss, preserving strength and metabolic resilience.
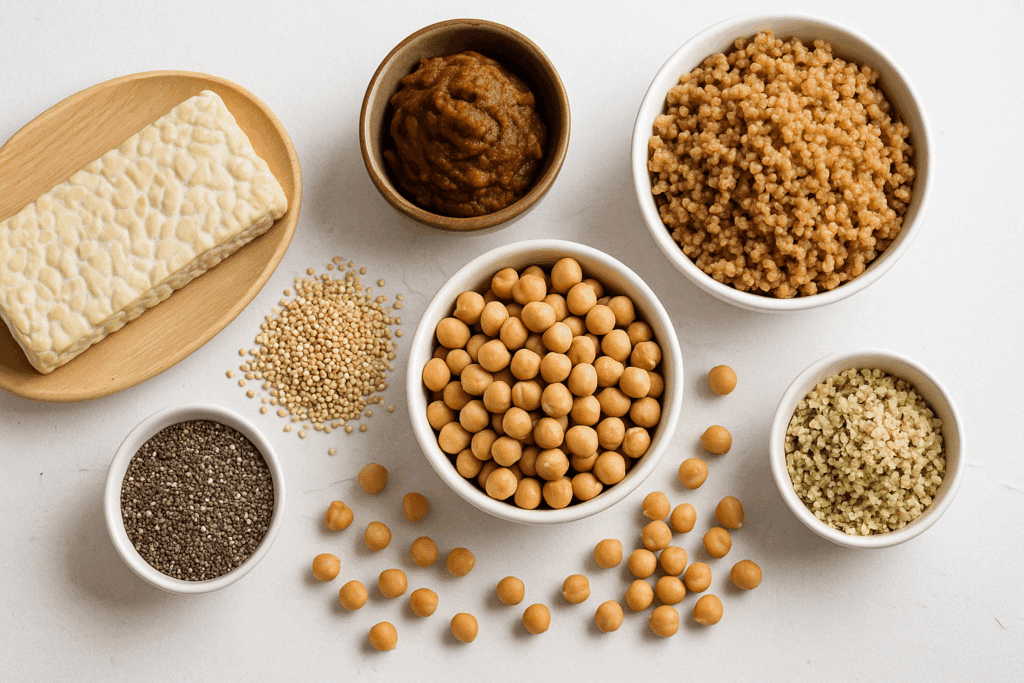
Not all protein is created equal, however. The best low calorie protein options also provide a rich array of amino acids without excessive saturated fat or sodium. Examples include hemp seeds, chia seeds, and unsweetened soy products, which supply complete protein profiles within a modest caloric envelope. These foods are staples in plant-based healthy eating and are widely considered among the best low calorie high protein foods for active individuals and those in calorie deficit phases.
Exploring the Role of Fruits and Whole Foods in a Low Calorie High Nutrient Diet
While vegetables and legumes often steal the spotlight, low calorie fruits and veggies together offer a holistic solution to nutrient adequacy in a low calorie diet. Fruits like berries, melons, kiwi, grapefruit, and apples are examples of what fruits are low calorie yet high in antioxidants and water content. These support hydration, digestion, and recovery while adding natural sweetness to meals.
Fruits also offer important psychological benefits by enhancing the sensory enjoyment of a low calorie meal plan. Many people find that including naturally sweet, fiber-rich fruits helps reduce cravings for processed sugars. When combined with a source of low calorie protein, such as a scoop of plant-based protein powder or a handful of almonds, fruits create a snack that’s not only satisfying but metabolically balanced.
Low calorie whole foods—those that are minimally processed and nutrient dense—should form the foundation of any plan focused on foods with low calories for weight loss. From quinoa and buckwheat to lentils and leafy greens, these choices deliver high nutrient-to-calorie ratios, promoting health while facilitating fat loss. Whether you’re designing a full-day menu or seeking the best foods for low calorie diet adherence, whole foods remain the gold standard.
Comparing the Ketogenic Diet vs Low Carb: Sustainability and Protein Intake
As people explore various strategies for weight loss, many encounter the debate around the ketogenic diet vs low carb approaches. At first glance, both seem aligned in minimizing carbohydrate intake. However, there are key differences that influence sustainability, satiety, and nutrient diversity.
The low carb diet keto diet distinction lies primarily in carb limits. While a standard low carb diet might allow 50 to 150 grams of carbohydrates per day, a ketogenic diet typically restricts intake to under 50 grams. This extreme reduction pushes the body into ketosis—a metabolic state where fat becomes the primary fuel. But is keto a low carb diet in practice? Yes, but not all low carb diets are ketogenic.
The bigger question is: is keto a good diet when long-term adherence is considered? While short-term weight loss can be impressive, the keto diet’s restrictive nature makes it difficult for many to maintain. Social eating, fiber intake, and plant diversity all suffer on strict keto. Moreover, is a keto diet sustainable when it discourages many of the low calorie high nutrient foods that support long-term health? Most studies suggest not.
For those seeking balance and diversity, the best path may lie somewhere in the middle. A flexible, high protein low calorie version of a low carb plan—featuring legumes, tofu, seeds, and low starch vegetables—can deliver many of the metabolic benefits of keto without the rigidity. In this light, the keto diet vs low carb diet conversation becomes less about ideology and more about individualization, food freedom, and long-term viability.
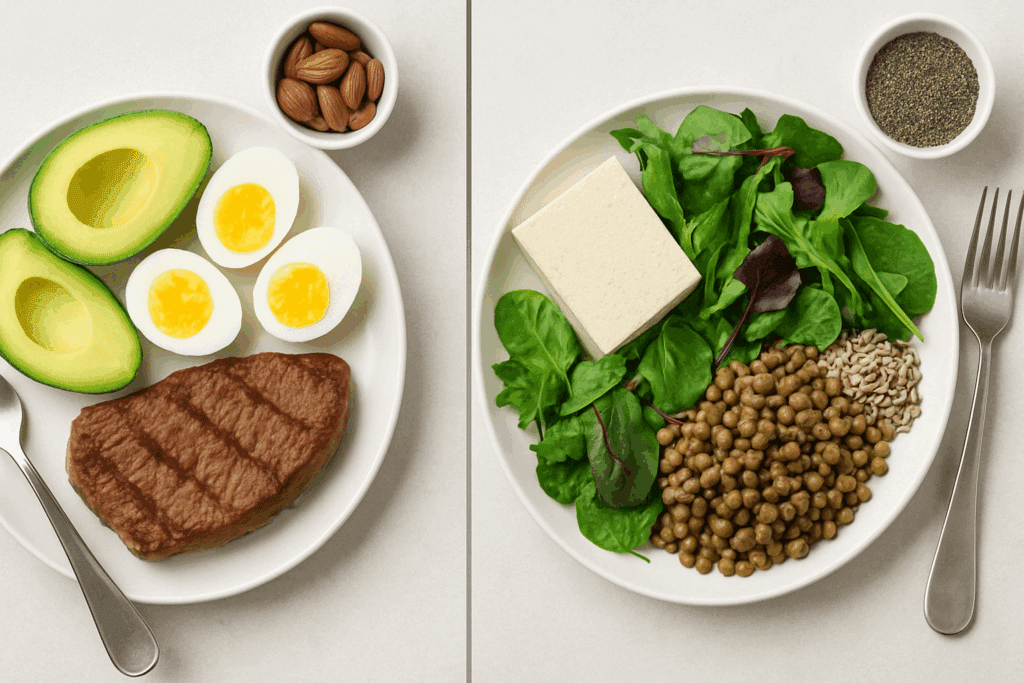
How to Build the Best Low Calorie High Protein Meals with Plant-Based Ingredients
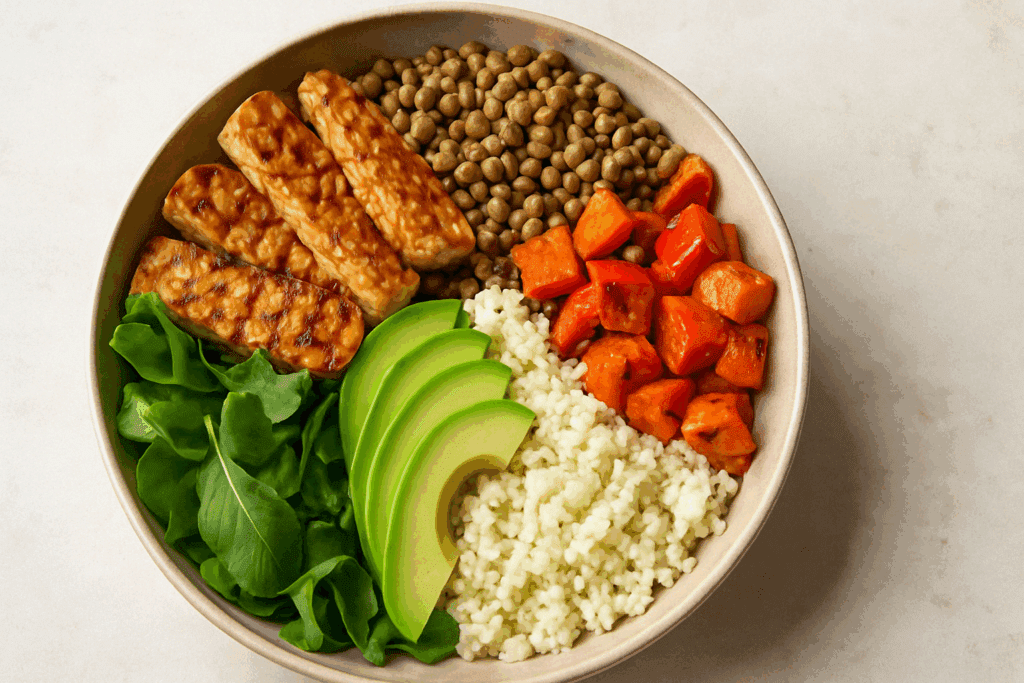
Creating meals that center on high protein low calorie foods doesn’t have to be complicated. In fact, it can be a joyful, nourishing process when guided by whole-food, plant-based principles. A typical balanced plate might include a protein anchor such as tempeh, lentils, or seitan, paired with low calorie vegetables like zucchini, spinach, or cauliflower rice. Adding a source of healthy fat such as avocado or hemp seeds rounds out the meal with flavor and nutrient density.
Meal prep becomes significantly easier when you identify your go-to low calorie protein sources. Cooking large batches of chickpeas, marinating tofu in tamari and spices, or pre-chopping high volume vegetables can streamline the process. The goal is to create a structure where healthy choices are convenient and enjoyable—not a burden.
For snacks, combining foods that are low calorie but filling ensures that between-meal cravings don’t derail your progress. Apple slices with almond butter, edamame, or chia pudding with berries all strike the right balance. These choices also support a steady blood sugar curve, reducing energy crashes and emotional eating.
Side-by-side plates comparing keto and plant-based meals featuring the best low calorie high protein foods for weight loss
Why Protein Quality Matters in the Context of Low Calorie Diet Foods
While quantity of protein is crucial in a filling low calorie diet, quality is equally important. Plant-based eaters must pay close attention to amino acid completeness, particularly in a calorie deficit. Fortunately, combining a variety of low calorie protein sources throughout the day easily ensures coverage. Grains and legumes, for instance, are complementary—together offering all essential amino acids.
Fermented protein sources like tempeh and miso not only deliver complete protein but also support gut health. These foods foster microbial diversity, which in turn enhances digestion, immune function, and even mental health. When building a diet centered on the best low calorie high protein foods, gut-friendly options should never be overlooked.
Avoiding over-reliance on processed protein products is also a consideration. While bars and powders have their place, whole foods offer more than just macros—they deliver enzymes, fiber, and phytonutrients. Opting for low calorie protein options that are minimally processed supports overall vitality and makes the eating experience more enjoyable.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Best Low Calorie High Protein Foods for Weight Loss
1. How can I make a low calorie diet feel more satisfying without increasing portion sizes?
One of the most effective ways to enhance satiety on a low calorie diet is by incorporating highprotein low calorie foods that are naturally dense in nutrients and fiber. For example, foods that are low calorie but filling, such as lentils, chickpeas, and tofu, offer sustained energy and help blunt hunger hormones like ghrelin. Another overlooked strategy is incorporating textures and temperatures—adding crunch with low cal veggies or warming up low calorie high protein soups can psychologically extend the eating experience. Mindful eating practices, like chewing thoroughly and avoiding distractions during meals, have also been linked to greater satisfaction, even with reduced calorie intake. Lastly, don’t underestimate the power of hydration; drinking water-rich broths or enjoying low calorie whole foods with high water content (like cucumbers or oranges) can enhance volume without adding extra calories.
2. Are there specific low calorie vegetables that also offer meaningful protein content?
Yes, while vegetables aren’t typically known for their protein, some do contribute a surprisingamount, especially when paired correctly. For instance, spinach, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts are among the vegetables with least calories yet contain measurable amounts of plant-based protein. When eaten in larger quantities or combined with other low calorie protein sources like nutritional yeast or edamame, they become more impactful. These low calorie vegetables also deliver a wide spectrum of micronutrients that support metabolic health, making them some of the best foods for low calorie diet goals. The fiber and antioxidant load in these vegetables with least amount of calories enhances digestion and satiety, reinforcing their place in any balanced, high protein low cal foods strategy.
3. What are some lesser-known sources of low calorie protein that support muscle maintenance during weight loss?
Beyond the usual suspects like Greek yogurt and legumes, there are several underrated options thatdeliver low calorie protein without compromising flavor or texture. Seitan, for instance, is one of the highest protein low calorie foods and is often overlooked outside of vegan circles. Lupini beans are another powerhouse that offers the food with most protein and least calories per bite when drained and rinsed. Pumpkin seeds, when used sparingly, offer concentrated low calorie protein rich foods alongside key minerals like magnesium and zinc. Incorporating these into salads or snacks can provide sustained energy without derailing a calorie deficit. Maintaining muscle during weight loss hinges on adequate protein, and expanding your repertoire beyond the basics gives you an edge in preserving lean mass.
4. How do I balance a filling low calorie diet with long-term nutrient sufficiency?
Sustainable weight loss isn’t just about cutting calories—it’s about achieving nutrient density withinthose calories. That means emphasizing low calorie high nutrient foods, which are both filling and rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Incorporating a colorful array of vegetables with least amount of calories (like kale, cauliflower, and carrots) alongside diverse protein sources ensures micronutrient coverage. Rotating your food choices weekly helps avoid repetitive nutrient gaps, especially with foods with low calories for weight loss. Supplementing strategically with B12 or omega-3s may be necessary, particularly for those on a plant-based path. Ultimately, the best low calorie high protein foods are those that offer more than just macros—they support cellular health, hormone balance, and immune function too.
5. What fruits are low calorie and help curb sugar cravings?
When trying to satisfy a sweet tooth without sabotaging a low calorie diet, fruits with high fiber andwater content are ideal. Berries, especially raspberries and strawberries, are among the best low calorie fruits and veggies for their antioxidant punch and low glycemic load. Kiwi, grapefruit, and melon also fit the bill as what fruits are low calorie yet hydrating and refreshing. To amplify the impact, pair them with a low calorie protein like almond butter or a few sunflower seeds, which can blunt blood sugar spikes. This strategy supports the principle of combining low calorie high protein and carb sources to promote steadier energy and reduced cravings.
6. How can low calorie diet foods help with portion control and emotional eating?
Portion control becomes easier when meals are designed with a volume-rich approach, using foodswith low calories for weight loss that also provide a satisfying sensory experience. Steamed vegetables like zucchini and green beans—both low cal veggies that offer crunch and fiber—can anchor a plate without contributing excess energy. For emotional eaters, incorporating warm, savory dishes like soups made from low calorie protein rich foods such as lentils and mushrooms can offer comfort without overeating. Practicing cognitive reframing, where you associate fullness with nourishment instead of restriction, is another psychological tactic. Additionally, visual cues like using smaller plates or pre-plating snacks can reinforce healthier habits over time.
7. What are the best low calorie protein options for people with busy schedules?
For those on the go, convenience doesn’t have to come at the cost of health. The best low calorieprotein options for busy people include pre-cooked lentils, unsweetened plant-based protein shakes, and roasted chickpeas. Hard-boiled eggs and low-fat cottage cheese also fall into the category of highest protein low calorie foods that require minimal prep. Pre-chopped vegetables with hummus or air-popped tofu cubes are additional low calorie diet foods that travel well and keep you full. Prioritizing foods that are low calorie but filling ensures you stay energized throughout the day without frequent hunger pangs.
8. Can combining multiple low calorie protein sources improve overall amino acid balance?
Absolutely. While some plant-based options are incomplete proteins individually, combining lowcalorie high protein foods with complementary amino profiles leads to complete protein synthesis. A classic example is pairing rice with beans, or hummus with whole grain pita, creating meals that maximize both satiety and muscle support. Even within vegetables with least calories, combinations like quinoa and black beans or tempeh with leafy greens provide robust nutrition. This strategy is especially important in low calorie whole foods diets where reliance on minimally processed ingredients can sometimes limit amino acid diversity. Planning your meals around variety ensures you’re not just meeting protein quotas, but optimizing how your body uses that protein.
9. What strategies help people stick with low calorie diet foods during social events or dining out?
Maintaining a low calorie diet in social settings starts with preemptive planning and flexible thinking.Reviewing restaurant menus in advance allows you to identify dishes built around low calorie vegetables or lean protein. Asking for dressings and sauces on the side, or swapping fries for a side salad with low cal veggies, is a simple but effective move. Bringing a low calorie high protein dish to potlucks ensures you have at least one anchor option that aligns with your goals. Mentally reframing the experience as a celebration of connection rather than just food can also shift your focus away from indulgence. With practice, you can enjoy meals without abandoning your commitment to the best foods for low calorie diet success.
10. How do I evaluate which has less calories when comparing similar protein foods?
Evaluating the calorie density of proteins requires more than just glancing at a label. For example, while peanut butter is high in protein, it’s also energy dense compared to something like tempeh or plain edamame. Focusing on the highest protein foods with lowest calories means examining the protein-to-calorie ratio. Tools like nutrition tracking apps can offer precise macros, but practical rules of thumb—like prioritizing grilled over fried options and choosing unseasoned products—can help too. Learning to identify which has less calories while still being satisfying supports sustainable progress, especially when paired with a filling low calorie diet that includes variety and personalization.

Final Thoughts on Crafting a Sustainable, High Protein Low Calorie Diet
The journey to sustainable weight loss and vibrant health begins with understanding what to eat to feel full on a low calorie plan without falling into deprivation. Embracing low calorie high protein foods—especially those rooted in whole, plant-based nutrition—lays the groundwork for metabolic health, emotional well-being, and long-term dietary success.
While the allure of trends like the ketogenic diet vs low carb may be tempting, the deeper question remains: is a keto diet sustainable for your lifestyle, values, and health goals? For many, the answer is no. Instead, a more inclusive, evidence-backed approach that emphasizes highest protein low calorie foods, low calorie vegetables, and low calorie whole foods provides not only results, but resilience.
In the end, weight loss isn’t about eating less—it’s about eating smart. With a thoughtful focus on protein density, plant diversity, and practical meal planning, anyone can discover a way of eating that’s as enjoyable as it is effective. Whether you’re optimizing a current routine or beginning a new chapter in your health journey, the best low calorie high protein foods will be your steadfast allies—not just in shedding pounds, but in building a life of vitality, strength, and sustained wellness.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
Weight loss: Feel full on fewer calories
What foods are high in protein?
13 Low Calorie Foods That Are Surprisingly Filling
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as medical, legal, or professional advice. While NewsHealthWatch strives to present accurate, up-to-date, and reliable content, no warranty or guarantee, expressed or implied, is made regarding the completeness, accuracy, or adequacy of the information provided. Readers are strongly advised to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider or other relevant professionals before acting on any information contained in this article. NewsHealthWatch, its authors, editors, and contributors expressly disclaim any liability for any damages, losses, or consequences arising directly or indirectly from the use, interpretation, or reliance on any information presented herein. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policies or positions of NewsHealthWatch.